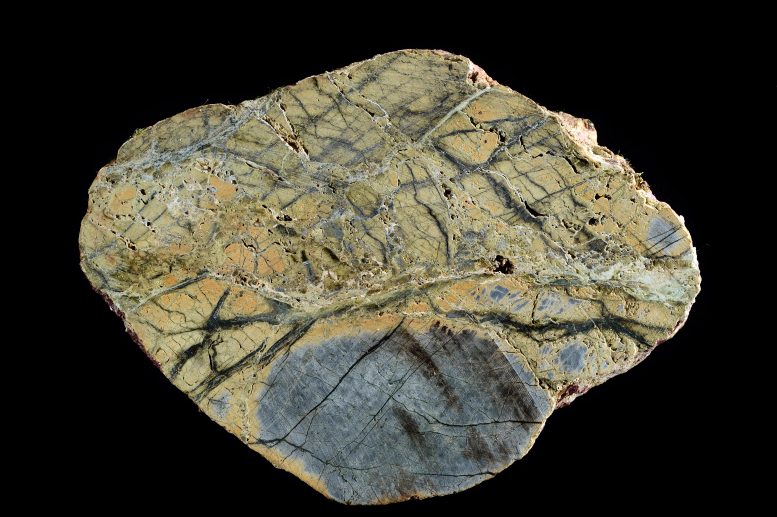
New analysis has known oceanic turn out to be faults as vital, in the past underestimated sinks for CO2, difficult present notions concerning the Earth’s geological carbon cycle. This analysis emphasizes the the most important position of herbal geological emissions in shaping Earth’s local weather historical past and highlights the will for a deeper working out of those processes within the context of addressing fresh local weather alternate. Above is a minimize slice of altered mantle rock. Credit score: Solvin ZanklStudying a rock is like studying a e book. The rock has a tale to inform, says Frieder Klein, an affiliate scientist within the Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry Division on the Woods Hollow Oceanographic Establishment (WHOI).The rocks that Klein and his colleagues analyzed from the submerged flanks of the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago within the St. Paul’s oceanic turn out to be fault, about 500 km off the coast of Brazil, inform a captivating and in the past unknown tale about portions of the geological carbon cycle.Turn out to be faults, the place tectonic plates transfer previous every different, are one in every of 3 primary plate obstacles on Earth and about 48,000 km in period globally, with the others being the worldwide mid-ocean ridge gadget (about 65,000 km) and subduction zones (about 55,000 km).The Position of Turn out to be Faults in Carbon CyclingCarbon biking at mid-ocean ridges and subduction zones has been studied for many years. Against this, scientists have paid moderately scant consideration to CO2 in oceanic turn out to be faults. The turn out to be faults had been regarded as “relatively uninteresting” puts for slightly a while as a result of the low magmatic task there, says Klein. “What we’ve now pieced in combination is that the mantle rocks which can be uncovered alongside those ocean turn out to be faults constitute a doubtlessly huge sink for CO,” he says.Partial melting of the mantle releases CO2 that turns into entrained in hydrothermal fluid, reacts with the mantle nearer to the seafloor, and is captured there.
New analysis has known oceanic turn out to be faults as vital, in the past underestimated sinks for CO2, difficult present notions concerning the Earth’s geological carbon cycle. This analysis emphasizes the the most important position of herbal geological emissions in shaping Earth’s local weather historical past and highlights the will for a deeper working out of those processes within the context of addressing fresh local weather alternate. Above is a minimize slice of altered mantle rock. Credit score: Solvin ZanklStudying a rock is like studying a e book. The rock has a tale to inform, says Frieder Klein, an affiliate scientist within the Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry Division on the Woods Hollow Oceanographic Establishment (WHOI).The rocks that Klein and his colleagues analyzed from the submerged flanks of the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago within the St. Paul’s oceanic turn out to be fault, about 500 km off the coast of Brazil, inform a captivating and in the past unknown tale about portions of the geological carbon cycle.Turn out to be faults, the place tectonic plates transfer previous every different, are one in every of 3 primary plate obstacles on Earth and about 48,000 km in period globally, with the others being the worldwide mid-ocean ridge gadget (about 65,000 km) and subduction zones (about 55,000 km).The Position of Turn out to be Faults in Carbon CyclingCarbon biking at mid-ocean ridges and subduction zones has been studied for many years. Against this, scientists have paid moderately scant consideration to CO2 in oceanic turn out to be faults. The turn out to be faults had been regarded as “relatively uninteresting” puts for slightly a while as a result of the low magmatic task there, says Klein. “What we’ve now pieced in combination is that the mantle rocks which can be uncovered alongside those ocean turn out to be faults constitute a doubtlessly huge sink for CO,” he says.Partial melting of the mantle releases CO2 that turns into entrained in hydrothermal fluid, reacts with the mantle nearer to the seafloor, and is captured there.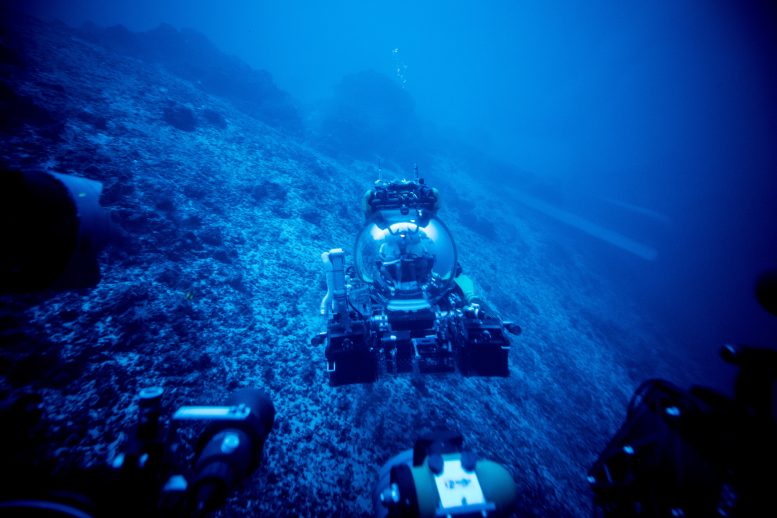 Leader Scientist Frieder Klein and Deep Rover Pilot Alan Scot exploring a submerged carbonate platform. Credit score: Novus SelectThis is part of the geological carbon cycle that used to be no longer recognized sooner than,” says Klein, lead writer of a brand new magazine learn about revealed within the Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS). As a result of turn out to be faults have no longer been accounted for in earlier estimates of world geological CO2 fluxes, the mass switch of magmatic CO2 to the altered oceanic mantle and seawater is also better than in the past concept.”Geological Emissions and Local weather”The volume of CO2 emitted on the turn out to be faults is negligible in comparison to the volume of anthropogenic – or human-driven – CO2,” says Klein. “Alternatively, on geological timescales and sooner than people emitted such a lot CO2, geological emissions from Earth’s mantle – together with from turn out to be faults – had been a significant driver of Earth’s local weather.”Because the paper states, “international anthropogenic CO2 emissions are estimated to be at the order of 36 gigatons (Gt) in line with 12 months, dwarfing estimates of moderate geological emissions (0.26 Gt in line with 12 months) to the ambience and hydrosphere. But, over geological timescales, emissions of CO2 sourced from Earth’s mantle had been pivotal in regulating Earth’s local weather and habitability, in addition to the C [carbon]-concentration in floor reservoirs, together with the oceans, environment, and lithosphere.” Klein provides that “that is sooner than anthropogenic combustion of fossil fuels, after all.”Working out Local weather Trade Thru Geological Research“With the intention to absolutely perceive fashionable human-caused local weather alternate, we want to perceive herbal local weather fluctuations in Earth’s deep previous, which might be tied to perturbations in Earth’s herbal carbon cycle. Our paintings supplies insights into long-timescale fluxes of carbon between Earth’s mantle and the sea/environment gadget,” says co-author Tim Schroeder, member of the school at Bennington School, Vermont. “Huge adjustments in such carbon fluxes over thousands and thousands of years have brought about Earth’s local weather to be a lot hotter or less warm than it’s nowadays.”To raised perceive carbon biking between Earth’s mantle and the sea, Klein, Schroeder, and co-workers studied the formation of soapstone “and different magnesite-bearing assemblages throughout mineral carbonation of mantle peridotite” within the St. Paul’s turn out to be fault, the paper notes. “Fueled by means of magmatism in or beneath the foundation zone of the turn out to be fault and next degassing, the fault constitutes a conduit for CO2-rich hydrothermal fluids, whilst carbonation of peridotite represents a doubtlessly huge sink for the emitted CO2.”The researchers argue within the paper that “the combo of low extents of melting, which generates melts enriched in incompatible parts, volatiles, and in particular CO2, and the presence of peridotite at oceanic turn out to be faults creates prerequisites conducive to in depth mineral carbonation.”The rocks had been accumulated the usage of human-occupied cars throughout a 2017 cruise to the world.Discovering and inspecting those rocks “used to be a dream come true. We had predicted the presence of carbonate-altered oceanic mantle rocks 12 years in the past, however we couldn’t to find them any place,” says Klein. “We went to the archipelago to probe for low-temperature hydrothermal task, and we failed miserably find this type of task there. It used to be implausible that we had been in a position to seek out those rocks in a turn out to be fault, as a result of we discovered them unintentionally whilst on the lookout for one thing else.”Reference: “Mineral carbonation of peridotite fueled by means of magmatic degassing and soften impregnation in an oceanic turn out to be fault” by means of Frieder Klein, Timothy Schroeder, Cédric M. John, Simon Davis, Susan E. Humphris, Jeffrey S. Seewald, Susanna Sichel, Wolfgang Bach and Daniele Brunelli, 12 February 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
Leader Scientist Frieder Klein and Deep Rover Pilot Alan Scot exploring a submerged carbonate platform. Credit score: Novus SelectThis is part of the geological carbon cycle that used to be no longer recognized sooner than,” says Klein, lead writer of a brand new magazine learn about revealed within the Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS). As a result of turn out to be faults have no longer been accounted for in earlier estimates of world geological CO2 fluxes, the mass switch of magmatic CO2 to the altered oceanic mantle and seawater is also better than in the past concept.”Geological Emissions and Local weather”The volume of CO2 emitted on the turn out to be faults is negligible in comparison to the volume of anthropogenic – or human-driven – CO2,” says Klein. “Alternatively, on geological timescales and sooner than people emitted such a lot CO2, geological emissions from Earth’s mantle – together with from turn out to be faults – had been a significant driver of Earth’s local weather.”Because the paper states, “international anthropogenic CO2 emissions are estimated to be at the order of 36 gigatons (Gt) in line with 12 months, dwarfing estimates of moderate geological emissions (0.26 Gt in line with 12 months) to the ambience and hydrosphere. But, over geological timescales, emissions of CO2 sourced from Earth’s mantle had been pivotal in regulating Earth’s local weather and habitability, in addition to the C [carbon]-concentration in floor reservoirs, together with the oceans, environment, and lithosphere.” Klein provides that “that is sooner than anthropogenic combustion of fossil fuels, after all.”Working out Local weather Trade Thru Geological Research“With the intention to absolutely perceive fashionable human-caused local weather alternate, we want to perceive herbal local weather fluctuations in Earth’s deep previous, which might be tied to perturbations in Earth’s herbal carbon cycle. Our paintings supplies insights into long-timescale fluxes of carbon between Earth’s mantle and the sea/environment gadget,” says co-author Tim Schroeder, member of the school at Bennington School, Vermont. “Huge adjustments in such carbon fluxes over thousands and thousands of years have brought about Earth’s local weather to be a lot hotter or less warm than it’s nowadays.”To raised perceive carbon biking between Earth’s mantle and the sea, Klein, Schroeder, and co-workers studied the formation of soapstone “and different magnesite-bearing assemblages throughout mineral carbonation of mantle peridotite” within the St. Paul’s turn out to be fault, the paper notes. “Fueled by means of magmatism in or beneath the foundation zone of the turn out to be fault and next degassing, the fault constitutes a conduit for CO2-rich hydrothermal fluids, whilst carbonation of peridotite represents a doubtlessly huge sink for the emitted CO2.”The researchers argue within the paper that “the combo of low extents of melting, which generates melts enriched in incompatible parts, volatiles, and in particular CO2, and the presence of peridotite at oceanic turn out to be faults creates prerequisites conducive to in depth mineral carbonation.”The rocks had been accumulated the usage of human-occupied cars throughout a 2017 cruise to the world.Discovering and inspecting those rocks “used to be a dream come true. We had predicted the presence of carbonate-altered oceanic mantle rocks 12 years in the past, however we couldn’t to find them any place,” says Klein. “We went to the archipelago to probe for low-temperature hydrothermal task, and we failed miserably find this type of task there. It used to be implausible that we had been in a position to seek out those rocks in a turn out to be fault, as a result of we discovered them unintentionally whilst on the lookout for one thing else.”Reference: “Mineral carbonation of peridotite fueled by means of magmatic degassing and soften impregnation in an oceanic turn out to be fault” by means of Frieder Klein, Timothy Schroeder, Cédric M. John, Simon Davis, Susan E. Humphris, Jeffrey S. Seewald, Susanna Sichel, Wolfgang Bach and Daniele Brunelli, 12 February 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2315662121Funding for this analysis used to be equipped by means of the Dalio Ocean Initiative, the Unbiased Analysis & Construction Program at WHOI, and the Nationwide Science Basis.
Unintended Deep Ocean Discovery Adjustments Our Working out of Earth