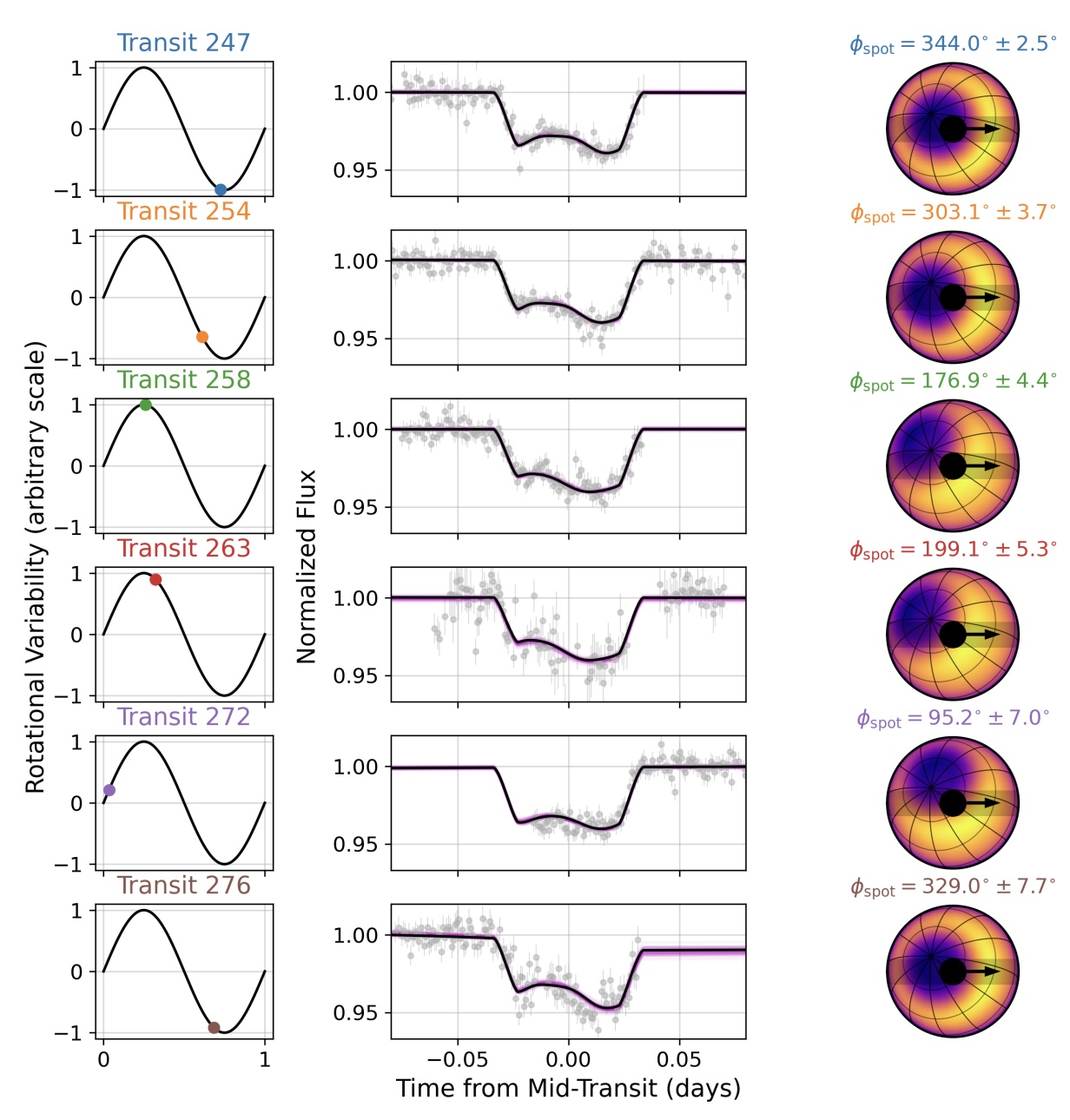
Felix Elling, a former postdoctoral fellow at Harvard and lead creator of the learn about. Credit score: Felix Elling
For biochemists, it is the which-came-first query: oxygen manufacturing via photosynthesis or oxygen intake via cardio metabolism?
In photosynthesis, algae and crops absorb daylight to show carbon dioxide and water into gas for enlargement, liberating oxygen as a byproduct. Animals, then again, use oxygen to transform the gas they eat into power and emit carbon dioxide, a procedure known as cardio metabolism.
So which got here first? A brand new paper within the Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences main points an unintended discovery via a global consortium of researchers of a imaginable missing-link molecule that can result in a solution to the evolutionary query.
“Proper from the beginning, we had this concept that this may well be associated with the evolution of photosynthesis and the facility to respire oxygen,” stated Felix Elling, a former postdoctoral fellow within the Division of Earth and Planetary Sciences and lead creator at the paper.
Elling, who used to be running in Professor Ann Pearson’s Lab for Molecular Biogeochemistry and Natural Geochemistry, used to be searching for explicit molecules unrelated to questions concerning the evolution of cardio metabolism when he found out one thing atypical: a slight alternate in a molecule in a nitrogen-utilizing bacterium, Nitrospirota, that gave the impression extra like one thing {that a} plant would want for photosynthesis, relatively than a bacterium.
“We had been screening micro organism for a fully other mission,” stated Elling, who’s now at the college on the College of Kiel in Germany.
What the researchers had discovered used to be methyl-plastoquinone, a variation on a molecule sort known as a quinone. Present in all existence paperwork, quinones were idea to exist in two fundamental types: cardio quinones that require oxygen and anaerobic ones that don’t.
Cardio quinones additional subdivide into two varieties—ones utilized by crops to accomplish photosynthesis and every other utilized by micro organism and animals to respire oxygen.
“Mainly, all sorts of existence use quinones for his or her metabolism,” defined Elling. Discovering a quinone, “which has similarities to what crops use to accomplish photosynthesis,” in a bacterium that breathes oxygen used to be extremely atypical. Methyl-plastoquinone, the researchers learned, used to be a 3rd sort, and perhaps a lacking hyperlink between the 2.
The analysis sheds mild on what is known as the Nice Oxidation Tournament. That length—more or less 2.3 to two.4 billion years in the past—marked when cyanobacteria (a kind of algae) started producing important amounts of oxygen because of photosynthesis, making cardio metabolism imaginable.
Whilst that building would appear to suggest that photosynthesis got here first, the invention of methyl-plastoquinone helps every other speculation. Merely put, some micro organism already had the facility to make use of oxygen—even sooner than cyanobacteria started generating it.
In different phrases, “the white meat and the egg had been on the similar time,” Elling stated.
Pearson, the PVK Professor of Arts and Sciences and Murray and Martha Ross Professor of Environmental Sciences, in whose lab Elling’s analysis started, wired that having a biochemical processing device for oxygen on the creation of its technology via photosynthesis used to be an enormous step.
Uncover the most recent in science, tech, and area with over 100,000 subscribers who depend on Phys.org for day by day insights.
Join our loose e-newsletter and get updates on breakthroughs,
inventions, and analysis that subject—day by day or weekly.
“The reactions that contain oxygen are very destructive and may also be slightly fatal to cells that lack mechanisms to deal with the metabolic byproducts,” she stated. Despite the fact that we take them with no consideration, “the chemical programs that all of us make use of in our cells to live on our cardio metabolic way of life are in truth slightly subtle.”
Put merely, “that is how we discovered to respire,” Pearson stated. “And as soon as you’ll be able to breathe oxygen and do it safely, it paves the way in which for the diversification of the entire existence we see round us.”
Lines of the diversification of quinone constructions may also be present in our personal our bodies, together with the basic distinctions between quinones in human mitochondria, in comparison to the ones in crops.
“We expect what we discovered is the main or ancestral type of this molecule that then later used to be tailored to have two paperwork—one with explicit purposes within the algae and crops, and the other shape in mitochondria that we have got as of late,” stated Elling.
“This molecule is a time pill,” stated Elling. “A dwelling fossil of a molecule that has survived over greater than 2 billion years.”
Additional information:
Felix J. Elling et al, A unique quinone biosynthetic pathway illuminates the evolution of cardio metabolism, Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2025). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2421994122
Equipped via
Harvard Gazette
This tale is revealed courtesy of the Harvard Gazette, Harvard College’s legitimate newspaper. For extra college information, talk over with Harvard.edu.
Quotation:
Unintended discovery might trace at solution to a chicken-or-egg query on evolution (2025, February 24)
retrieved 24 February 2025
from
This file is topic to copyright. Except any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions best.