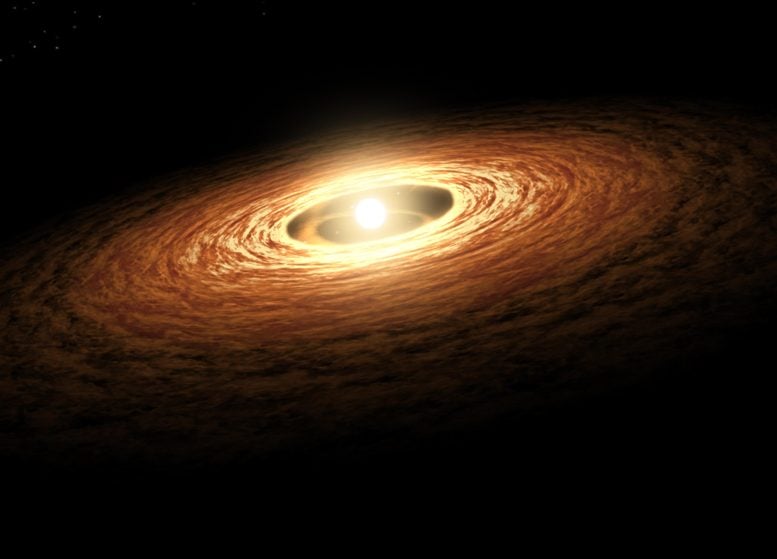
 That is an artist’s impact of a tender megastar surrounded by means of a disk of fuel and dirt. A world workforce of astronomers has used NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope to check the disk round a tender and really low-mass megastar referred to as ISO-ChaI 147. The consequences expose the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechUsing the James Webb Area Telescope, scientists have came upon a wealthy number of carbon molecules in a protoplanetary disk round a low-mass megastar, suggesting a novel form of planet-forming atmosphere that would result in the advent of carbon-poor planets.A world workforce of astronomers studied the disk of fuel and dirt round a tender, very low-mass megastar the usage of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope (JWST). The consequences expose the biggest collection of carbon-containing molecules seen in the sort of disk to this point. Those findings have implications for the possible composition of any planets that would possibly shape round this megastar.Implications for Planet FormationRocky planets are much more likely than fuel giants to shape round low-mass stars, making them the commonest planets round the commonest stars in our galaxy. Little is understood concerning the chemistry of such worlds, that may be very similar to or very other from Earth. Through learning the disks from which such planets shape, astronomers hope to higher perceive the planet formation procedure and the compositions of the ensuing planets.Planet-forming disks round very low-mass stars are tough to check as a result of they’re smaller and fainter than disks round high-mass stars. A program known as the MIRI (Mid-Infrared Software) Mid-INfrared Disk Survey (MINDS) goals to make use of Webb’s distinctive features to construct a bridge between the chemical stock of disks and the houses of exoplanets.“Webb has higher sensitivity and spectral answer than earlier infrared area telescopes,” defined lead writer Aditya Arabhavi of the College of Groningen within the Netherlands. “Those observations aren’t imaginable from Earth, for the reason that emissions from the disk are blocked by means of our environment.”
That is an artist’s impact of a tender megastar surrounded by means of a disk of fuel and dirt. A world workforce of astronomers has used NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope to check the disk round a tender and really low-mass megastar referred to as ISO-ChaI 147. The consequences expose the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechUsing the James Webb Area Telescope, scientists have came upon a wealthy number of carbon molecules in a protoplanetary disk round a low-mass megastar, suggesting a novel form of planet-forming atmosphere that would result in the advent of carbon-poor planets.A world workforce of astronomers studied the disk of fuel and dirt round a tender, very low-mass megastar the usage of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope (JWST). The consequences expose the biggest collection of carbon-containing molecules seen in the sort of disk to this point. Those findings have implications for the possible composition of any planets that would possibly shape round this megastar.Implications for Planet FormationRocky planets are much more likely than fuel giants to shape round low-mass stars, making them the commonest planets round the commonest stars in our galaxy. Little is understood concerning the chemistry of such worlds, that may be very similar to or very other from Earth. Through learning the disks from which such planets shape, astronomers hope to higher perceive the planet formation procedure and the compositions of the ensuing planets.Planet-forming disks round very low-mass stars are tough to check as a result of they’re smaller and fainter than disks round high-mass stars. A program known as the MIRI (Mid-Infrared Software) Mid-INfrared Disk Survey (MINDS) goals to make use of Webb’s distinctive features to construct a bridge between the chemical stock of disks and the houses of exoplanets.“Webb has higher sensitivity and spectral answer than earlier infrared area telescopes,” defined lead writer Aditya Arabhavi of the College of Groningen within the Netherlands. “Those observations aren’t imaginable from Earth, for the reason that emissions from the disk are blocked by means of our environment.”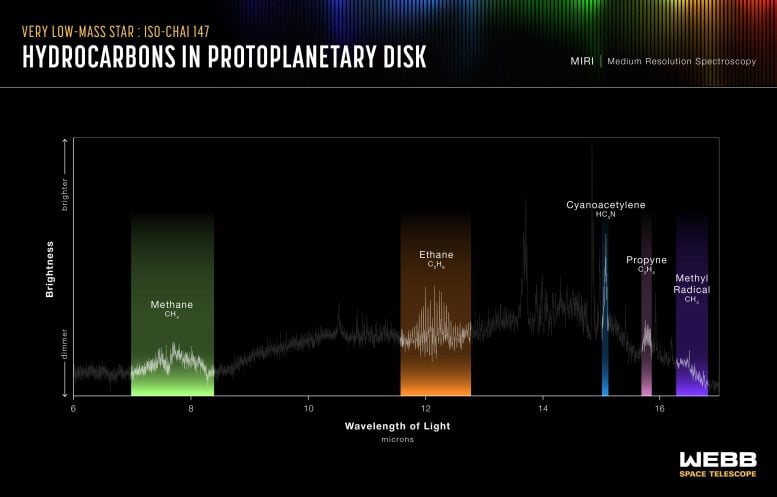 The spectrum of the megastar ISO-ChaI 147 printed by means of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Software) presentations the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk, consisting of 13 carbon-bearing molecules. This contains the primary extrasolar detection of ethane (C2H6). The workforce additionally effectively detected ethylene (C2H4), propyne (C3H4), and the methyl radical CH3, for the primary time in a protoplanetary disk. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, R. Crawford (STScI)Groundbreaking Discoveries in Exoplanetary ChemistryIn a brand new learn about, this workforce explored the area round a completely low-mass megastar referred to as ISO-ChaI 147, a 1 to two million-year-old megastar that weighs simply 0.11 occasions up to the Solar. The spectrum printed by means of Webb’s MIRI presentations the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk – a complete of 13 other carbon-bearing molecules. The workforce’s findings come with the primary detection of ethane (C2H6) outdoor of our photo voltaic device, in addition to ethylene (C2H4), propyne (C3H4), and the methyl radical CH3.“Those molecules have already been detected in our photo voltaic device, like in comets reminiscent of 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko and C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy),” added Arabhavi. “Webb allowed us to remember the fact that those hydrocarbon molecules aren’t simply numerous but in addition ample. It’s superb that we will now see the dance of those molecules within the planetary cradles. This can be a very other planet-forming atmosphere than we in most cases recall to mind.”The workforce signifies that those effects have huge implications for the chemistry of the internal disk and the planets that would possibly shape there. Since Webb printed the fuel within the disk is so wealthy in carbon, there may be most probably little carbon left within the cast fabrics that planets would shape from. Because of this, the planets that would possibly shape there would possibly in the long run be carbon-poor. (Earth itself is regarded as carbon-poor.)“That is profoundly other from the composition we see in disks round solar-type stars, the place oxygen bearing molecules like water and carbon dioxide dominate,” added workforce member Inga Kamp, additionally of the College of Groningen. “This object establishes that those are a novel magnificence of items.”“It’s implausible that we will stumble on and quantify the volume of molecules that we all know smartly on Earth, reminiscent of benzene, in an object this is greater than 600 light-years away,” added workforce member Agnés Perrin of Centre Nationwide de los angeles Recherche Scientifique in France.Long run Analysis DirectionsNext, the science workforce intends to enlarge their learn about to a bigger pattern of such disks round very low-mass stars to expand their working out of the way not unusual or unique such carbon-rich terrestrial planet-forming areas are. “The growth of our learn about may also permit us to higher know the way those molecules can shape,” defined workforce member and important investigator of the MINDS program, Thomas Henning, of the Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy in Germany. “A number of options within the Webb information also are nonetheless unidentified, so extra spectroscopy is needed to totally interpret our observations.”This paintings additionally highlights the a very powerful want for scientists to collaborate throughout disciplines. The workforce notes that those effects and the accompanying information can give a contribution against different fields together with theoretical physics, chemistry, and astrochemistry, to interpret the spectra and to research new options on this wavelength vary.For extra in this discovery, see Webb Unmasks the Carbon-Wealthy Secrets and techniques of Protoplanetary Disks.Reference: “Plentiful hydrocarbons within the disk round a very-low-mass megastar” by means of A. M. Arabhavi, I. Kamp, Th. Henning, E. F. van Dishoeck, V. Christiaens, D. Gasman, A. Perrin, M. Güdel, B. Tabone, J. Kanwar, L. B. F. M. Waters, I. Pascucci, M. Samland, G. Perotti, G. Bettoni, S. L. Grant, P. O. Lagage, T. P. Ray, B. Vandenbussche, O. Absil, I. Argyriou, D. Barrado, A. Boccaletti, J. Bouwman, A. Caratti o Garatti, A. M. Glauser, F. Lahuis, M. Mueller, G. Olofsson, E. Pantin, S. Scheithauer, M. Morales-Calderón, R. Franceschi, H. Jang, N. Pawellek, D. Rodgers-Lee, J. Schreiber, Okay. Schwarz, M. Temmink, M. Vlasblom, G. Wright, L. Colina and G. Östlin, 6 June 2024, Science.
The spectrum of the megastar ISO-ChaI 147 printed by means of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Software) presentations the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk, consisting of 13 carbon-bearing molecules. This contains the primary extrasolar detection of ethane (C2H6). The workforce additionally effectively detected ethylene (C2H4), propyne (C3H4), and the methyl radical CH3, for the primary time in a protoplanetary disk. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, R. Crawford (STScI)Groundbreaking Discoveries in Exoplanetary ChemistryIn a brand new learn about, this workforce explored the area round a completely low-mass megastar referred to as ISO-ChaI 147, a 1 to two million-year-old megastar that weighs simply 0.11 occasions up to the Solar. The spectrum printed by means of Webb’s MIRI presentations the richest hydrocarbon chemistry observed to this point in a protoplanetary disk – a complete of 13 other carbon-bearing molecules. The workforce’s findings come with the primary detection of ethane (C2H6) outdoor of our photo voltaic device, in addition to ethylene (C2H4), propyne (C3H4), and the methyl radical CH3.“Those molecules have already been detected in our photo voltaic device, like in comets reminiscent of 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko and C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy),” added Arabhavi. “Webb allowed us to remember the fact that those hydrocarbon molecules aren’t simply numerous but in addition ample. It’s superb that we will now see the dance of those molecules within the planetary cradles. This can be a very other planet-forming atmosphere than we in most cases recall to mind.”The workforce signifies that those effects have huge implications for the chemistry of the internal disk and the planets that would possibly shape there. Since Webb printed the fuel within the disk is so wealthy in carbon, there may be most probably little carbon left within the cast fabrics that planets would shape from. Because of this, the planets that would possibly shape there would possibly in the long run be carbon-poor. (Earth itself is regarded as carbon-poor.)“That is profoundly other from the composition we see in disks round solar-type stars, the place oxygen bearing molecules like water and carbon dioxide dominate,” added workforce member Inga Kamp, additionally of the College of Groningen. “This object establishes that those are a novel magnificence of items.”“It’s implausible that we will stumble on and quantify the volume of molecules that we all know smartly on Earth, reminiscent of benzene, in an object this is greater than 600 light-years away,” added workforce member Agnés Perrin of Centre Nationwide de los angeles Recherche Scientifique in France.Long run Analysis DirectionsNext, the science workforce intends to enlarge their learn about to a bigger pattern of such disks round very low-mass stars to expand their working out of the way not unusual or unique such carbon-rich terrestrial planet-forming areas are. “The growth of our learn about may also permit us to higher know the way those molecules can shape,” defined workforce member and important investigator of the MINDS program, Thomas Henning, of the Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy in Germany. “A number of options within the Webb information also are nonetheless unidentified, so extra spectroscopy is needed to totally interpret our observations.”This paintings additionally highlights the a very powerful want for scientists to collaborate throughout disciplines. The workforce notes that those effects and the accompanying information can give a contribution against different fields together with theoretical physics, chemistry, and astrochemistry, to interpret the spectra and to research new options on this wavelength vary.For extra in this discovery, see Webb Unmasks the Carbon-Wealthy Secrets and techniques of Protoplanetary Disks.Reference: “Plentiful hydrocarbons within the disk round a very-low-mass megastar” by means of A. M. Arabhavi, I. Kamp, Th. Henning, E. F. van Dishoeck, V. Christiaens, D. Gasman, A. Perrin, M. Güdel, B. Tabone, J. Kanwar, L. B. F. M. Waters, I. Pascucci, M. Samland, G. Perotti, G. Bettoni, S. L. Grant, P. O. Lagage, T. P. Ray, B. Vandenbussche, O. Absil, I. Argyriou, D. Barrado, A. Boccaletti, J. Bouwman, A. Caratti o Garatti, A. M. Glauser, F. Lahuis, M. Mueller, G. Olofsson, E. Pantin, S. Scheithauer, M. Morales-Calderón, R. Franceschi, H. Jang, N. Pawellek, D. Rodgers-Lee, J. Schreiber, Okay. Schwarz, M. Temmink, M. Vlasblom, G. Wright, L. Colina and G. Östlin, 6 June 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adi8147The James Webb Area Telescope is the sector’s premier area science observatory. Webb is fixing mysteries in our photo voltaic device, taking a look past to far-off worlds round different stars, and probing the mysterious buildings and origins of our universe and our position in it. Webb is a global program led by means of NASA with its companions, ESA (Ecu Area Company) and CSA (Canadian Area Company).
Webb Telescope Uncovers a Mysterious Carbon Treasure Trove Round Younger Famous person














