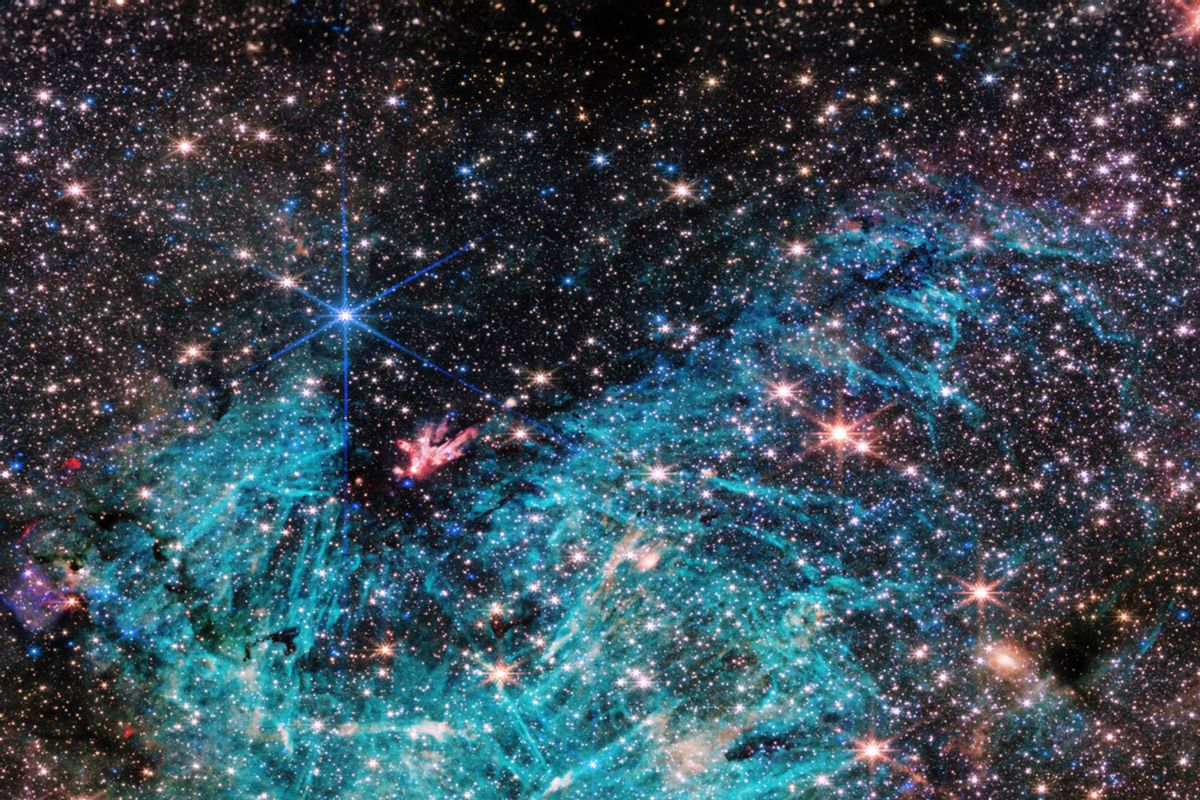
A brand new picture from the James Webb Area Telescope of the deep heart of the Milky Approach highlights never-before-features that experience but to be scientifically defined. In particular, JWST narrowed in at the area known as Sagittarius C (Sgr C), which is set 300 light-years clear of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hollow on the Milky Approach’s heart. The unheard of element casts the area in a brand new gentle to astronomers, letting them find out about it in ways in which were not conceivable earlier than.
Astronomers say the extent of solution is letting them see new points for the first actual time, like how the galactic heart is in reality an overly crowded position with round 500,000 stars — together with a cluster of protostars, that are stars which might be nonetheless forming. On the middle of this cluster is a prior to now identified huge protostar this is 30 instances the mass of our personal Solar. JWST’s NIRCam (Close to-Infrared Digicam) device additionally captured large-scale emission from ionized hydrogen bordering the decrease aspect of an infrared-dark cloud. Astronomers say they’re excited to dig in, and hope this new symbol will result in unheard of data on how stars shape.
“There’s by no means been any infrared knowledge in this area with the extent of solution and sensitivity we get with Webb, so we’re seeing a whole lot of points right here for the primary time,” mentioned the statement staff’s most important investigator Samuel Crowe, in a media commentary. “The picture from Webb is shocking, and the science we will be able to get from it’s even higher.”