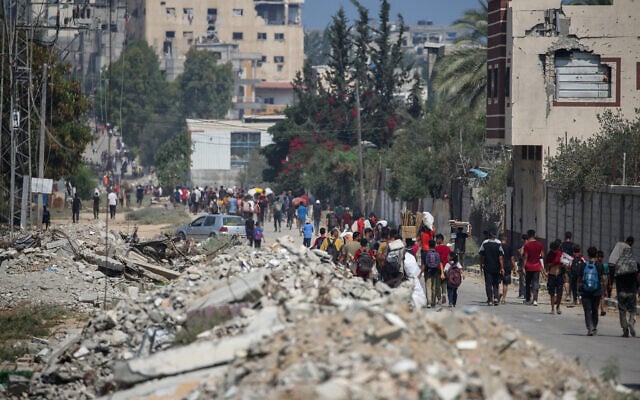
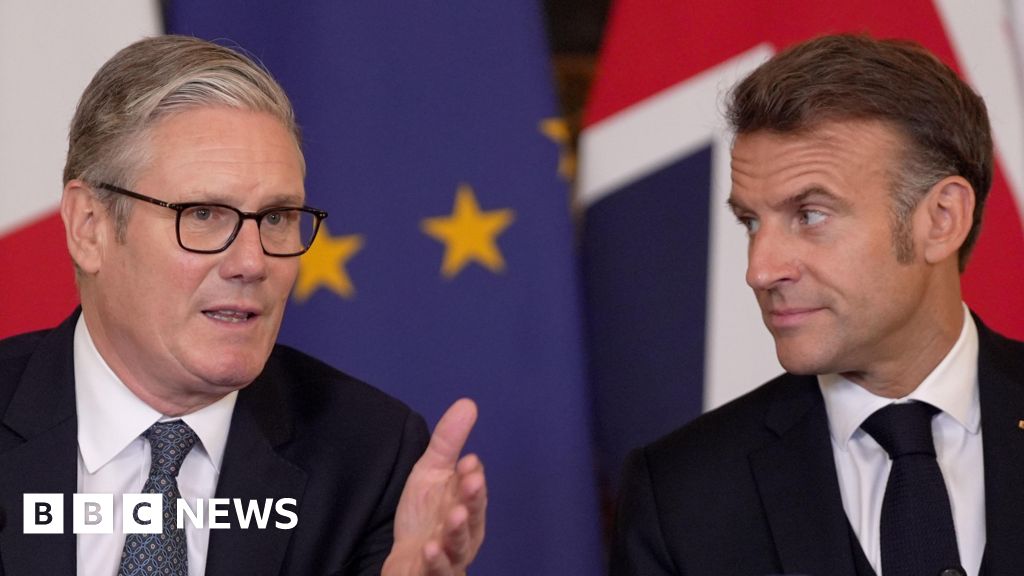
A burial group in Liberia awaits decontamination after acting “protected burials” for individuals who died of Ebola all through the 2014-15 outbreak. Traces of the virus are harbored through bats and primates. A brand new learn about seems at how human job impacts the transmission of infectious sicknesses like Ebola.
John Moore/Getty Pictures
cover caption
toggle caption
John Moore/Getty Pictures

A burial group in Liberia awaits decontamination after acting “protected burials” for individuals who died of Ebola all through the 2014-15 outbreak. Traces of the virus are harbored through bats and primates. A brand new learn about seems at how human job impacts the transmission of infectious sicknesses like Ebola.
John Moore/Getty Pictures
Scientists have lengthy identified that human job incessantly is helping pathogens unfold. Human-caused local weather alternate can push disease-carrying mosquitoes or ticks into new puts as temperatures upward thrust, and deforestation can reveal people to viruses circulating in once-isolated species. However regardless of loads of research investigating human affect on infectious sicknesses, scientists were not certain whether or not positive actions subject greater than others for expanding chance. Now, new analysis clarifies that image – and means that humanity’s reshaping of the planet is stoking the unfold of bad infectious sicknesses no longer only for folks but additionally for different animals and crops. Local weather alternate, the unfold of invasive species and the lack of biodiversity (when species decline or pass extinct) are all triggers that can play oversized roles in sparking infectious illness outbreaks international, consistent with an evaluation of present analysis revealed this month in Nature. The learn about discovered those adjustments had somewhat constant results at the unfold of infectious sicknesses without reference to geographic location or species, underlining the want to scale back greenhouse gasoline emissions and preserve biodiversity, scientists say.
“This can be a essentially enormous paper,” stated Colin Carlson, a world alternate biologist at Georgetown College who wasn’t concerned within the analysis. Whilst it’s a must to be conservative about what these kind of meta-analyses can divulge, he says, “the foundational message this is that world alternate is totally re-determining illness chance in each and every machine in each and every type of lifestyles on Earth.” A focal point on ‘world alternate drivers’ Whilst parasites and pathogens can also be influenced through a number of various components, the researchers interested in 5 key “world alternate drivers” which might be upending ecosystems — biodiversity alternate (as an example, declines within the numbers of species in an ecosystem or their inhabitants measurement), local weather alternate, chemical air pollution, invasive species and habitat loss. “There are restricted sources for tracking, controlling and managing infectious sicknesses,” says Jason Rohr, a biologist on the College of Notre Dame and learn about co-author. “It is actually treasured for policymakers to have a greater snatch on which world alternate drivers build up the chance of outbreaks probably the most.” To get that broader view, Rohr and his colleagues constructed a dataset from just about 1,000 research throughout all continents except for Antarctica. The group checked out 1,497 host-pathogen/parasite combos (reminiscent of people and malaria, or crops and fungal sicknesses). Throughout all the ones combinations, the group analyzed a number of thousand cases of those world alternate drivers influencing infectious sicknesses results for crops, animals and people, reminiscent of expanding circumstances or the severity of a illness.
Through taking one of these sweeping view of the way sicknesses affect such a lot of other species, as a substitute of focusing only on human sicknesses, the researchers had been ready to search for basic mechanisms that could be performing widely. “We search for basic patterns as a result of in the event that they cling true, they could practice to people,” stated Carlson. “Even supposing those are findings that practice to bats and rodents and primates, however no longer essentially us, it is nonetheless unhealthy for us if bats and rodents are sicker, he says, partially as a result of the ones sicknesses would possibly soar to us. For these types of species, biodiversity loss emerged as the most important consider expanding infectious illness chance, adopted through the advent of recent species, local weather alternate and, to a smaller extent, chemical air pollution. Adjustments in biodiversity can fan the flames of sicknesses in different techniques. When a species is presented to a brand new position, they incessantly deliver their parasites and sicknesses, as has came about when the Asian tiger mosquito arrived in Europe, bringing alongside sicknesses like dengue and chikungunya. An general decline in biodiversity can build up infectious sicknesses thru what ecologists name the dilution impact. Illness-causing parasites and pathogens generally tend to continue to exist and unfold higher in the event that they infect animal hosts which might be plentiful slightly than rarer host species just because there are extra hosts for them to contaminate. And when biodiversity declines as a result of human job, uncommon species have a tendency to be the primary to move, Rohr says. Of their absence, extra commonplace species — and the sicknesses they bring — can incessantly build up, resulting in extra illness general. Bats, which harbor lots of probably bad viruses, be offering an instance. A learn about revealed in April discovered that bat teams that contained plenty of other bat species harbor fewer coronaviruses than much less various teams. That discovering bolsters the concept that biodiversity conservation can save you the forms of animal-to-human pathogen spillover occasions that the majority scientists suspect brought about the COVID-19 pandemic.
Unusually, habitat loss — which is a significant explanation for biodiversity decline — was once related to a lower in infectious illness results. The fast tempo of urbanization most likely explains this counterintuitive end result, Rohr says. When a grassland or wooded area is bulldozed for human construction, many of the crops and animals are burnt up – in conjunction with their disease-causing parasites. City spaces additionally generally tend to have higher sanitation and get right of entry to to well being care, which might additionally account for the sudden end result, too. Nonetheless, the loss of an impact of habitat loss is fairly sudden, given scientists have drawn transparent hyperlinks between deforestation and greater chance of sicknesses like Ebola. The learn about displays “a actually transparent impact of biodiversity loss and no longer a transparent impact of deforestation,” says Carlson. “That does not essentially imply deforestation does not purpose illness emergence, in particular given we all know that deforestation reasons biodiversity loss.” The discrepancy highlights how nuance can get misplaced in meta-analyses. Caveats and obstacles Viewing this drawback from one of these prime vantage level could make it laborious to come across the main function positive forces would possibly play in particular places, or for positive sicknesses that pose a better chance to people, says Erin Mordecai, a illness ecologist at Stanford College who wasn’t concerned within the learn about. When the researchers centered only on sicknesses that unfold between animals and people, for example, local weather alternate emerged because the clearest driving force of worse results, with biodiversity loss taking part in much less of a task. That does not imply biodiversity loss is not expanding infectious illness chance for people for positive sicknesses, however that present proof suggests it could be just a little extra sophisticated. Some other wrinkle stems from the truth that many of the research integrated within the evaluation handled biodiversity loss, local weather alternate and invasive species as separate entities. “International alternate drivers are performing at the same time as,” says Mordecai. Local weather alternate is itself inflicting biodiversity loss and pushing some species into new spaces. Habitat loss and deforestation can in flip exacerbate local weather alternate. “Teasing out their separate contributions and interactions stays very tricky and no longer one thing prone to display up simply in a meta-analysis.”
Caveats apart, the learn about demonstrates the profound, planetary affect people are having on illness chance for a wide variety of lifestyles. It additionally issues to conceivable answers, says Mordecai. “I’m hoping this proof can be utilized in global coverage to spur motion on local weather alternate and biodiversity loss because of their detrimental affects on illness.” Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, well being and coverage. He is been a body of workers creator at Grid and Science Information and has contributed to NPR, Nature Information, Quanta Mag and the Dallas Morning Information. He holds a Grasp’s level in evolutionary biology from Cornell College. Practice him on twitter @evolambert, or on bluesky @jonlambert.bsky.social.