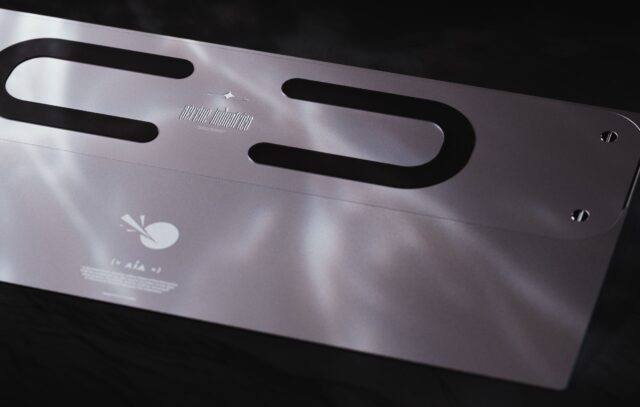
A supermassive thriller lurks on the heart of the Milky Method. Supermassive black holes are gigantic ruptures in space-time that take a seat in the course of many galaxies, periodically sucking in subject prior to spitting it out at close to gentle speeds to form how galaxies evolve.But how they got here to be so monumental is a prevailing thriller in astrophysics, made even deeper through the James Webb House Telescope (JWST). Because it got here on-line in 2022, the telescope has discovered that the cosmic monsters are shockingly ample and large within the few million years after the Large Bang — a discovery that defies lots of our perfect fashions for the way black holes grew.Sophie Koudmani is an astrophysicist on the College of Cambridge looking for solutions to this drawback. Reside Science sat down together with her on the New Scientist Reside tournament in London to talk about the cosmic monsters, how they might have shaped, and the way her paintings the use of supercomputers to simulate them may just rewrite the historical past of our universe.Ben Turner: Why are supermassive black holes so necessary for working out our universe?Sophie Koudmani: Within the universe, the whole thing is hooked up and supermassive black holes play a vital position. They generate an enormous quantity of power that comes from the area across the black holes. As gasoline falls in, its gravitational possible power is transformed into radiation. This makes the gasoline highly regarded, and because it heats up it begins sparkling.The gasoline is heated as much as tens of millions of levels, and its radiation then influences the entire galaxy. It stops gasoline clumping in combination to shape stars, pausing megastar formation in some way that is necessary to provide life like galaxies. The power [from supermassive black holes] can then trip out even additional and affect the large-scale construction of the universe — which is actually necessary for cosmology and working out cosmic evolution.BT: So while you communicate in regards to the power flowing outwards, you are regarding relativistic jets, or near-light velocity outflows from some black holes, proper?Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered immediately for your inbox.SK: Sure. There is 3 types of ways in which black holes “‘discuss”‘ to their host galaxies. One is thru relativistic jets, every other is through winds given off through the accretion disk [the cloud-like structure of gas, dust and plasma that orbits black holes] — those aren’t as skinny as jets — after which there’s radiation. So normally disks give off X-rays and radiation from different portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.BT: You touched in this already, however what would galaxies appear to be if black holes did not exist?SK: So what it’s essential get is what’s continuously referred to as “runaway megastar formation.” All the gasoline would get in no time fed on, and you could possibly get balls of stars. This isn’t what galaxies appear to be. To get the disk galaxies [we see in our universe] it is actually necessary to have some more or less black hollow. You wish to have to get a practical ratio between gasoline and stars, with out them being eaten up right away. Sophie Koudmani. (Symbol credit score: Elodie Guige)BT: What drew you to learning black holes? What questions do you need to reply to about them?SK: Something that I actually like about supermassive black holes is that they’re apparently easy, however then this extremely wealthy physics comes off them. You’ll in reality signify black holes with simply two numbers — their mass and their spin — and that totally tells you what they behave like, it is referred to as the “no hair theorem.” From those two numbers you’ll be able to get all of those other chances. As an example, some black holes have jets and others do not, some have brightly-glowing accretion disks and others are utterly quiet. It is the interplay with the galaxies that brings this out.So it is a easy object on the heart that may be extremely robust. It interacts with one thing that may be reasonably complicated and messy, the galaxy — you get the gasoline, the mud, the celebs, all being held in combination through darkish subject which we do not perceive rather well. And all of those parts have interaction with every different in techniques which might be actually complicated to grasp.BT: It is attention-grabbing that you just described them as easy, as a result of in relativistic physics they are the place all of our equations ruin down and the place we may wish to search for theories of quantum gravity. Do they just glance easy as a result of our theories of them are?SK: It relies what you are desirous about. In case you are desirous about what is going on throughout the tournament horizon, then yeah, certain, the singularity is the place our theories ruin down. We do not know precisely about different bodily phenomena, like Hawking radiation, that would in reality come from within the black hollow.In case you are being concerned about all of this, sure, you may have an overly tricky process! However in case you are enthusiastic about astrophysical black holes, you are within the gasoline flows and radiation across the black hollow. As an astrophysicist, you’ll be able to be reasonably satisfied to find the development horizon, see what it does to the area round it, and be reasonably agnostic about what is inside of. The positioning of that horizon itself is uniquely made up our minds through the mass and the spin.BT: What mysteries has JWST published about black holes that we did not know prior to? SK: We did not know that there could be such a lot of supermassive black holes so early on. They exist in such prime numbers [in the early universe] and inside of beautiful small galaxies, that used to be sudden.My PhD used to be on modeling black holes in small galaxies, it used to be fortunate that I came about to be operating on that as a result of it is change into very related for the early universe. JWST is telling us that black hollow process came about at very early instances and in additional galaxies than used to be idea imaginable. Actually, the process appears to be extra environment friendly than within the present-day universe.
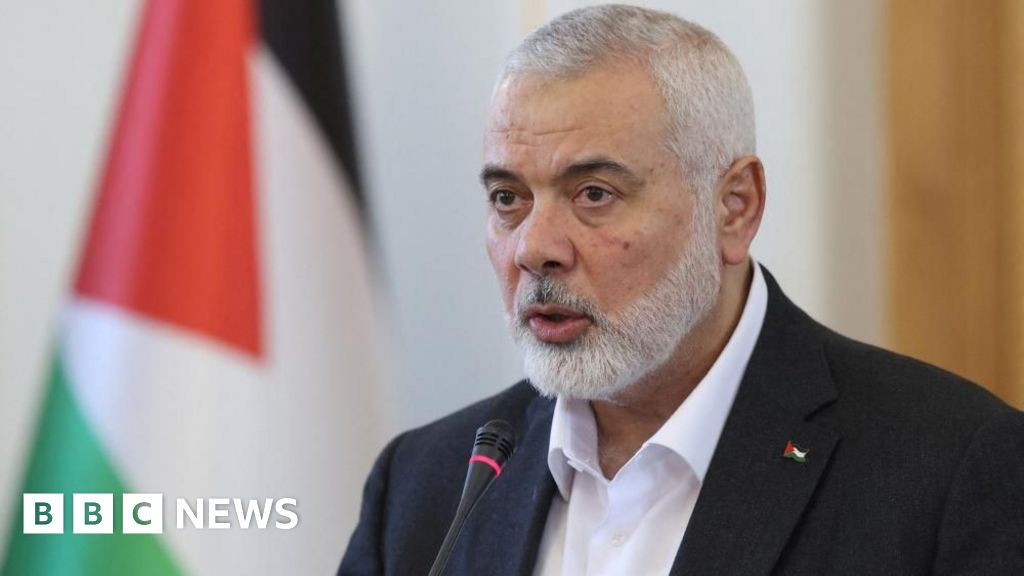
Sophie Koudmani. (Symbol credit score: Elodie Guige)BT: What drew you to learning black holes? What questions do you need to reply to about them?SK: Something that I actually like about supermassive black holes is that they’re apparently easy, however then this extremely wealthy physics comes off them. You’ll in reality signify black holes with simply two numbers — their mass and their spin — and that totally tells you what they behave like, it is referred to as the “no hair theorem.” From those two numbers you’ll be able to get all of those other chances. As an example, some black holes have jets and others do not, some have brightly-glowing accretion disks and others are utterly quiet. It is the interplay with the galaxies that brings this out.So it is a easy object on the heart that may be extremely robust. It interacts with one thing that may be reasonably complicated and messy, the galaxy — you get the gasoline, the mud, the celebs, all being held in combination through darkish subject which we do not perceive rather well. And all of those parts have interaction with every different in techniques which might be actually complicated to grasp.BT: It is attention-grabbing that you just described them as easy, as a result of in relativistic physics they are the place all of our equations ruin down and the place we may wish to search for theories of quantum gravity. Do they just glance easy as a result of our theories of them are?SK: It relies what you are desirous about. In case you are desirous about what is going on throughout the tournament horizon, then yeah, certain, the singularity is the place our theories ruin down. We do not know precisely about different bodily phenomena, like Hawking radiation, that would in reality come from within the black hollow.In case you are being concerned about all of this, sure, you may have an overly tricky process! However in case you are enthusiastic about astrophysical black holes, you are within the gasoline flows and radiation across the black hollow. As an astrophysicist, you’ll be able to be reasonably satisfied to find the development horizon, see what it does to the area round it, and be reasonably agnostic about what is inside of. The positioning of that horizon itself is uniquely made up our minds through the mass and the spin.BT: What mysteries has JWST published about black holes that we did not know prior to? SK: We did not know that there could be such a lot of supermassive black holes so early on. They exist in such prime numbers [in the early universe] and inside of beautiful small galaxies, that used to be sudden.My PhD used to be on modeling black holes in small galaxies, it used to be fortunate that I came about to be operating on that as a result of it is change into very related for the early universe. JWST is telling us that black hollow process came about at very early instances and in additional galaxies than used to be idea imaginable. Actually, the process appears to be extra environment friendly than within the present-day universe. Two merging black holes. (Symbol credit score: Mark Garlick/Science Photograph Library by means of Getty Pictures)BT: Why may that be?SK: Everyone knows about cosmic enlargement — so the Large Bang occurs and the entire universe expands — and which means within the early instances of the universe the whole thing used to be somewhat nearer in combination so gasoline inflows had been more potent, this may have helped to feed black holes.One drawback is that black holes and supernovae more or less compete with one every other. Each megastar formation and black holes eat gasoline. The black hollow blows gasoline away, so do the supernovae, and supernovae additionally evacuate the gasoline from the central area, after which black holes cannot develop for the reason that supernovae have kicked out all the gasoline. It may well be that within the early universe, for one reason why or every other, this does not occur as a lot, and the black hollow simply wins out in that procedure.Actually, there is a robust trace that the black holes win out [in the early universe]. It virtually suggests, on account of how huge those black holes are, that black holes assembled quicker than their host galaxies.BT: You additionally discussed black hollow potency. What does that imply, how can black holes have potency?SK: There are quite a lot of techniques. A method is, once they attract gasoline, how extremely accreting [the speed at which the accretion disk grows] is it? There is a factor referred to as a black hollow velocity restrict referred to as the Eddington Restrict. We continuously measure, as a fragment of that theoretical higher restrict, how a lot the black hollow is rising through sucking in gasoline. For some gadgets measured through the JWST the potency is over 100% — so they’re actually extraordinarily environment friendly.That still signifies that it is not a difficult restrict, and there is at all times some idea and assumptions that went into it, and a few of the ones assumptions could be improper. Actually, Webb has proven us they’re obviously improper in the ones situations as a result of they organize to wreck the restrict and develop even quicker.BT: And so why does that potency lower as we get into the later phases of the cosmos, the native universe?SK: So you probably have extra megastar formation, there is merely much less gasoline round. So galaxies may get gradually extra gasoline deficient, a few of it being ejected in other places, some became stars, and a few being fed on through black holes. Very outdated galaxies are generally ruled through their stars, so-called elliptical galaxies.BT: How do black holes develop within the first position? There are 3 key techniques, proper? Take us thru them.SK: So, the primary one is to the primary technology of stars. So those would were a lot more huge than our solar, round 100 instances its mass. When those come to the tip in their lifestyles and cave in, they cave in into black holes. This generally is a excellent place to begin [for supermassive black holes], or it generally is a difficult one, as we are beginning at 100 [solar masses] and we wish to get to at least one million.A far more straightforward place to begin could be massive gasoline clouds. Those cave in without delay into black holes, and so they get started off at one thing like 100,000 instances the mass of the solar, that makes it a lot more straightforward to get to supermassive black hollow [mass scales]. After which there’s an in-between state of affairs referred to as nuclear megastar clusters, the place plenty of stars spawn within the heart of galaxies and those cave in into black holes.
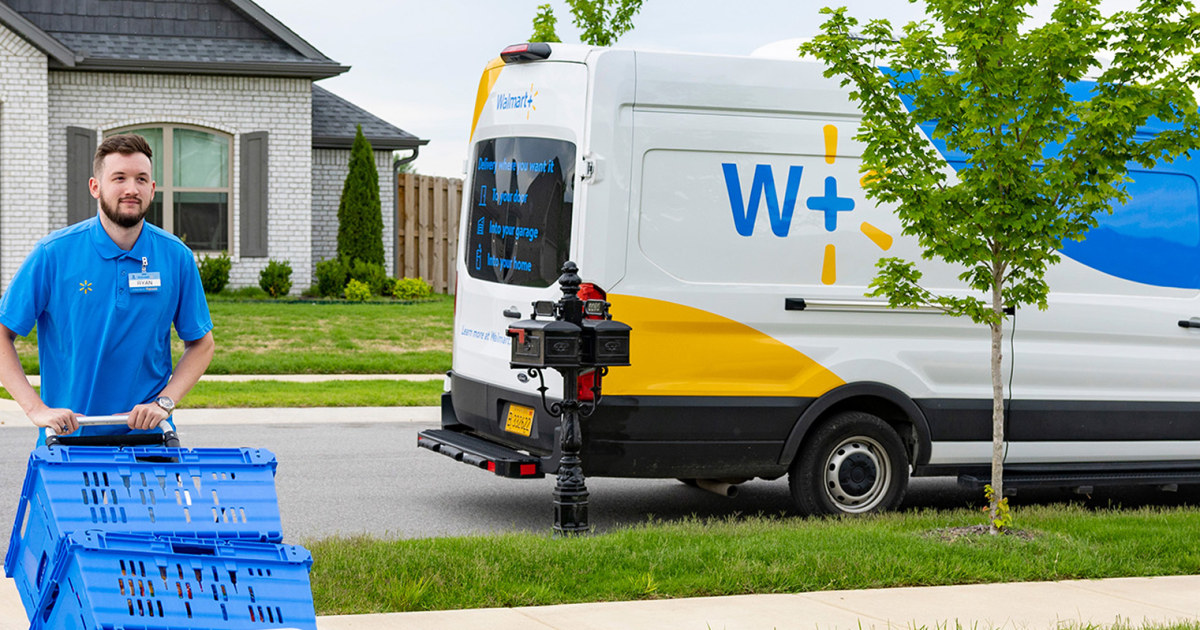
Two merging black holes. (Symbol credit score: Mark Garlick/Science Photograph Library by means of Getty Pictures)BT: Why may that be?SK: Everyone knows about cosmic enlargement — so the Large Bang occurs and the entire universe expands — and which means within the early instances of the universe the whole thing used to be somewhat nearer in combination so gasoline inflows had been more potent, this may have helped to feed black holes.One drawback is that black holes and supernovae more or less compete with one every other. Each megastar formation and black holes eat gasoline. The black hollow blows gasoline away, so do the supernovae, and supernovae additionally evacuate the gasoline from the central area, after which black holes cannot develop for the reason that supernovae have kicked out all the gasoline. It may well be that within the early universe, for one reason why or every other, this does not occur as a lot, and the black hollow simply wins out in that procedure.Actually, there is a robust trace that the black holes win out [in the early universe]. It virtually suggests, on account of how huge those black holes are, that black holes assembled quicker than their host galaxies.BT: You additionally discussed black hollow potency. What does that imply, how can black holes have potency?SK: There are quite a lot of techniques. A method is, once they attract gasoline, how extremely accreting [the speed at which the accretion disk grows] is it? There is a factor referred to as a black hollow velocity restrict referred to as the Eddington Restrict. We continuously measure, as a fragment of that theoretical higher restrict, how a lot the black hollow is rising through sucking in gasoline. For some gadgets measured through the JWST the potency is over 100% — so they’re actually extraordinarily environment friendly.That still signifies that it is not a difficult restrict, and there is at all times some idea and assumptions that went into it, and a few of the ones assumptions could be improper. Actually, Webb has proven us they’re obviously improper in the ones situations as a result of they organize to wreck the restrict and develop even quicker.BT: And so why does that potency lower as we get into the later phases of the cosmos, the native universe?SK: So you probably have extra megastar formation, there is merely much less gasoline round. So galaxies may get gradually extra gasoline deficient, a few of it being ejected in other places, some became stars, and a few being fed on through black holes. Very outdated galaxies are generally ruled through their stars, so-called elliptical galaxies.BT: How do black holes develop within the first position? There are 3 key techniques, proper? Take us thru them.SK: So, the primary one is to the primary technology of stars. So those would were a lot more huge than our solar, round 100 instances its mass. When those come to the tip in their lifestyles and cave in, they cave in into black holes. This generally is a excellent place to begin [for supermassive black holes], or it generally is a difficult one, as we are beginning at 100 [solar masses] and we wish to get to at least one million.A far more straightforward place to begin could be massive gasoline clouds. Those cave in without delay into black holes, and so they get started off at one thing like 100,000 instances the mass of the solar, that makes it a lot more straightforward to get to supermassive black hollow [mass scales]. After which there’s an in-between state of affairs referred to as nuclear megastar clusters, the place plenty of stars spawn within the heart of galaxies and those cave in into black holes.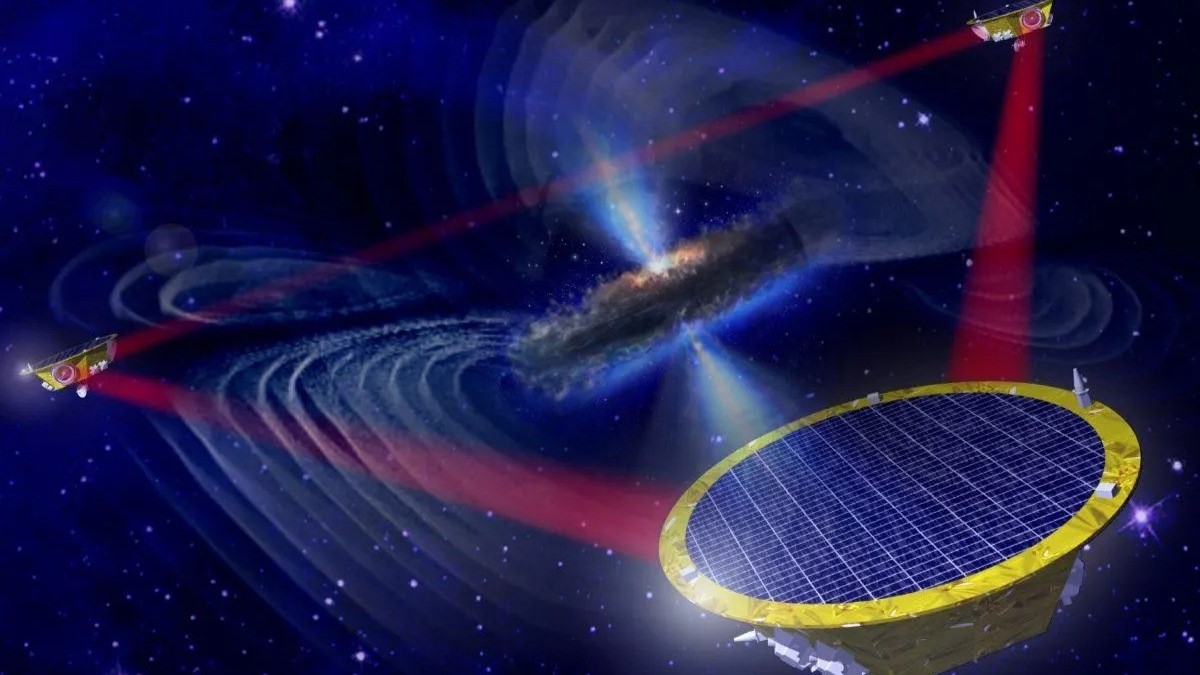 An artist’s impact of the LISA detector, and the gravitational waves it is going to seek for. (Symbol credit score: EADS ASTRUM)BT: There is additionally an alternative choice in the market, hypothesized primordial black holes — imaginable relics from a time prior to the Large Bang. It is a very out-there idea, will we see a lot proof for it?SK: This is a very out-there idea. We are getting extra constraints on it, and it is by no means dominated out. I believe the thrilling factor about this query presently is that not anything is dominated out. The limitations get tighter as we push nearer and nearer to the days those black holes shaped.BT: How may just we in spite of everything rule it out? What are the ones constraints?SK: Some persons are pronouncing that, now that we’ve got discovered huge black holes so early within the universe, that this implies they’ve to have shaped from direct cave in. There are a number of papers printed suggesting that the observations turn out this.However what we at the moment are doing is that we’re revising our fashions of ways black holes grew within the early universe to peer if there are nonetheless different choices for different fashions. Particularly if black holes develop successfully, there is nonetheless simply sufficient time for them to develop from an overly gentle seed. So I’d say presently, the thrilling factor is that not one of the fashions are dominated out.BT: So how are we in search of solutions? We have discussed the JWST recognizing previous and previous black holes, are there different pathways we are exploring to search out solutions?SK: A actually cool manner is with gravitational waves. [Detecting them] will let us map the supermassive black hollow inhabitants in an entire other manner. As a result of presently, until a black hollow may be very with regards to us and we will map out those stellar orbits, the one approach to spot supermassive black holes is that if they are in an lively section.But if we’ve got gravitational wave tools that may spot supermassive black hollow mergers we can have a 2nd channel that may assist us estimate their lots. And that may return to the early universe as a result of those tools could be extremely delicate. Then we will spot merger indicators and to find viable mechanisms for his or her enlargement.BT: Your paintings is on the use of simulations to identify imaginable enlargement pathways. How do they assist us to search out solutions?SK: It is a consistent interaction between statement and simulation. So an statement, for instance the early supermassive black holes, offers us one thing to give an explanation for. That then method we may want to alter fashions to permit for that more or less enlargement early on. The simulations then assist us know what to search for, and when the ones observations come again we will alter our fashions once more.I paintings very carefully with observers, and I am a part of a big program of the JWST that may take observations subsequent yr and do observe ups of those supermassive black holes of their infancy to grasp them higher.BT: So in spite of everything, what spaces of latest analysis into massive black holes are you maximum interested by?SK: I am tremendous interested by the gravitational wave detector LISA that may come on-line within the 2030s then we will in spite of everything be in a position measure gravitational waves now not simply from small black holes however supermassive black holes. You wish to have to be in area to try this.I am additionally reasonably nerdy in relation to coding and development fashions, so I am additionally interested by technical construction. A actually attention-grabbing instance that is everywhere the scoop is, in fact, AI.We are the use of AI to boost up our simulations, to lead them to much more correct, and to check out and bridge the entire scales from the large area of the cosmic internet the entire manner right down to tournament horizons. That is one thing that is not possible to do even without delay presently, for the reason that computational assets of even the most important, perfect supercomputers to find it too in depth, however we will use AI to expand answers to that.Editor’s notice: This interview has been condensed and edited for readability.
An artist’s impact of the LISA detector, and the gravitational waves it is going to seek for. (Symbol credit score: EADS ASTRUM)BT: There is additionally an alternative choice in the market, hypothesized primordial black holes — imaginable relics from a time prior to the Large Bang. It is a very out-there idea, will we see a lot proof for it?SK: This is a very out-there idea. We are getting extra constraints on it, and it is by no means dominated out. I believe the thrilling factor about this query presently is that not anything is dominated out. The limitations get tighter as we push nearer and nearer to the days those black holes shaped.BT: How may just we in spite of everything rule it out? What are the ones constraints?SK: Some persons are pronouncing that, now that we’ve got discovered huge black holes so early within the universe, that this implies they’ve to have shaped from direct cave in. There are a number of papers printed suggesting that the observations turn out this.However what we at the moment are doing is that we’re revising our fashions of ways black holes grew within the early universe to peer if there are nonetheless different choices for different fashions. Particularly if black holes develop successfully, there is nonetheless simply sufficient time for them to develop from an overly gentle seed. So I’d say presently, the thrilling factor is that not one of the fashions are dominated out.BT: So how are we in search of solutions? We have discussed the JWST recognizing previous and previous black holes, are there different pathways we are exploring to search out solutions?SK: A actually cool manner is with gravitational waves. [Detecting them] will let us map the supermassive black hollow inhabitants in an entire other manner. As a result of presently, until a black hollow may be very with regards to us and we will map out those stellar orbits, the one approach to spot supermassive black holes is that if they are in an lively section.But if we’ve got gravitational wave tools that may spot supermassive black hollow mergers we can have a 2nd channel that may assist us estimate their lots. And that may return to the early universe as a result of those tools could be extremely delicate. Then we will spot merger indicators and to find viable mechanisms for his or her enlargement.BT: Your paintings is on the use of simulations to identify imaginable enlargement pathways. How do they assist us to search out solutions?SK: It is a consistent interaction between statement and simulation. So an statement, for instance the early supermassive black holes, offers us one thing to give an explanation for. That then method we may want to alter fashions to permit for that more or less enlargement early on. The simulations then assist us know what to search for, and when the ones observations come again we will alter our fashions once more.I paintings very carefully with observers, and I am a part of a big program of the JWST that may take observations subsequent yr and do observe ups of those supermassive black holes of their infancy to grasp them higher.BT: So in spite of everything, what spaces of latest analysis into massive black holes are you maximum interested by?SK: I am tremendous interested by the gravitational wave detector LISA that may come on-line within the 2030s then we will in spite of everything be in a position measure gravitational waves now not simply from small black holes however supermassive black holes. You wish to have to be in area to try this.I am additionally reasonably nerdy in relation to coding and development fashions, so I am additionally interested by technical construction. A actually attention-grabbing instance that is everywhere the scoop is, in fact, AI.We are the use of AI to boost up our simulations, to lead them to much more correct, and to check out and bridge the entire scales from the large area of the cosmic internet the entire manner right down to tournament horizons. That is one thing that is not possible to do even without delay presently, for the reason that computational assets of even the most important, perfect supercomputers to find it too in depth, however we will use AI to expand answers to that.Editor’s notice: This interview has been condensed and edited for readability.