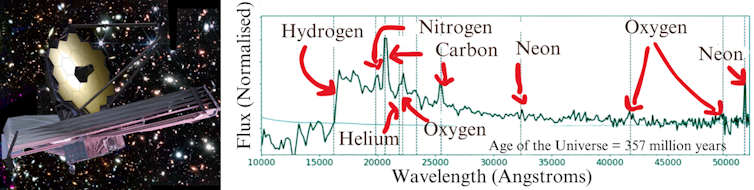
The JWST has allowed astronomers to look again additional into the previous than some other infrared or optical telescope, seeing infrared mild that was once emitted through far-off galaxies simply 300 million years after the Giant Bang.With the infrared telescope, we had been hoping to be told extra concerning the formation of galaxies, in addition to transparent up mysteries about how supermassive black holes was so huge. However we’ve been thrown a couple of surprises as we glance additional again into the previous.One such wonder is the tiny, brilliant purple dots of sunshine that seem to be dotted during the early universe, round 600-800 million years after its start. Once they had been first detected and analyzed, astronomers believed they might be large galaxies. However this was once at odds with how cosmological fashions be expecting galaxies to shape – as small clouds of mud and stars that develop better over lengthy classes of time.“The revelation that huge galaxy formation started extraordinarily early within the historical past of the universe upends what many people had concept was once settled science,” Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State, mentioned in a commentary following early observations. “We’ve been informally calling those gadgets ‘universe breakers’ – and they’ve been dwelling as much as their identify up to now.”After all, seeing gadgets that would upend our fashions of galaxy formation, the staff sought after to make sure of what they had been seeing, and aimed to take spectrum pictures of those galaxies to get a greater thought of the gap of the galaxies, what the galaxies are manufactured from, and the way large they in reality are. Following that evaluation, they’ve discovered those gadgets are certainly lovely bizarre, and in numerous tactics.First off, regardless of being handiest 600-800 million years outdated, the galaxies seem to be full of historical stars, elderly loads of thousands and thousands of years outdated. In addition to the oddity in their formation, this implies the staff was once taking a look on the earliest signatures of outdated starlight ever discovered.“Those early galaxies could be so dense with stars – stars that will have to have shaped in some way we have by no means noticed, beneath prerequisites we’d by no means be expecting all through a length wherein we’d by no means be expecting to look them,” Leja mentioned in a commentary following the most recent paintings. “And for no matter reason why, the universe stopped making gadgets like those after simply a few billion years. They’re distinctive to the early universe.”However there are extra mysteries to resolve. The staff estimates that the galaxies have strangely huge supermassive black holes at their facilities, between 100 and 1,000 occasions better than Sagittarius A* on the heart of the Milky Method. That is a ways too large for the galaxy surrounding it. If the galaxy had been compressed to the scale of the Milky Method, the staff says that the closest famous person could be simply out of doors our Sun Device, and the supermassive black hollow on the heart could be simply 26 light-years clear of Earth, visual as an enormous pillar of sunshine.“Typically supermassive black holes are paired with galaxies,” Leja added. “They develop up in combination and undergo all their primary lifestyles reports in combination. However right here, we’ve a completely shaped grownup black hollow dwelling inside what will have to be a toddler galaxy. That does not truly make sense, as a result of this stuff will have to develop in combination, or no less than that’s what we concept.” Supermassive black holes we see within the closer (newer) universe are, because the identify would recommend, lovely large. Cosmologists want to understand how those supermassive black holes, that are discovered on the heart of maximum (however now not all) galaxies, got here to be this kind of huge measurement. There were numerous theories, together with mergers of black holes, and that the black holes grew via feeding. Those early black holes, and others found out through the JWST, seem to be too huge to be defined through those concepts, and far better than cosmologists have been anticipating compared to the galaxies surrounding them.One thought, which is possibly changing into extra favorable in mild of new observations, is “direct cave in” or “heavy seed” black holes. Normally, to get a stellar mass black hollow (within the present age of the universe), a celeb undergoes cave in. With heavy seed black holes the speculation is that supermassive black holes would have began out at round 10,000 to 100,000 sun plenty, during the direct gravitational cave in of gigantic fuel clouds, with out an intermediate stellar segment. There are some things that would make this situation not going too. The fuel cloud would wish to cave in with out fragmenting and forming clumps because it does so, regardless that astronomers have steered that this might be averted if the cloud is heated through within reach younger stars in pre-galactic fuel disks, or if the fuel cloud was once transferring at supersonic speeds in “flows” within the early universe, permitting it to develop for longer, till the gravity is enough to get started the cloud’s cave in right into a seed black hollow.It’s recently tough to tell apart the fitting mass of the supermassive black holes on the heart of those galaxies from the celebrities surrounding them. Extra observations are deliberate, taking spectra over an extended time frame, to get a greater image. “It’s very complicated,” Leja added. “You’ll make this uncomfortably are compatible in our present style of the universe, however provided that we evoke some unique, insanely fast formation initially of time. That is, indisputably, probably the most ordinary and engaging set of gadgets I have noticed in my profession.”The newest find out about is revealed in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
“Universe Breakers”: Unexplainable Shiny Purple Dots Discovered In The Early Universe