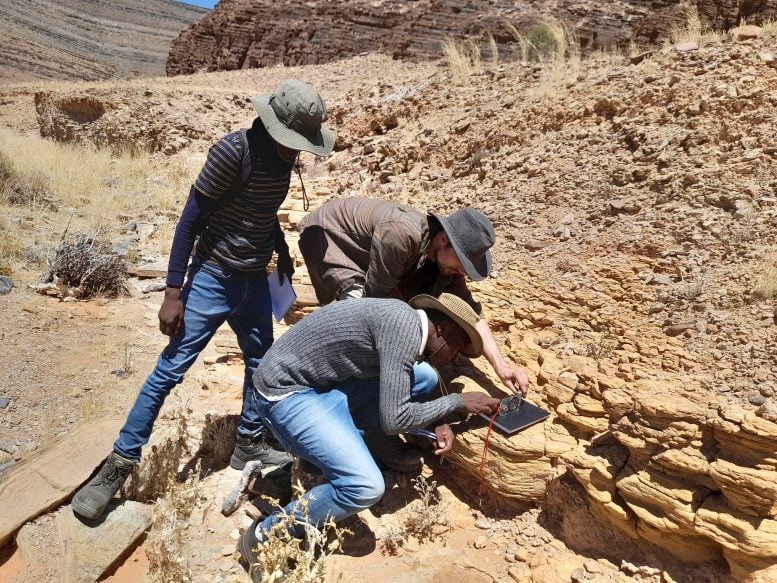
Researchers read about proof of animal fossils, that are about 550 million years previous, in box paintings in Namibia. Credit score: Rachel Picket
Researchers read about proof of animal fossils, that are about 550 million years previous, in box paintings in Namibia. Credit score: Rachel Picket
Researchers have connected adjustments in sea ranges and marine oxygen to the evolution of early animals in a learn about that mixes fossil research with geological knowledge from 580–510 million years in the past, bettering our figuring out of early biodiversity.
A newly evolved timeline of early animal fossils presentations a connection between sea ranges, marine oxygen adjustments, and the emergence of the earliest ancestors of recent animals. This learn about supplies insights into the forces that spurred the evolution of the primary organisms, from which all primary animal teams originated.
A workforce from the College of Edinburgh studied a compilation of rocks and fossils from the so-called Ediacaran-Cambrian period – a slice of time 580–510 million years in the past. This era witnessed an explosion of biodiversity in keeping with fossil data, the reasons of that have baffled scientists since Charles Darwin.
Evolutionary Complexity within the Ediacaran Length
The early animals discovered from this period had been all sea-dwellers, at a time when oxygen ranges within the air and ocean had been a lot not up to as of late.
Whilst the first actual lifeforms sooner than this time had been most commonly single-cell, and easy multi-celled organisms, creatures within the Ediacaran Length began to develop into extra complicated, with a couple of cells arranged into frame plans that allowed them to feed, reproduce, and transfer around the ocean flooring.
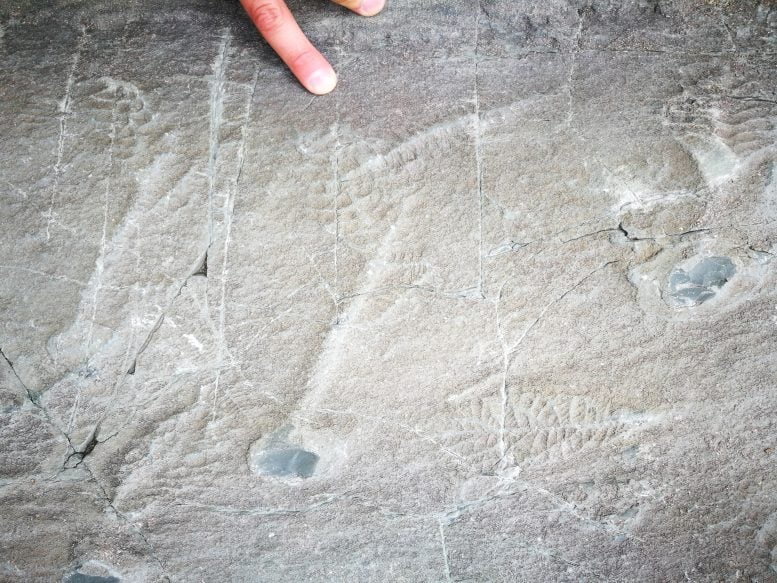 Fossils of early animals of the Avalon assemblage c.565 million years previous at Fallacious Level Ecological Reserve, Newfoundland, Canada. Credit score: Fred Bowyer
Fossils of early animals of the Avalon assemblage c.565 million years previous at Fallacious Level Ecological Reserve, Newfoundland, Canada. Credit score: Fred Bowyer
This period additionally marked the emergence of so-called bilaterian animals – which show symmetrical frame plans, in commonplace with maximum present-day species together with people.
Via compiling knowledge from other resources – together with radioactive relationship and geochemical details about the layers of rock during which fossils had been discovered – the workforce mapped all primary fossil unearths and quite a lot of environmental datasets onto a unmarried timeline.
The brand new chronology allowed the workforce to review traits in biodiversity for the length in query with extra element than sooner than.
They mixed those insights with additional chemical clues from the geological report – confirming a hyperlink between primary adjustments in world sea ranges, durations when shallow marine environments received extra oxygen, and the illusion and diversification of early animal teams.
Organic Range and Environmental Prerequisites
This dynamic set the degree for a number of important bursts in organic range, referred to as the Avalon, White Sea, and Cambrian assemblages, each and every marking the coming of recent animal teams and the decline of others.
Via reconstructing environmental prerequisites within the private time, the learn about unlocks new insights into the traditional forces and pressures that formed the earliest lifestyles on our planet.
The workforce additionally recognized gaps within the fossil report, suggesting that present wisdom about early animals is biased by means of the clusters of websites international the place fossils had been discovered and studied.
Dr Fred Bowyer of the College of Edinburgh’s Faculty of Geosciences, mentioned: “Setting up a timescale of early animal evolution the usage of the rock report is a frightening activity, most effective made conceivable via global and interdisciplinary analysis. However an built-in world method is a very powerful. It exposes biases in our data, whilst additionally revealing patterns in fossil appearances, sea stage cycles, and environmental oxygen.”
Mariana Yilales Agelvis, a PhD pupil within the Faculty of Geosciences who co-authored the learn about, mentioned: “Understanding what drives biodiversity is a elementary piece of information within the puzzle of lifestyles. I believe very privileged to have constructed upon many years of interdisciplinary world analysis, and contributed to a greater figuring out of the function that sea stage performs in early animal evolution.”
Reference: “Sea stage controls on Ediacaran-Cambrian animal radiations” by means of Fred T. Bowyer, Rachel A. Picket and Mariana Yilales, 31 July 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6462
The paper used to be funded by means of the Herbal Setting Analysis Council (NERC).
Unlocking the Deep Previous: New Find out about Maps the Daybreak of Animal Lifestyles