The USSR inadvertently items its secret spacecraft to antagonistic China
On Nov. 28, 1969, the Soviet Union introduced in all probability essentially the most difficult to understand project of the Moon Race, however after a rocket malfunction, the extremely categorised pill onboard went wayward and ended up intact within the fingers of the USSR’s Chinese language adversaries.
Earlier bankruptcy: Soyuz-8 touchdown

From the writer: Tempo of our building is dependent essentially at the degree of give a boost to from our readers!
The L1E No. 1 project at a look:
Spacecraft designations
7K-L1E No. 1, 11F91
Release car
8K82K UR-500K (Proton-Ok) No. 245-01 / Block D 11S824 No. 25
Release web page
Tyuratam, Website online 81 “Left” (Pad No. 23)
Team
Unpiloted
Release date and time
1969 Nov. 28, 12:00 Moscow Time
Project effects
Release failure all over the operation of the 3rd level
Beginning of the venture
Within the Spring 1967, Soviet engineers flight-tested one of the crucial components of the L3 lunar expeditionary advanced — the Block D higher level. Not like maximum rocket boosters designed to perform in a snappy succession straight away after liftoff, Block D was once meant for maneuvering within the lunar neighborhood and all over essentially the most crucial descent of the LK cosmonaut lander to the Moon, days after departing Earth and within the prerequisites of extended weightlessness.
As part of the L1 circumlunar car, Block D was once introduced into Earth orbit for the primary time in March 1967. The result of that flight are nonetheless clouded in thriller, however it’s identified that the second one such project, a month later, failed to accomplish the maneuver simulating the break out from the Earth’s orbit onto a trans-lunar trajectory.
On the time, the TsKBEM design bureau, which led the Soviet lunar effort, it sounds as if had some doubts in regards to the efficiency of huge rocket levels in long-duration expeditions. It’s evidenced within the contemporaneous notes by means of the top of the TsKBEM bureau Vasily Mishin. In what gave the look to be a to-do record dated April 9, 1967, Mishin wrote down to determine whether or not it might be conceivable to fireplace an engine on Block D as overdue as 4 or seven days into the flight, relying at the availability of electrical energy. This is as regards to the period of time which might be required for Block D to serve as all over a regular lunar expedition as proposed for the N1/L3 venture. (774)
To handle quite a lot of questions with the operation of Block D, TsKBEM began making plans an experimental program, which might find out about the conduct of liquid propellant within the tanks of the Block D all over flight in weightlessness. This enjoy was once it sounds as if thought to be crucial for certifying the distance tug for a piloted project. The hassle incorporated the development of a floor take a look at unit, which might be fitted with particular home windows and lights apparatus that may make it conceivable to {photograph} and movie the fluid processes throughout the car’s tanks all over a very powerful maneuvers and specifically, see the method of propellant consumption from the tank into the engine. Most significantly, floor experiments had been anticipated pave easy methods to exact launches of Block D geared up with cameras for documenting the liquid conduct with the transmission of ensuing photos again to Earth.
As was once the follow on the time, a couple of changed Block D levels, with manufacturing numbers 25 and 26, had been allotted for take a look at flights. Each area tugs had been to be introduced on UR-500K (Proton) rockets, wearing experimental spacecraft derived from the L1 venture and thus designated L1E. The {hardware} from the experimental Block D, constructed for floor checks underneath designation 6S1, may be cannibalized to gather flight-worthy levels No. 25 and 26. (1075)
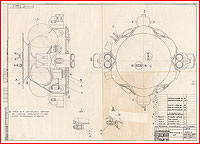
Design of the L1E car
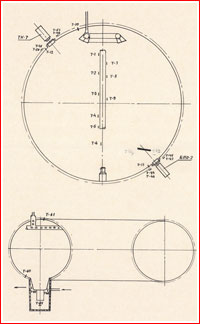
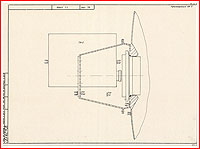
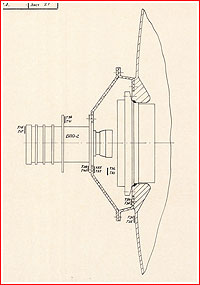
Part a century after the Moon Race, the precise design of the L1E spacecraft remained in large part a thriller. Obviously, it carefully resembled the baseline L1 spacecraft, however it sounds as if, it was once additionally supplied with an extra perspective regulate and maneuver phase, referred to as DOK from the Russian Dvigateli Oreintatsii i Korektsii, which was once fastened on best of the L1’s battery phase. The DOK propulsion phase was once extensively utilized at the L1A take a look at car, meant for the primary release of the N1 Moon rocket, and it was once in the end meant for the LOK lunar orbiting spacecraft from the L3 expeditionary advanced, so its use at the L1E may just assist validate any other part of the lunar {hardware}.
The addition of the DOK phase supposed that the usual payload fairing and the release break out tower of the L1 spacecraft weren’t suitable with the L1E interfaces and, subsequently, a special payload fairing could be required. However, as a result of L1E by no means meant to hold a workforce, it didn’t want an break out rocket.
The Descent Module of the L1E spacecraft was once almost definitely borrowed unchanged from the L1 car, which in flip derived from the Soyuz spacecraft. Aboard the L1E, the pressurized pill almost definitely contained some avionics and, in all probability, different apparatus no longer designed to perform within the vacuum of area. As long run trends would display, the Descent Module on L1E was once geared up with workable ablative thermal coverage enabling the standard reentry and touchdown, although there is not any documental proof that the go back had ever been deliberate.
Similarly little is understood in regards to the L1E flight program. In additional than 3 many years of the post-Soviet duration, no longer a unmarried authentic supply make clear the flight profile of the project. In accordance with the monitoring information of 1 a success L1E project, it’s logical to suppose that the primary project aimed to simulate the maneuvers of the lunar lander of the L3 advanced, however within the Earth’s orbit.
Building
On April 20, 1968, an meantime head of TsKBEM Yuri Semenov, signed the technical task for the development of an experimental floor unit for the longer term L1E spacecraft. The development of the 2 flight cars was once continuing as neatly. Consequently, on the top of the Moon Race with the USA in 1968, TsKBEM discovered itself growing a minimum of 5 Soyuz-derived workforce cars, together with the 7K-OK ships for missions within the Earth orbit, L1 ships for circumlunar flights, the L1A variant for the N1 rocket, the LOK orbiter for the L3 lunar expeditionary advanced and the L1E. The LK lunar lander and a mess of alternative components of the lunar program had been additionally within the building pipeline. No longer strangely, extra urgent problems, specifically two failed launches of the N1 rocket in 1969, driven the primary L1E project till the top of that yr.
L1E project lifts off
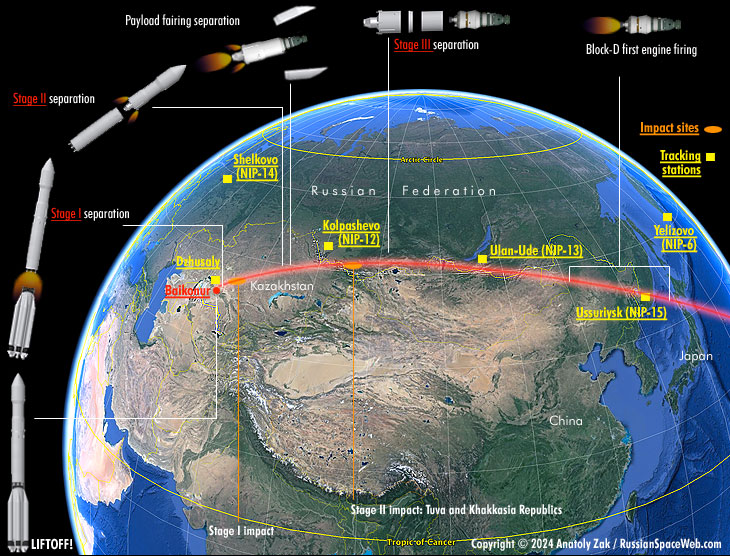
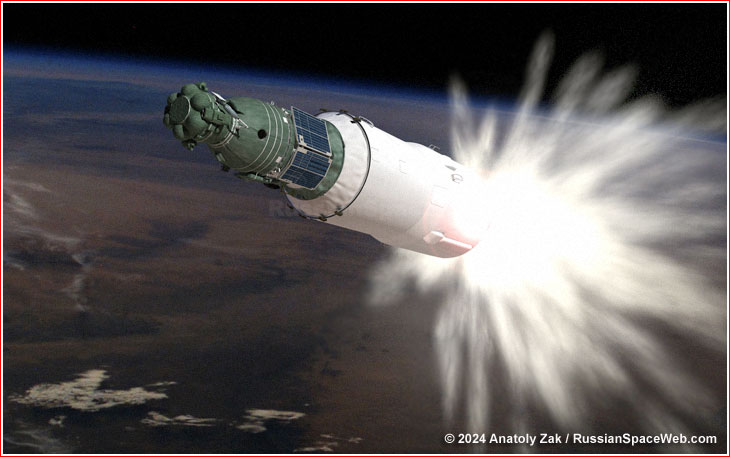
The UR-500K rocket wearing the 7K-L1E spacecraft lifted off on Nov. 28, 1969, at 12:00 Moscow Time, from the “Left” pad at Website online 81 in Tyuratam. (400) The primary two levels of the car finished their paintings as deliberate, however at L+556.6 seconds into the flight, the telemetry confirmed a violent jolt close to the decrease bulkhead of the gas tank of the 3rd level, indicating an explosion of its 8D48 engine.
Underneath standard cases, the 3rd level was once meant to split in a suborbital trajectory, simply in need of orbital pace, and after reentry, to splash down within the Pacific Ocean, east of Japan. Then again, relying at the actual time of the untimely engine shutdown, the have an effect on web page for the 3rd level and its payload would shift westward alongside the bottom observe of the ascent trajectory to Sea of Japan, the Russian Pacific Coast, Jap China and the Russian A long way East. In most cases, possibilities for depositing the level at the Chinese language territory had been reasonably small, however this is precisely what came about within the Nov. 28, 1969, release. Clearly, the location was once additional difficult by means of the truth that the L1E spacecraft incorporated the Descent Module designed to live to tell the tale the reentry. And by means of that point, the USSR stopped equipping its returnable cars with explosive units to stop them from falling into the improper fingers.
Consequently, after the remainder of the L1E car disintegrated underneath the searing warmth of reentry, the freed Descent Module landed reputedly intact some 200 kilometers from town of Harbin in China.
Coincidently, the Soviet-Sino family members had been at their lowest on the time of the L1E release, coming at the heels of a brief however bloody border warfare previous in 1969.
As a result of even a nuclear change between the 2 powers was once no longer out of the world of probabilities in this type of heated political environment, losing a Soviet rocket payload into the Chinese language territory was once no longer a trivial subject. And naturally, even after the surprising touchdown was once deemed to be an twist of fate, the Soviets had no alternative for buying their pill again. In line with the post-Chilly Warfare studies, the Descent Module was once, if truth be told, recovered intact by means of the Chinese language government, and after, without a doubt, cautious exam, it ended up in a museum of the Other folks’s Liberation Military. (1076)
Obviously, the Soviet spacecraft was once a literal “reward from the skies” for the nascent Chinese language area program, which on the time, was once simply 5 months clear of launching a satellite tv for pc of its personal, however a minimum of a decade at the back of the Soviet area program. In spite of a overdue get started, China temporarily advanced aspirations in piloted area missions and by means of 1975, the primary Chinese language recoverable area pill went into orbit. When the primary Chinese language workforce car in any case made its public debut on the finish of the Nineties and the early 2000s, observers had been surprised by means of its uncanny resemblance to the Soyuz spacecraft…
Subsequent bankruptcy: Soyuz-9 project