Scientists are assured Mars was once as soon as ample with water, as observed in huge flood-carved channels, historic river valleys, and minerals that shape handiest in liquid water. However how the Purple Planet misplaced its water, leaving in the back of the arid global we see nowadays, continues to be up for debate.Now, a brand new problem to a contemporary principle surrounding huge quantities of water saved underneath the Martian floor suggests the Purple Planet is probably not hiding liquid water underneath its crust in any case.In a letter to Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS) revealed on March 6, Bruce Jakosky, a senior analysis scientist on the College of Colorado Boulder and previous important investigator of NASA’s Mars Setting and Risky EvolutioN project (MAVEN), argues that remaining 12 months’s principle has another clarification.”We predict there to be water or ice in [Mars’] crust,” Jakosky stated in a remark. “In fact detecting it and in all probability figuring out its abundance is difficult, however extraordinarily necessary for figuring out how a lot water there may be on Mars and what its historical past has been.”InSight and hidden water on MarsIn 2024, a staff led via Vaughan Wright on the Scripps Establishment of Oceanography, the College of California San Diego, made up our minds {that a} mid-crust made up of fractured, water-saturated igneous rock best possible explains knowledge accrued via NASA’s now-retired Inside Exploration the use of Seismic Investigations, Geodesy, and Warmth Delivery (InSight) project.Whilst earlier missions concerned about floor options, figuring out Mars’ formation calls for learning its deep inside. The InSight lander, introduced in 2018, was once designed to measure the planet’s inner process, together with its temperature, seismic waves, and core dynamics.Wright and his colleagues analyzed InSight’s knowledge to type the kinds of rocks and water saturation ranges that would possibly give an explanation for the seismic process detected about 10 to twelve kilometers under the Martian floor.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra! Gray clouds scoot around the Martian sky on this view from NASA’s InSight lander. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)In keeping with their findings, Wright and associates estimated that Mars’ crust may grasp the similar of 0.62 to at least one.24 miles (1 to two kilometers) of water if it have been unfold lightly around the planet’s floor—that is referred to as the worldwide similar layer. For comparability, Earth’s world similar layer is set 3.6 kilometers, which is most commonly made up of water within the oceans, with just a small quantity within the crust.”Whilst the way and research are affordable and suitable, the result of their modeling counsel another conclusion,” Jakosky commented.Each Wright’s and Jakosky’s examinations of the modeling knowledge assessment a metric referred to as liquid water saturation, which is the fraction of pore areas within the rock full of liquid water.Wright’s modeling steered that the liquid water saturation within the mid-crust underneath InSight is close to 1, which means virtually the entire pore areas within the rocks are full of liquid water. This conclusion, they stated, helped give an explanation for InSight’s seismic knowledge, as water-saturated rocks would behave another way underneath seismic waves.On the other hand, Jakosky’s reexamination of the knowledge introduced in different chances.
Gray clouds scoot around the Martian sky on this view from NASA’s InSight lander. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)In keeping with their findings, Wright and associates estimated that Mars’ crust may grasp the similar of 0.62 to at least one.24 miles (1 to two kilometers) of water if it have been unfold lightly around the planet’s floor—that is referred to as the worldwide similar layer. For comparability, Earth’s world similar layer is set 3.6 kilometers, which is most commonly made up of water within the oceans, with just a small quantity within the crust.”Whilst the way and research are affordable and suitable, the result of their modeling counsel another conclusion,” Jakosky commented.Each Wright’s and Jakosky’s examinations of the modeling knowledge assessment a metric referred to as liquid water saturation, which is the fraction of pore areas within the rock full of liquid water.Wright’s modeling steered that the liquid water saturation within the mid-crust underneath InSight is close to 1, which means virtually the entire pore areas within the rocks are full of liquid water. This conclusion, they stated, helped give an explanation for InSight’s seismic knowledge, as water-saturated rocks would behave another way underneath seismic waves.On the other hand, Jakosky’s reexamination of the knowledge introduced in different chances.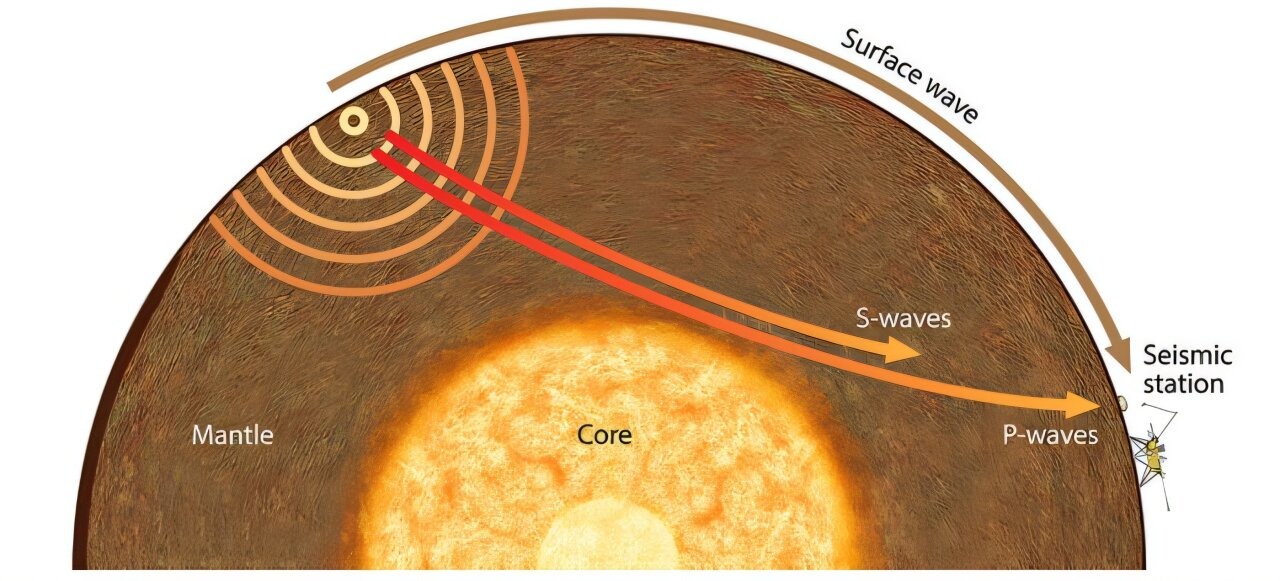 A diagram depicting how other seismic waves shuttle throughout Mars. (Symbol credit score: Ikuo Katayama)Jakosky and associates regarded as that the pore areas within the crust may additionally include cast ice and even be empty somewhat than being crammed fully with liquid water. They suspect this would nonetheless give an explanation for the seismic and gravity knowledge InSight accrued.Jakosky identified that whilst the InSight knowledge doesn’t ascertain that liquid water is provide within the mid-crust, it additionally doesn’t utterly rule it out. After factoring within the distribution of pore area and the possible presence of ice or empty areas, Jakosky proposed that the volume of water may vary from 0 to at least one.24 miles (0 to two kilometers) if unfold lightly around the planet’s floor. This adjusted the decrease estimate from Wright’s staff, suggesting a broader vary of chances.”It can be conceivable with long term spacecraft measurements to constrain the abundance of water within the crust via extra exact choice of the crustal homes,” Jakosky concluded.So, a minimum of for now, the Mars water debate is about to rage on.
A diagram depicting how other seismic waves shuttle throughout Mars. (Symbol credit score: Ikuo Katayama)Jakosky and associates regarded as that the pore areas within the crust may additionally include cast ice and even be empty somewhat than being crammed fully with liquid water. They suspect this would nonetheless give an explanation for the seismic and gravity knowledge InSight accrued.Jakosky identified that whilst the InSight knowledge doesn’t ascertain that liquid water is provide within the mid-crust, it additionally doesn’t utterly rule it out. After factoring within the distribution of pore area and the possible presence of ice or empty areas, Jakosky proposed that the volume of water may vary from 0 to at least one.24 miles (0 to two kilometers) if unfold lightly around the planet’s floor. This adjusted the decrease estimate from Wright’s staff, suggesting a broader vary of chances.”It can be conceivable with long term spacecraft measurements to constrain the abundance of water within the crust via extra exact choice of the crustal homes,” Jakosky concluded.So, a minimum of for now, the Mars water debate is about to rage on.
What came about to all of the water on Mars? Here is why the talk continues













