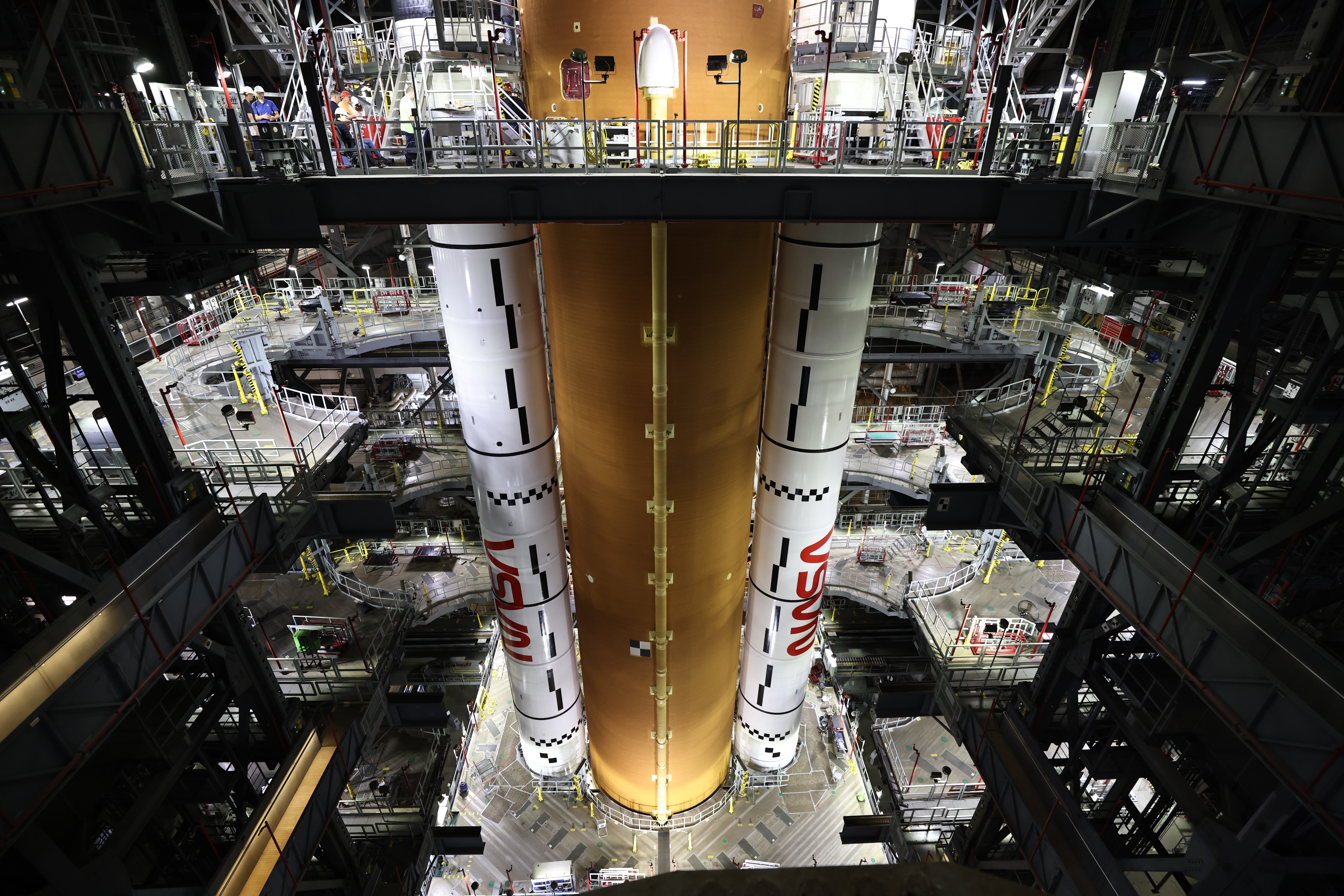
NASA’s new moon rover prototype effectively finished a disadvantage direction simulating the rugged terrain of the lunar floor. The rover, known as VIPER (Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover), is predicted to release to the lunar south pole in November 2024 atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. To check the rover’s mobility, engineers at NASA’s Glenn Analysis Heart in Cleveland created a simulated lunar atmosphere, together with massive rocks, steep slopes and deep craters. VIPER is slated to land on Mons Mouton, a mountain close to the moon’s south pole. It is going to contact down close to the western rim of Nobile crater, the place it’s going to be tasked with characterizing the lunar atmosphere to assist in opting for long run Artemis program touchdown websites all over its more or less 100-day project. Similar: Watch NASA’s VIPER moon rover observe leaving its lunar lander (video) NASA’s VIPER rover traverses a “moon impediment direction” on the company’s Glenn Analysis Heart. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Ames Analysis Heart)NASA shared a video of the rover’s contemporary mobility checks, appearing it was once in a position to triumph over the prospective demanding situations it’s going to face at the lunar floor. As a part of the checks, the rover rolled over giant rocks and needed to maneuver itself via quicksand-like soil because it climbed up steep slopes and over craters.
NASA’s VIPER rover traverses a “moon impediment direction” on the company’s Glenn Analysis Heart. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Ames Analysis Heart)NASA shared a video of the rover’s contemporary mobility checks, appearing it was once in a position to triumph over the prospective demanding situations it’s going to face at the lunar floor. As a part of the checks, the rover rolled over giant rocks and needed to maneuver itself via quicksand-like soil because it climbed up steep slopes and over craters.  An engineer maps out the location of rocks all over VIPER checking out at The NASA Glenn Analysis Heart. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Glenn Analysis Heart)A part of NASA’s Artemis program objectives to arrange an everlasting agreement on the moon’s south pole. VIPER will play a key function in serving to resolve places the place water and different sources might be harvested to maintain people all over prolonged remains at the moon. The VIPER project staff additionally objectives to handle open questions surrounding how frozen water and different volatiles were given at the moon within the first position, the place they got here from, what has saved a few of them preserved over billions of years and the place they cross once they break out the lunar soil, NASA officers mentioned. Engineers at NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston additionally lately examined VIPER’s ultimate science tool — a drill aptly named TRIDENT, which stands for The Regolith Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain.
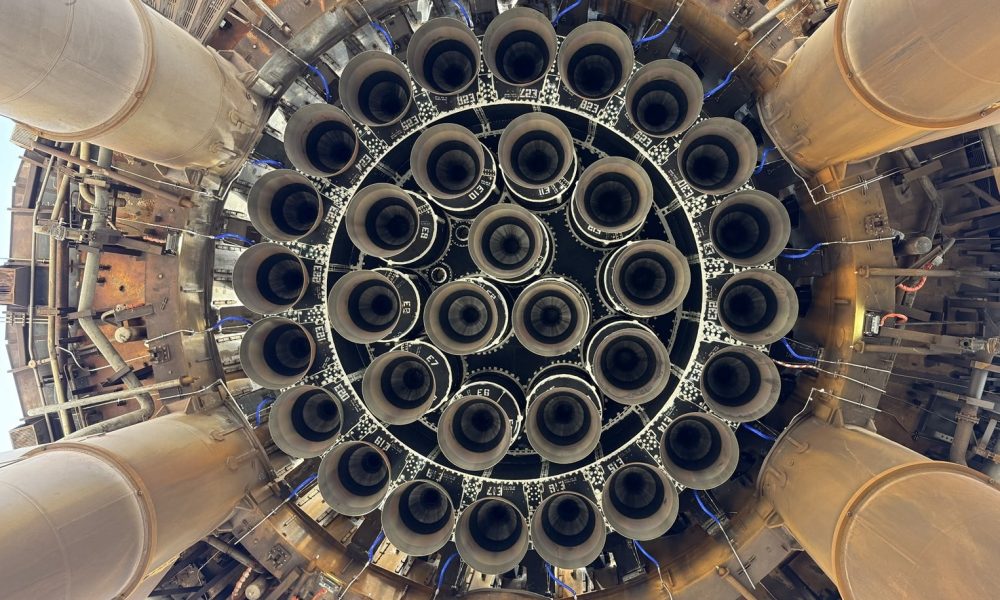
An engineer maps out the location of rocks all over VIPER checking out at The NASA Glenn Analysis Heart. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Glenn Analysis Heart)A part of NASA’s Artemis program objectives to arrange an everlasting agreement on the moon’s south pole. VIPER will play a key function in serving to resolve places the place water and different sources might be harvested to maintain people all over prolonged remains at the moon. The VIPER project staff additionally objectives to handle open questions surrounding how frozen water and different volatiles were given at the moon within the first position, the place they got here from, what has saved a few of them preserved over billions of years and the place they cross once they break out the lunar soil, NASA officers mentioned. Engineers at NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston additionally lately examined VIPER’s ultimate science tool — a drill aptly named TRIDENT, which stands for The Regolith Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain.  A staff of engineers from NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston and Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California investigate cross-check TRIDENT – brief for The Regolith Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain – in a while after its arrival on the integration and take a look at facility. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Robert Markowitz)The drill is the fourth and ultimate science tool to reach on the blank room, the place VIPER is being constructed. The NASA staff, along engineers from Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California, carried out a chain of pre-integration inspections of the drill, which might be used to dig up soil cuttings from up to 3 ft beneath the lunar floor. TRIDENT is a rotary percussive drill, because of this it spins to chop into the bottom whilst hammering to fragment laborious subject material. The drill will have the ability to measure the energy and compactness of the lunar soil, in addition to measure the temperature beneath the skin, in line with a remark from NASA.
A staff of engineers from NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston and Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California investigate cross-check TRIDENT – brief for The Regolith Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain – in a while after its arrival on the integration and take a look at facility. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Robert Markowitz)The drill is the fourth and ultimate science tool to reach on the blank room, the place VIPER is being constructed. The NASA staff, along engineers from Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California, carried out a chain of pre-integration inspections of the drill, which might be used to dig up soil cuttings from up to 3 ft beneath the lunar floor. TRIDENT is a rotary percussive drill, because of this it spins to chop into the bottom whilst hammering to fragment laborious subject material. The drill will have the ability to measure the energy and compactness of the lunar soil, in addition to measure the temperature beneath the skin, in line with a remark from NASA.
Watch NASA’s VIPER moon rover overcome a lunar ‘impediment direction’ (video)