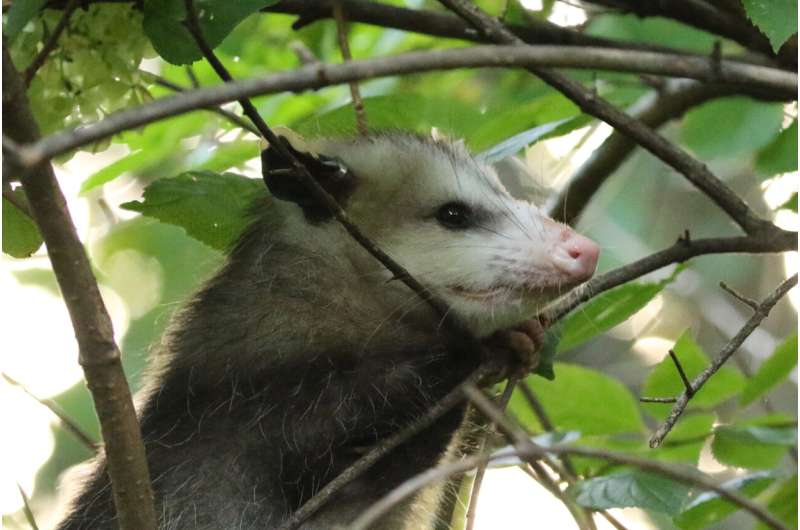
A Virginia Tech find out about of flora and fauna not unusual in Virginia discovered that SARS-CoV-2, the virus chargeable for COVID-19, is fashionable in animals, specifically round spaces of excessive human process. The researchers recognized variants in keeping with the ones circulating in people on the time, and one opossum with prior to now unreported viral mutations, underscoring the potential of adjustments that may probably have an effect on people and their immune reaction. Credit score: Joseph Hoyt/Virginia Tech
SARS-CoV-2, the virus chargeable for COVID-19, is fashionable amongst flora and fauna species, in keeping with Virginia Tech analysis printed July 29, 2024 in Nature Communications. The virus was once detected in six not unusual yard species, and antibodies indicating prior publicity to the virus have been present in 5 species, with charges of publicity starting from 40 to 60% relying at the species.
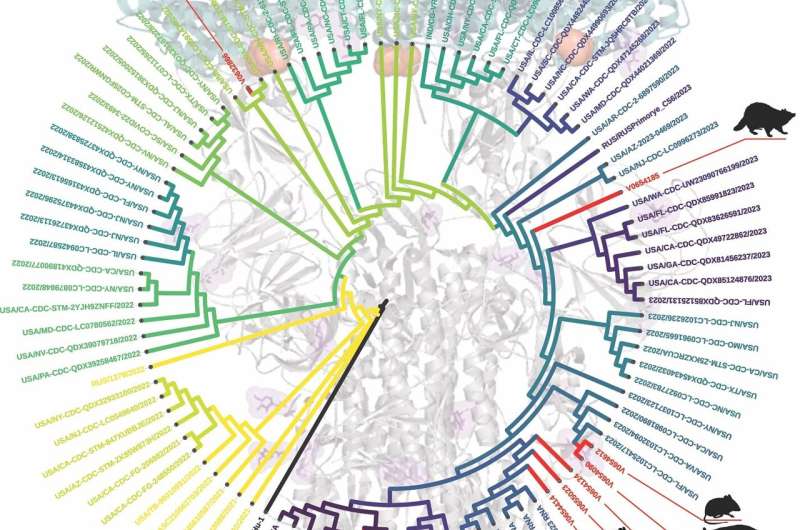
Genetic monitoring in wild animals showed each the presence of SARS-CoV-2 and the lifestyles of distinctive viral mutations with lineages intently matching variants circulating in people on the time, additional supporting human-to-animal transmission, the find out about discovered.
The very best publicity to SARS CoV-2 was once present in animals close to mountain climbing trails and high-traffic public spaces, suggesting the virus handed from people to flora and fauna, in keeping with scientists on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute at VTC, the Division of Organic Sciences in Virginia Tech’s Faculty of Science, and the Fralin Lifestyles Sciences Institute.
The findings spotlight the identity of novel mutations in SARS-CoV-2 in flora and fauna and the will for huge surveillance, researchers say. Those mutations might be extra damaging and transmissible, growing demanding situations for vaccine construction.
The scientists wired, then again, that they discovered no proof of the virus being transmitted from animals to people, and other folks must no longer concern standard interactions with flora and fauna.
Investigators examined animals from 23 not unusual Virginia species for each energetic infections and antibodies indicating earlier infections. They discovered indicators of the virus in deer mice, Virginia opossums, raccoons, groundhogs, Japanese cottontail rabbits, and Japanese purple bats. The virus remoted from one opossum confirmed viral mutations that have been prior to now unreported and will probably have an effect on how the virus impacts people and their immune reaction.
Consider a virulent disease is sort of a key, and the cells it may well infect are like locks. A plague can not infect any cellular of any animal; it must discover a cellular with the best “lock” (referred to as a receptor) or exchange its key (the viral proteins) to suit a brand new lock. To do that, a key wishes to switch form through obtaining mutations to suit the brand new lock. That is what Carla Finkielstein and the Virginia Tech Molecular Diagnostic Lab on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute famous with the keys found in SARS-CoV-2 when the virus jumped to wild species like opossums and squirrels. The important thing S-protein bought no less than two mutations, displayed in yellow on this simulation, that equipped an evolutionary trail for the virus to leap and transmit to different species. Credit score: Carla Finkielstein/Virginia Tech
“The virus can soar from people to flora and fauna after we are involved with them, like a hitchhiker switching rides to a brand new, extra appropriate host,” mentioned Carla Finkielstein, professor of organic sciences on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute at VTC and some of the paper’s corresponding authors.
“The objective of the virus is to unfold to be able to live on. The virus goals to contaminate extra people, however vaccinations offer protection to many people. So, the virus turns to animals, adapting and mutating to thrive within the new hosts.”
SARS CoV-2 infections have been prior to now recognized in flora and fauna, basically in white-tailed deer and feral mink. The Virginia Tech find out about considerably expands the choice of species tested and the working out of virus transmission to and amongst flora and fauna. The knowledge suggests publicity to the virus has been fashionable in flora and fauna and that spaces with excessive human process might function issues of touch for cross-species transmission.
“This find out about was once truly motivated through seeing a big, necessary hole in our wisdom about SARS-CoV-2 transmission in a broader flora and fauna group,” mentioned Joseph Hoyt, assistant professor of Organic Sciences in Virginia Tech’s Faculty of Science and corresponding creator at the paper. “A large number of research up to now have keen on white-tailed deer, whilst what is going on in a lot of our not unusual yard flora and fauna stays unknown.”
The analysis crew amassed 798 nasal and oral swabs throughout Virginia from animals both live-trapped within the box and launched, or being handled through flora and fauna rehabilitation facilities. The crew additionally received 126 blood samples from six species. The places have been selected to check the presence of the virus in animals in websites with various ranges of human process, from city spaces to faraway wasteland.
The find out about additionally recognized two mice on the similar website online at the similar day with the very same variant, indicating they both each were given it from the similar human, or one inflamed the opposite.
Researchers aren’t sure in regards to the way of transmission from people to animals. One chance is wastewater, however the Virginia Tech scientists imagine trash receptacles and discarded meals are much more likely resources.
Consider a virulent disease is sort of a key, and the cells it may well infect are like locks. A plague can not infect any cellular of any animal; it must discover a cellular with the best “lock” (referred to as a receptor) or exchange its key (the viral proteins) to suit a brand new lock. To do that, a key wishes to switch form through obtaining mutations to suit the brand new lock. That is what Carla Finkielstein and the Virginia Tech Molecular Diagnostic Lab on the Fralin Biomedical Analysis Institute famous with the keys found in SARS-CoV-2 when the virus jumped to wild species like opossums and squirrels. The important thing S-protein bought no less than two mutations, displayed in yellow on this simulation, that equipped an evolutionary trail for the virus to leap and transmit to different species. The pink section is the receptor that is identified through the S-protein so the virus can input. Credit score: Carla Finkielstein/Virginia Tech
“I believe the massive take house message is the virus is lovely ubiquitous,” mentioned Amanda Goldberg, a former postdoctoral affiliate in Hoyt’s lab, who’s the find out about’s first creator. “We discovered positives in a big suite of not unusual yard animals.”
Whilst this find out about centered at the state of Virginia, most of the species that examined certain are not unusual flora and fauna discovered all over North The us. It’s most likely they’re being uncovered in different spaces as neatly, and surveillance throughout a broader area is urgently wanted, Hoyt mentioned.
“The virus is detached as to if its host walks on two legs or 4. Its number one purpose is survival. Mutations that don’t confer a survival or replication merit to the virus is not going to persist and can in the end disappear,” mentioned Finkielstein, who may be director of the Virginia Tech Molecular Diagnostics Lab. The Roanoke lab was once established in April 2020 to amplify COVID-19 trying out.
“We understood the essential significance of sequencing the genome of the virus infecting the ones species,” Finkielstein mentioned. “It was once a huge process that would best be completed through a skilled team of molecular biologists, bioinformaticians, and modelers in a cutting-edge facility. I’m pleased with my crew and my collaborators, their professionalism, and the whole thing they contributed to make sure our luck.”
Surveillance for those mutations must proceed and no longer be pushed aside, the scientists mentioned. Extra analysis is wanted about how the virus is transmitted from people to flora and fauna, how it would unfold inside of a species, and in all probability from one species to some other.
“This find out about highlights the doubtless massive host vary SARS-CoV-2 could have in nature and truly how fashionable it may well be,” Hoyt mentioned. “There’s numerous paintings to be achieved to grasp which species of flora and fauna, if any, will likely be necessary within the long-term upkeep of SARS-CoV-2 in people.”
“However what now we have already realized,” Finkielstein mentioned, “is that SARS CoV-2 is not just a human downside, and that it takes a multidisciplinary crew to handle its have an effect on on more than a few species and ecosystems successfully.”
Additional info:
Fashionable publicity to SARS-CoV-2 in flora and fauna communities, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49891-w
Equipped through
Virginia Tech
Quotation:
Virus that reasons COVID-19 is fashionable in flora and fauna, scientists in finding (2024, July 29)
retrieved 29 July 2024
from
This record is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.













