Abstract: Opposite to fears of “virtual dementia,” new analysis reveals that the use of virtual generation is related to a discounted chance of cognitive decline in older adults. A big-scale meta-analysis of over 400,000 contributors published that virtual engagement correlates with a 58% decrease chance of cognitive impairment.Generation demanding situations the mind, fosters social connection, and permits compensatory gear like reminders and GPS that improve independence. Those findings recommend that wholesome, intentional tech use might improve psychological resilience as we age.Key Info:Cognitive Coverage: Virtual generation use is related to a 58% decrease chance of cognitive impairment.Psychological Stimulation: Enticing with evolving applied sciences might act as mind workout, bettering problem-solving and flexibility.Social Enhance: Gear like video calls and messaging cut back isolation and improve mind well being via higher social interplay.Supply: Baylor Faculty of MedicineAs the primary era that interacted with virtual generation reaches an age the place dementia dangers emerge, scientists have requested the query: Is there a correlation between virtual generation use and an higher chance of dementia? With the words “mind rot” and “mind drain” circulating on social media, it might seem that the general public would think the solution is sure.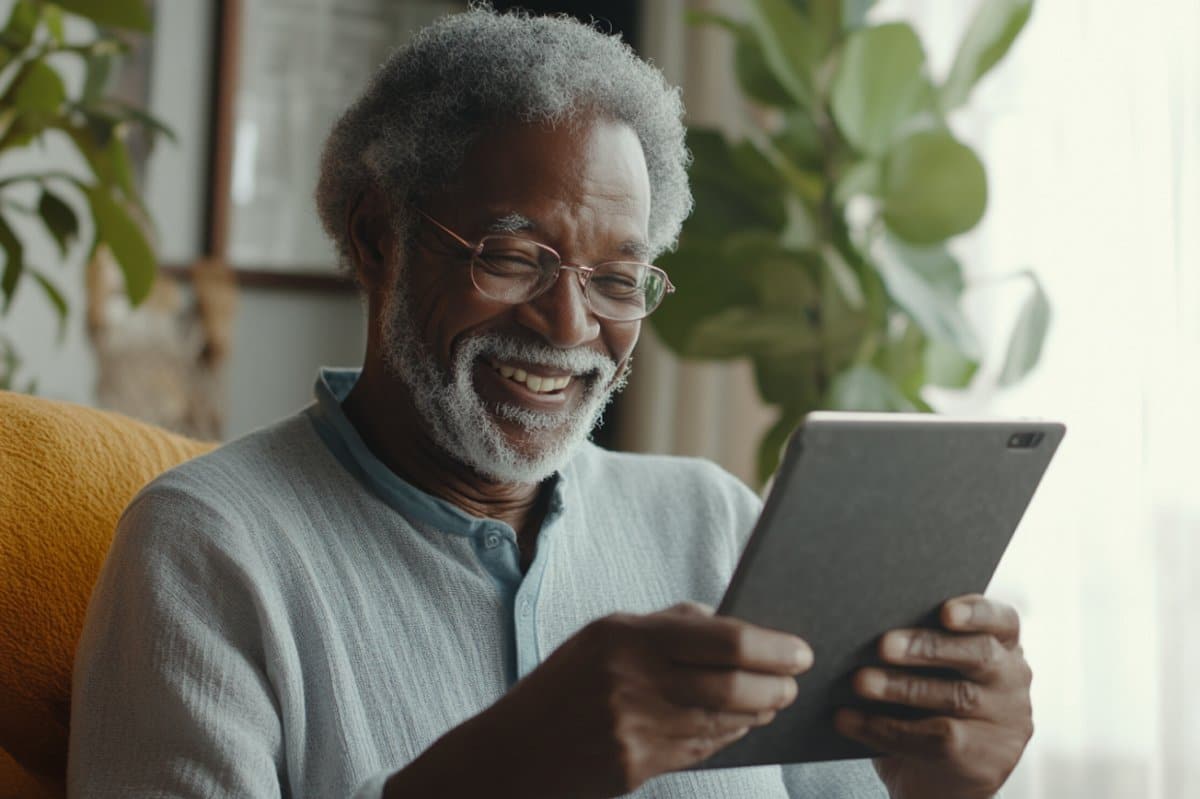  A dementia prognosis is indicated partly when cognitive adjustments result in a lack of independence with day-to-day duties. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsHowever, a brand new learn about in Nature Human Conduct by means of neuroscientists at Baylor College and the College of Texas at Austin Dell Clinical College finds the other – virtual applied sciences are in truth related to lowered cognitive decline.The learn about – A meta-analysis of generation use and cognitive growing older – was once sparked by means of the continuing worry in regards to the passive process of virtual applied sciences and their relation to accelerating dangers of dementia. Learn about co-authors are Jared F. Benge, Ph.D., medical neuropsychologist and affiliate professor of neurology at Dell Clinical College and UT Well being Austin’s Complete Reminiscence Middle throughout the Mulva Sanatorium for the Neurosciences, and Michael Ok. Scullin, Ph.D., affiliate professor of psychology and neuroscience at Baylor.“You’ll turn at the information on as regards to any day and also you’ll see other folks speaking about how applied sciences are harming us,” Scullin mentioned. “Other folks frequently use the phrases ‘mind drain’ and ‘mind rot,’ and now virtual dementia is an rising word. As researchers, we needed to understand if this was once true.”The “virtual dementia” speculation predicts that a life-time of publicity to virtual generation will irritate cognitive talents. To the contrary, the learn about’s findings problem this speculation, indicating as an alternative that engagement with virtual generation fosters cognitive resilience in those adults.Reviewing greater than 136 research with information that encompassed over 400,000 adults, and longitudinal research with a median of 6 years of follow-up information, Scullin and Benge discovered compelling proof that virtual generation use is related to higher cognitive growing older results, moderately than hurt. The researchers’ learn about supported the “technological reserve” speculation, discovering that virtual applied sciences can advertise behaviors that keep cognition. Actually, their learn about published that virtual generation use correlates with a 58% decrease chance of cognitive impairment.This development of cognitive coverage endured when the researchers managed for socioeconomic standing, schooling, age, gender, baseline cognitive skill, social improve, total well being, and engagement with psychological actions like studying that would possibly have defined the findings. Build up in problem-solving skillsScullin mentioned that for some, those findings are sudden as generation use is frequently related to being sedentary each bodily and mentally.On the other hand, for the present era of older adults who had been offered to the primary technological developments – computer systems, the Web and smartphones – previous their adolescence, the use of generation is cognitively difficult as a result of it’s everchanging. “One of the crucial first issues that middle-age and older adults had been pronouncing is that ‘I’m so annoyed by means of this pc. That is onerous to be informed.’ That’s in truth a mirrored image of the cognitive problem, that could be really useful for the mind even though it doesn’t really feel nice within the second.” Scullin mentioned. Generation calls for consistent adaption, he mentioned, akin to working out new instrument updates, troubleshooting Web loss or filtering out site commercials. “For those who’re doing that for years and also you’re in reality enticing with it, even if chances are you’ll revel in frustration, that can be an indication of you exercising your mind,” he mentioned. Social connectionTechnology additionally permits verbal exchange and engagement like by no means ahead of, which is able to make bigger alternatives for connectivity. Video calls, emails and messaging apps lend a hand deal with social networks, particularly for individuals who would no longer in a different way incessantly see their members of the family. “Now you’ll be able to connect to households throughout generations,” Scullin mentioned. “You no longer handiest can communicate to them, you’ll be able to see them. You’ll proportion photos. You’ll trade emails and it’s all inside of a 2d or much less. In order that approach there’s a better alternative for lowering loneliness.”Higher social connectedness is a well-documented correlate of cognitive functioning in older adults, offering a hyperlink between diminished isolation from virtual applied sciences and lowered dangers of dementia. Have an effect on of “virtual scaffolding”A dementia prognosis is indicated partly when cognitive adjustments result in a lack of independence with day-to-day duties. Gear akin to virtual reminders, GPS navigation and on-line banking permit older adults to stay impartial regardless of cognitive difficulties via virtual scaffolding.In step with the analysis article, this virtual scaffold “facilitates higher useful results in older adults whilst normal cognitive functioning declines.”Applied sciences can function a compensatory improve machine to deal with normal independence and cut back the chance of a dementia prognosis even with the presence of a few cognitive decline. “As medical apply continues to transport towards an individualized, precision-medicine means, it’ll be important for the sector to spot for whom and for the way lengthy, such virtual scaffolding is efficacious,” the researchers mentioned.Selling wholesome generation useWhile Scullin acknowledges the unintended effects of generation, akin to distracted riding or the use of generation over constant face-to-face interplay, he additionally emphasizes how selling a wholesome use of virtual gear in older adults is really useful for his or her cognitive well being. “You probably have a dad or mum or grandparent who’s simply staying clear of generation, perhaps revisit that. May they learn how to use photograph, messaging, or calendar apps on a smartphone or pill? Get started easy and be very affected person whilst they be told,” he mentioned.Social media use is every other extremely debated subject relating to cognitive results. Whilst he says it’s onerous to are expecting the cognitive results of without end scrolling on TikTok, Scullin does argue that producing movies via ingenious cognition might be really useful. As well as, he mentioned that interacting with communities on-line may give advantages by means of forming social connections.“Shall we spend a very long time speaking about all of the explicit tactics during which generation use will also be dangerous. On the other hand, the web impact because the Nineties has been sure for total cognition in older adults,” he mentioned.FUNDINGThe learn about was once supported by means of investment from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R01AG082783; M.Ok.S., J.F.B.).About this neurotech and dementia analysis newsAuthor: Shelby Cefaratti-Bertin
A dementia prognosis is indicated partly when cognitive adjustments result in a lack of independence with day-to-day duties. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsHowever, a brand new learn about in Nature Human Conduct by means of neuroscientists at Baylor College and the College of Texas at Austin Dell Clinical College finds the other – virtual applied sciences are in truth related to lowered cognitive decline.The learn about – A meta-analysis of generation use and cognitive growing older – was once sparked by means of the continuing worry in regards to the passive process of virtual applied sciences and their relation to accelerating dangers of dementia. Learn about co-authors are Jared F. Benge, Ph.D., medical neuropsychologist and affiliate professor of neurology at Dell Clinical College and UT Well being Austin’s Complete Reminiscence Middle throughout the Mulva Sanatorium for the Neurosciences, and Michael Ok. Scullin, Ph.D., affiliate professor of psychology and neuroscience at Baylor.“You’ll turn at the information on as regards to any day and also you’ll see other folks speaking about how applied sciences are harming us,” Scullin mentioned. “Other folks frequently use the phrases ‘mind drain’ and ‘mind rot,’ and now virtual dementia is an rising word. As researchers, we needed to understand if this was once true.”The “virtual dementia” speculation predicts that a life-time of publicity to virtual generation will irritate cognitive talents. To the contrary, the learn about’s findings problem this speculation, indicating as an alternative that engagement with virtual generation fosters cognitive resilience in those adults.Reviewing greater than 136 research with information that encompassed over 400,000 adults, and longitudinal research with a median of 6 years of follow-up information, Scullin and Benge discovered compelling proof that virtual generation use is related to higher cognitive growing older results, moderately than hurt. The researchers’ learn about supported the “technological reserve” speculation, discovering that virtual applied sciences can advertise behaviors that keep cognition. Actually, their learn about published that virtual generation use correlates with a 58% decrease chance of cognitive impairment.This development of cognitive coverage endured when the researchers managed for socioeconomic standing, schooling, age, gender, baseline cognitive skill, social improve, total well being, and engagement with psychological actions like studying that would possibly have defined the findings. Build up in problem-solving skillsScullin mentioned that for some, those findings are sudden as generation use is frequently related to being sedentary each bodily and mentally.On the other hand, for the present era of older adults who had been offered to the primary technological developments – computer systems, the Web and smartphones – previous their adolescence, the use of generation is cognitively difficult as a result of it’s everchanging. “One of the crucial first issues that middle-age and older adults had been pronouncing is that ‘I’m so annoyed by means of this pc. That is onerous to be informed.’ That’s in truth a mirrored image of the cognitive problem, that could be really useful for the mind even though it doesn’t really feel nice within the second.” Scullin mentioned. Generation calls for consistent adaption, he mentioned, akin to working out new instrument updates, troubleshooting Web loss or filtering out site commercials. “For those who’re doing that for years and also you’re in reality enticing with it, even if chances are you’ll revel in frustration, that can be an indication of you exercising your mind,” he mentioned. Social connectionTechnology additionally permits verbal exchange and engagement like by no means ahead of, which is able to make bigger alternatives for connectivity. Video calls, emails and messaging apps lend a hand deal with social networks, particularly for individuals who would no longer in a different way incessantly see their members of the family. “Now you’ll be able to connect to households throughout generations,” Scullin mentioned. “You no longer handiest can communicate to them, you’ll be able to see them. You’ll proportion photos. You’ll trade emails and it’s all inside of a 2d or much less. In order that approach there’s a better alternative for lowering loneliness.”Higher social connectedness is a well-documented correlate of cognitive functioning in older adults, offering a hyperlink between diminished isolation from virtual applied sciences and lowered dangers of dementia. Have an effect on of “virtual scaffolding”A dementia prognosis is indicated partly when cognitive adjustments result in a lack of independence with day-to-day duties. Gear akin to virtual reminders, GPS navigation and on-line banking permit older adults to stay impartial regardless of cognitive difficulties via virtual scaffolding.In step with the analysis article, this virtual scaffold “facilitates higher useful results in older adults whilst normal cognitive functioning declines.”Applied sciences can function a compensatory improve machine to deal with normal independence and cut back the chance of a dementia prognosis even with the presence of a few cognitive decline. “As medical apply continues to transport towards an individualized, precision-medicine means, it’ll be important for the sector to spot for whom and for the way lengthy, such virtual scaffolding is efficacious,” the researchers mentioned.Selling wholesome generation useWhile Scullin acknowledges the unintended effects of generation, akin to distracted riding or the use of generation over constant face-to-face interplay, he additionally emphasizes how selling a wholesome use of virtual gear in older adults is really useful for his or her cognitive well being. “You probably have a dad or mum or grandparent who’s simply staying clear of generation, perhaps revisit that. May they learn how to use photograph, messaging, or calendar apps on a smartphone or pill? Get started easy and be very affected person whilst they be told,” he mentioned.Social media use is every other extremely debated subject relating to cognitive results. Whilst he says it’s onerous to are expecting the cognitive results of without end scrolling on TikTok, Scullin does argue that producing movies via ingenious cognition might be really useful. As well as, he mentioned that interacting with communities on-line may give advantages by means of forming social connections.“Shall we spend a very long time speaking about all of the explicit tactics during which generation use will also be dangerous. On the other hand, the web impact because the Nineties has been sure for total cognition in older adults,” he mentioned.FUNDINGThe learn about was once supported by means of investment from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R01AG082783; M.Ok.S., J.F.B.).About this neurotech and dementia analysis newsAuthor: Shelby Cefaratti-Bertin
Supply: Baylor Faculty of Medication
Touch: Shelby Cefaratti-Bertin – Baylor Faculty of Medication
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Closed get entry to.
“A meta-analysis of generation use and cognitive growing older” by means of Jared F. Benge et al. Nature Human BehaviorAbstractA meta-analysis of generation use and cognitive agingThe first era who engaged with virtual applied sciences has reached the age the place dangers of dementia emerge. Has technological publicity helped or harmed cognition in virtual pioneers?The virtual dementia speculation predicts that a life-time of generation publicity worsens cognitive talents.An alternate speculation is that such exposures result in technological reserve, through which virtual applied sciences advertise behaviours that keep cognition.We examined those hypotheses in a meta-analysis and systematic evaluation of research revealed in Medline, PsycInfo, CINAHL, Science Direct, Scopus, Cochrane Library, ProQuest and Internet of Science. Research had been incorporated in the event that they had been observational or cohort research excited by normal virtual generation use in older adults (over age 50) and incorporated both a cognitive or dementia prognosis result.We recognized 136 papers that met inclusion standards, of which 57 had been appropriate with odds ratio or danger ratio meta-analysis.Those research incorporated 411,430 adults (baseline age M = 68.7 years; 53.5% feminine) from cross-sectional and longitudinal observational research (vary: 1–18 years, M = 6.2 years).Use of virtual applied sciences was once related to lowered chance of cognitive impairment (OR = 0.42, 95% CI 0.35–0.52) and lowered time-dependent charges of cognitive decline (HR = 0.74, 95% CI 0.66–0.84). Results remained vital when accounting for demographic, socioeconomic, well being and cognitive reserve proxies.All research had been evaluated for high quality at the foundation of a standardized tick list; the main results replicated when restricting analyses to the highest-quality research.Further paintings is had to check bidirectional causal interpretations, perceive mechanisms that underpin technological reserve, and establish how sorts and timings of generation exposures affect cognitive well being.
Virtual Tech Might Scale back Dementia Possibility – Neuroscience Information