The James Webb House Telescope would possibly now not have damaged our working out of the universe, in the end. Prior to now, astronomers used Webb to identify curious, faint, and very historical purple dots that they surmised had been large galaxies. However there was once an issue. It do not need been conceivable for such huge galaxies — the earliest of which shaped just a few 500 to 700 million years after the universe was once created — to have sufficient subject material to shape copious quantities of stars and sun methods. (The universe is set 13.7 billion years outdated.)New insights from the robust house observatory, orbiting 1 million miles past Earth, recommend the faint gentle of those far away “little purple dots” is if truth be told generated via energetic black holes on the middle of the galaxies. That suggests the purple gentle we see is not coming from the glow of a prodigious selection of stars.”That is the way you remedy the universe-breaking downside,” Anthony Taylor, an astronomer on the College of Texas at Austin who co-authored the analysis, mentioned in a commentary. “Opposite to Headlines, Cosmology Isn’t Damaged,” NASA added, referencing previous information protection of the cosmic dilemma.
SEE ALSO:
NASA scientist considered first Voyager photographs. What he noticed gave him chills.
The analysis was once offered on the 245th assembly of the American Astronomical Society. Astronomers checked out a large inhabitants of the purple gadgets noticed to this point, spanning a lot of other Webb surveys and elapsing masses of thousands and thousands of years. Round 70 p.c of the purple gadgets “confirmed proof for gasoline impulsively orbiting 2 million miles in step with hour (1,000 kilometers in step with 2nd),” NASA defined. That is a telltale signal of a robust black hollow: Black holes — which might be gadgets wielding excessive gravitational energy — amass accretion disks of super-heated, impulsively spinning mud, gasoline, and debris.If the researchers are right kind, the sunshine you might be seeing from the purple gadgets under is generated via the black holes on the middle of those early galaxies.

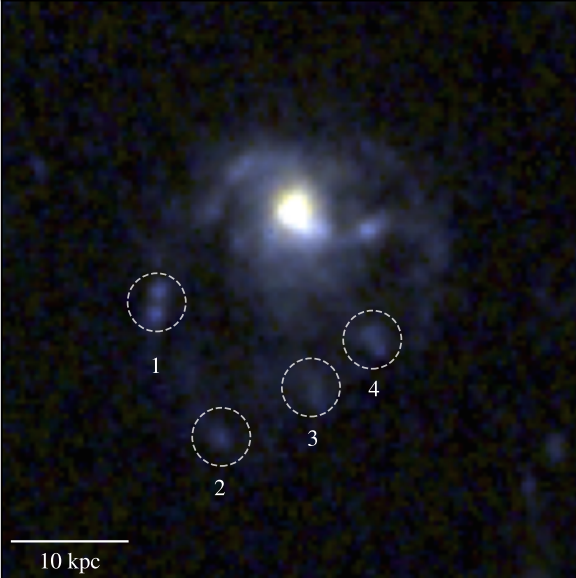
Probably the most “little purple dots” considered via the James Webb House Telescope.
Credit score: NASA / ESA / CSA / STScI / Dale Kocevski (Colby Faculty)
Tweet will have been deleted
The case, then again, is not absolutely settled.
Mashable Gentle Velocity
Astronomers intend to stay investigating the curious purple dots. As an example, those gadgets start showing in nice numbers round 600 million years after the Giant Bang, however then plummet in quantity round 900 hundred million years later (1.5 billion years after the Giant Bang). Why? Are they being obscured?Webb scientists will proceed weighing their novel observations with our working out of ways the universe works.”There’s at all times two or extra attainable techniques to give an explanation for the confounding houses of little purple dots,” Dale Kocevski, an astronomer at Colby Faculty in Waterville, Maine, who led the analysis, mentioned. “It’s a continual trade between fashions and observations, discovering a steadiness between what aligns smartly between the 2 and what conflicts.”The Webb telescope’s robust abilitiesThe Webb telescope — a systematic collaboration between NASA, ESA, and the Canadian House Company — is designed to look into the inner most cosmos and disclose new insights in regards to the early universe. It is usually analyzing intriguing planets in our galaxy, at the side of the planets and moons in our sun device.Here is how Webb is attaining extraordinary feats, and most probably will for many years to come back:
– Large replicate: Webb’s replicate, which captures gentle, is over 21 ft throughout. That is over two-and-a-half occasions better than the Hubble House Telescope’s replicate. Taking pictures extra gentle permits Webb to look extra far away, historical gadgets. The telescope is peering at stars and galaxies that shaped over 13 billion years in the past, only a few hundred million years after the Giant Bang. “We are going to see the first actual stars and galaxies that ever shaped,” Jean Creighton, an astronomer and the director of the Manfred Olson Planetarium on the College of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, instructed Mashable in 2021.- Infrared view: In contrast to Hubble, which in large part perspectives gentle that is visual to us, Webb is basically an infrared telescope, which means it perspectives gentle within the infrared spectrum. This permits us to look way more of the universe. Infrared has longer wavelengths than visual gentle, so the sunshine waves extra successfully slip via cosmic clouds; the sunshine does not as frequently collide with and get scattered via those densely packed debris. In the end, Webb’s infrared eyesight can penetrate puts Hubble can not.”It lifts the veil,” mentioned Creighton.- Peering into far away exoplanets: The Webb telescope carries specialised apparatus known as spectrographs that can revolutionize our working out of those far away worlds. The tools can decipher what molecules (similar to water, carbon dioxide, and methane) exist within the atmospheres of far away exoplanets — be they gasoline giants or smaller rocky worlds. Webb seems to be at exoplanets within the Milky Manner galaxy. Who is aware of what we will to find?”We would possibly be told issues we by no means thought of,” Mercedes López-Morales, an exoplanet researcher and astrophysicist on the Heart for Astrophysics-Harvard & Smithsonian, instructed Mashable in 2021.Already, astronomers have effectively discovered intriguing chemical reactions on a planet 700 light-years away, and feature began taking a look at one of the expected puts within the cosmos: the rocky, Earth-sized planets of the TRAPPIST sun device.