Sleep seems within the mind as sluggish waves surging around the floor at a fee of round one each 10th of a 2nd – or so we concept.A brand new find out about in mice suggests there are patterns of mind task associated with sleep that we’ve got overpassed – and that replicate the state of person mind cells quite than the collective task of hundreds of thousands or billions of neurons.
What is extra, in measuring those hyperlocal, sub-millimeter mind alerts the use of single-wire electrodes, researchers have discovered that portions of the mammalian mind may well be drowsing off for short naps whilst different areas stay wakeful.
“It was once unexpected to us as scientists to seek out that other portions of our brains if truth be told take little naps when the remainder of the mind is wide awake,” says David Haussler, a bioinformatician on the College of California (UC) Santa Cruz and a senior creator of the find out about.
For a century or so, brain-wide patterns {of electrical} task had been used to outline, in a quantitative sense, the adaptation between being asleep and wide awake. Those mind waves are maximum ceaselessly detected the use of an electroencephalogram (EEG), by way of electrodes positioned at the scalp.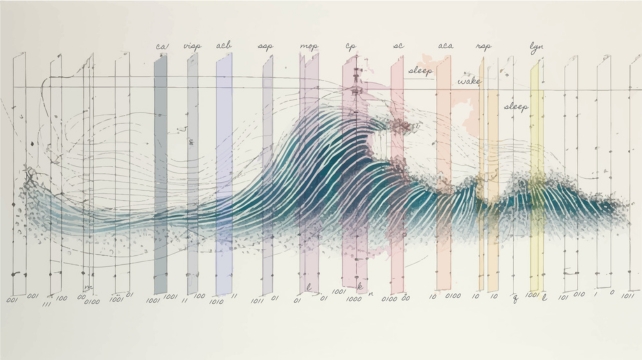 Inventive depiction of various mind wave patterns that produce states of sleep and wake. (Keith Hengen)However Haussler and his crew wondered how we’ve got measured sleep and prominent it from wakefulness – when obviously there may be some crossover within the brains of animals that keep alert whilst drowsing, a talent referred to as unihemispheric slow-wave sleep.
Inventive depiction of various mind wave patterns that produce states of sleep and wake. (Keith Hengen)However Haussler and his crew wondered how we’ve got measured sleep and prominent it from wakefulness – when obviously there may be some crossover within the brains of animals that keep alert whilst drowsing, a talent referred to as unihemispheric slow-wave sleep.
Within the Sixties, researchers first suspected after which detected how dolphins and different cetaceans can relaxation part in their mind whilst ultimate lively, from time to time conserving one eye open to observe for predators and care for touch with others of their pod.
Seals and birds additionally show permutations of this part-sleep, part-awake relaxation – a artful trade-off between sleep and survival.
People, too, can quickly show asymmetrical sleep patterns which might be paying homage to, however now not the similar as, the ones noticed in animals.
In 2016, researchers at Brown College in the United States discovered that the primary evening folks slept in an unfamiliar position, the left aspect mind was once extra alert to deviant sounds than the best. When we transform acquainted with a snooze atmosphere, this distinction subsides.
“The human mind, it seems, is endowed with a much less dramatic type of the unihemispheric sleep present in birds and a few mammals,” neuroscientist Christof Koch wrote in Clinical American when the ones effects have been revealed.
If the mouse mind is the rest to move via, the blurring of wake and sleep states in people may well be a neurological characteristic we percentage with different animals in the end.
Haussler and the crew accumulated weeks of knowledge from 9 mice that had thin-wire electrodes implanted into 10 other areas in their brains, and fed this information into a man-made neural community that discovered to tell apart between sleep and wake states.
Recordings have been sampled from 100 micrometers (one-tenth of a millimeter) of mind tissue, and the set of rules may just reliably establish sleep-wake cycles according to brief ‘glints’ in mind mobile task lasting simply 10 to 100 milliseconds.
Those ‘hyperlocal’ alerts prompt that a part of the animals’ brains dozed off to sleep whilst different areas stayed lively and wide awake. Coincidentally, the researchers spotted this took place proper when the mouse may forestall transferring for a break up 2nd, nearly adore it had ‘zoned out’.
“Lets take a look at the person time issues when those neurons fired, and it was once lovely transparent that [the neurons] have been transitioning to another state,” explains Aiden Schneider, a computational biologist at Washington College in St. Louis, who co-led the find out about with David Parks, a pc science graduate pupil at UC Santa Cruz.
“In some circumstances, those glints may well be constrained to the world of simply a person mind area, perhaps even smaller than that.”
The crew thinks their new approach of measuring sleep-wake states may just divulge new secrets and techniques about how we shut eye, if those ‘glints’ may also be noticed via different analysis teams.
“They [the flickers] smash the principles that you’d be expecting according to 100 years of literature,” says neuroscientist Keith Hengen from Washington College in St. Louis.The find out about has been revealed in Nature Neuroscience.
Unexpected Sleep Discovery Suggests We now have Been Lacking The Mind’s Micro-Naps










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/maggieoneill-16204cf3e01b424bbbd66733f6fb4668.jpeg)



