Monstrous mud storms steadily ravage Mars, engulfing the Crimson Planet for months. Now, a brand new learn about suggests those world storms could also be associated with a abnormal power imbalance not too long ago came upon around the Martian floor.The sun gadget’s planets and moons soak up power from the solar, yet in addition they emit power again into area. The variation between those two is known as the radiative power price range, or REB. “The REB and its spatial distribution [across latitudes] at once affect the thermal traits of the skin and surroundings” of planets, Liming Li, a professor of physics on the College of Houston and the learn about’s 2d creator, advised Reside Science by way of electronic mail. This implies a planet’s REB determines its local weather.Scientists have studied Earth’s REB in nice element, discovering “an power surplus within the tropics and an power deficit within the polar areas,” Li mentioned. Alternatively, Earth’s annual REB is in large part balanced, with the volume of solar power absorbed kind of balancing the warmth radiated over a yr’s time (even supposing greenhouse gases are converting this to a tiny web absorption).By contrast, researchers know little about Mars’ REB, particularly if it is balanced. Even though principle suggests this must be the case, it is onerous to grasp with out onerous numbers.Similar: Massive ‘kidney beans’ noticed in Mars satellite tv for pc photographs may level to indicators of water and lifeNot figuring out Mars’ REB has additionally averted researchers from gaining a greater working out of the planet’s local weather. Interest and different NASA rovers have captured heaps of Martian climate phenomena. Essentially the most placing of those are the planet-engulfing mud storms that stand up in Mars’ southern hemisphere, a few of that are robust sufficient to imperil present and long term exploration missions. However those observations do not expose the long-term local weather over all the planet. An estimate of Mars’ REB would resolve a part of that puzzle, in keeping with lead learn about creator Larry Guan, a doctoral pupil on the College of Houston.To try this, Guan, Li and researchers from U.S., Spanish and South Korean universities drew on knowledge concerning the infrared and visual radiation that Mars’ floor emitted and mirrored over a number of years. Accumulated by means of the Thermal Emission Spectrometer aboard NASA’s now-defunct Mars International Surveyor, those observations spanned 5 Martian years (about 10 Earth years, since one Martian yr is 687 Earth days). From those measurements, the researchers calculated how a lot power Mars absorbed and emitted throughout its latitudes, from the equator to the poles. For comparability, the researchers additionally calculated Earth’s REB, averaged over 10 Earth years, throughout bands of latitudes.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered immediately on your inbox.The researchers discovered that once Mars’ northern hemisphere reviews spring and summer time, the realm across the northern latitudes absorbs extra power than it emits, growing an “power extra” focused on the earth’s north pole. Likewise, all through the northern hemisphere’s autumn and iciness — the southern hemisphere’s spring and summer time — the opposite happens, with an power extra creating over extra southerly areas, even supposing that is more potent and cloaks all the hemisphere. The researchers reasoned that this excessive situation happens as a result of, all through the southern spring, Mars is at its closest to the solar, which maximizes the solar power the planet receives.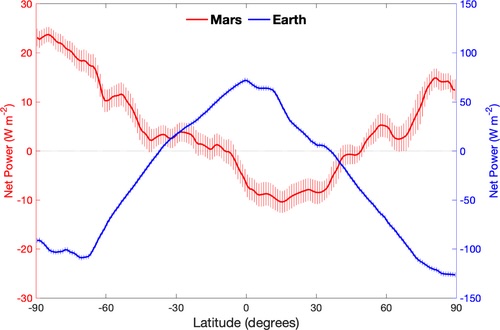 While Mars’ radiative power price range has an uneven U form, Earth’s looks as if a symmetric-but-inverted U. (Symbol credit score: Guan et al., 2024, CC BY)The power surplus might also cause the worldwide mud storms, the analysis suggests. Because the southern hemisphere warms up, so does the layer of Mars’ skinny surroundings involved with it. This creates stipulations that may loft mud debris, thus kicking off the storms, the researchers steered.However the opposite is correct, too: The mud storms most likely affect the planet’s REB. The Mars International Surveyor dataset incorporated measurements all through a dirt hurricane that originated within the southerly Hellas Planitia affect basin and swathed the entire planet one southern spring. Research of this knowledge printed that the storms generally tend to scale back each the solar power absorbed and the warmth emitted by means of Mars, in all probability owing to the a lot of mud debris floating within the surroundings.In spite of those seasonal imbalances, Mars’ annual REB is kind of balanced. But if regarded as throughout latitudes, it differs profoundly from Earth’s. “Earth’s deficits are on the poles; Mars has deficits on the tropics — and vice versa for excesses,” Guan advised Reside Science by way of electronic mail. Which means that while Earth’s poles soak up much less power than they emit, Mars’ poles behave precisely the other.Plus, Guan mentioned, in contrast to Earth, Mars’ polar REB can range by means of 100% between seasons. This can be because of the planet’s skinny surroundings, Li steered, which prevents power distribution between the tropics and the poles.The learn about was once printed Dec. 19 within the magazine AGU Advances.
While Mars’ radiative power price range has an uneven U form, Earth’s looks as if a symmetric-but-inverted U. (Symbol credit score: Guan et al., 2024, CC BY)The power surplus might also cause the worldwide mud storms, the analysis suggests. Because the southern hemisphere warms up, so does the layer of Mars’ skinny surroundings involved with it. This creates stipulations that may loft mud debris, thus kicking off the storms, the researchers steered.However the opposite is correct, too: The mud storms most likely affect the planet’s REB. The Mars International Surveyor dataset incorporated measurements all through a dirt hurricane that originated within the southerly Hellas Planitia affect basin and swathed the entire planet one southern spring. Research of this knowledge printed that the storms generally tend to scale back each the solar power absorbed and the warmth emitted by means of Mars, in all probability owing to the a lot of mud debris floating within the surroundings.In spite of those seasonal imbalances, Mars’ annual REB is kind of balanced. But if regarded as throughout latitudes, it differs profoundly from Earth’s. “Earth’s deficits are on the poles; Mars has deficits on the tropics — and vice versa for excesses,” Guan advised Reside Science by way of electronic mail. Which means that while Earth’s poles soak up much less power than they emit, Mars’ poles behave precisely the other.Plus, Guan mentioned, in contrast to Earth, Mars’ polar REB can range by means of 100% between seasons. This can be because of the planet’s skinny surroundings, Li steered, which prevents power distribution between the tropics and the poles.The learn about was once printed Dec. 19 within the magazine AGU Advances.
We might in the end know what reasons Mars’ gigantic, planet-wide mud storms