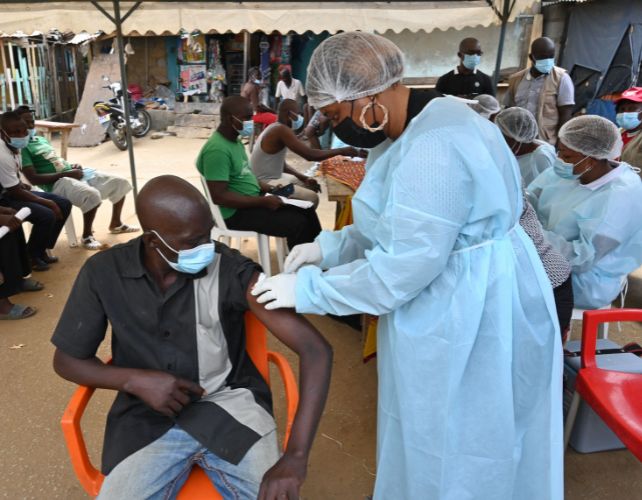
 Getty Pictures(Credit score: Getty Pictures)The method of constructing vaccines for parasites is terribly difficult – however scientists may well be at the cusp of primary breakthroughs.There used to be a lot birthday celebration in January, when Cameroon changed into the 1st nation on this planet to roll out regimen vaccination towards malaria. In February, Burkina Faso adopted swimsuit.”Regulate of malaria has now not been moving into a excellent route, for numerous other causes,” explains Kate O’Brien, who directs the dep. of immunisation, vaccines and biologicals on the International Well being Group (WHO). Malaria instances are emerging, and kind of 600,000 other people die of malaria each and every yr. Components come with local weather alternate, battle, the lingering results of Covid-19 on well being techniques, and the tenacious adaptability of malaria-carrying mosquitoes. This has supposed that the stalwarts of malaria prevention – pesticides sprayed indoors and mattress nets handled with pesticides – are dropping a few of their punch.Mass malaria vaccination provides yet one more instrument to this bundle, and person who takes a fully other means, says O’Brien. “Coming in with an immune-based means is an overly historical and vital addition,” she says. In 2019 the RTS,S vaccine towards malaria started pilots in Ghana, Kenya and Malawi, and in 2021 the WHO really useful it to be used in kids. The RTS,S vaccine used to be adopted via the R21 vaccine.But a similar milestone has long past much less heralded. RTS,S used to be the first-ever vaccine towards a parasitic illness. Whilst illnesses brought about via parasites are a lot of and sundry, as a gaggle they’re understudied and answers are underfunded. Many of the disregarded tropical illnesses, together with leishmaniasis and Chagas illness, are parasitic illnesses, in keeping with the WHO.
Getty Pictures(Credit score: Getty Pictures)The method of constructing vaccines for parasites is terribly difficult – however scientists may well be at the cusp of primary breakthroughs.There used to be a lot birthday celebration in January, when Cameroon changed into the 1st nation on this planet to roll out regimen vaccination towards malaria. In February, Burkina Faso adopted swimsuit.”Regulate of malaria has now not been moving into a excellent route, for numerous other causes,” explains Kate O’Brien, who directs the dep. of immunisation, vaccines and biologicals on the International Well being Group (WHO). Malaria instances are emerging, and kind of 600,000 other people die of malaria each and every yr. Components come with local weather alternate, battle, the lingering results of Covid-19 on well being techniques, and the tenacious adaptability of malaria-carrying mosquitoes. This has supposed that the stalwarts of malaria prevention – pesticides sprayed indoors and mattress nets handled with pesticides – are dropping a few of their punch.Mass malaria vaccination provides yet one more instrument to this bundle, and person who takes a fully other means, says O’Brien. “Coming in with an immune-based means is an overly historical and vital addition,” she says. In 2019 the RTS,S vaccine towards malaria started pilots in Ghana, Kenya and Malawi, and in 2021 the WHO really useful it to be used in kids. The RTS,S vaccine used to be adopted via the R21 vaccine.But a similar milestone has long past much less heralded. RTS,S used to be the first-ever vaccine towards a parasitic illness. Whilst illnesses brought about via parasites are a lot of and sundry, as a gaggle they’re understudied and answers are underfunded. Many of the disregarded tropical illnesses, together with leishmaniasis and Chagas illness, are parasitic illnesses, in keeping with the WHO. Getty ImagesIt’s was hoping that malaria vaccines will pave the way in which for jabs towards different parasitic illnesses, akin to schistosomiasis (Credit score: Getty Pictures)There wasn’t essentially a concerted effort to make the malaria vaccine the 1st antiparasitic vaccine. However it is in all probability unsurprising that it in the long run used to be, because the top dying toll exacted via malaria has resulted in extra consideration to growing vaccines for malaria than for different parasitic sicknesses (although nonetheless now not up to for vaccines affecting rich populations, akin to Covid-19).This top mortality charge from malaria makes it a little of an outlier amongst parasitic sicknesses. Total, “the dying charge from parasitic illnesses…is moderately low in comparison to a couple different infectious illnesses”, O’Brien says. The consequences may also be disabling and devastating, however now not essentially deadly. On account of this, and since parasitic illnesses continuously are restricted to precise portions of low- and middle-income nations, they have not been prioritised via typical vaccine builders.Peter Hotez isn’t a standard vaccine developer. The professor on the Baylor School of Medication in Houston, who additionally co-directs the Texas Youngsters’s Health center Heart for Vaccine Building, labored with colleagues to create a late-entrant Covid-19 vaccine that used to be transferred, freed from patent, to vaccine producers in India and Indonesia. A minimum of 100 million doses of the Indian model, Corbevax, had been provided at roughly $3 (£2.38) in line with dose. The builders selected an reasonably priced vaccine era: necessarily generating a protein in yeast thru microbial fermentation. The crew are hoping to use one of the crucial courses realized from this enjoy to their paintings on antiparasitic vaccines, he says.Parasites pose many demanding situations to vaccine developersOf path, large power and fiscal sources have been poured into the advent of more than one Covid-19 vaccines. However this is not the one explanation why the ones vaccines gave the impression moderately briefly. “There is no query that parasites are way more difficult objectives than viruses,” Hotez says. “In comparison to a coronavirus vaccine, which is concerning the lowest putting fruit there may be…it is not as easy with one thing like a hookworm vaccine,” he says.One technical problem of operating with parasites is their monumental genetic range, which may make it tough to focus on a particular species or strainA hookworm is a parasitic malicious program that feeds on intestinal blood, resulting in anaemia and nutrient deficiencies. “Bring to mind it as an animal. You are making a vaccine towards an animal,” Hotez says.Nearly all current vaccines paintings towards micro organism and viruses, there are these days no vaccines towards fungi any place on this planet, and there is only one form of vaccine – the anti-malarial one – towards parasites. Parasites continuously have refined tactics of evading a number’s immune device. They adapt to their hosts all over complicated lifestyles cycles, involving a number of developmental levels. “Every a kind of levels, both in an animal or a human host, has other proteins which can be expressed within the other lifestyles levels. And that makes it extra difficult to spot what the objectives may well be of the parasite for building of a vaccine,” says O’Brien.
Getty ImagesIt’s was hoping that malaria vaccines will pave the way in which for jabs towards different parasitic illnesses, akin to schistosomiasis (Credit score: Getty Pictures)There wasn’t essentially a concerted effort to make the malaria vaccine the 1st antiparasitic vaccine. However it is in all probability unsurprising that it in the long run used to be, because the top dying toll exacted via malaria has resulted in extra consideration to growing vaccines for malaria than for different parasitic sicknesses (although nonetheless now not up to for vaccines affecting rich populations, akin to Covid-19).This top mortality charge from malaria makes it a little of an outlier amongst parasitic sicknesses. Total, “the dying charge from parasitic illnesses…is moderately low in comparison to a couple different infectious illnesses”, O’Brien says. The consequences may also be disabling and devastating, however now not essentially deadly. On account of this, and since parasitic illnesses continuously are restricted to precise portions of low- and middle-income nations, they have not been prioritised via typical vaccine builders.Peter Hotez isn’t a standard vaccine developer. The professor on the Baylor School of Medication in Houston, who additionally co-directs the Texas Youngsters’s Health center Heart for Vaccine Building, labored with colleagues to create a late-entrant Covid-19 vaccine that used to be transferred, freed from patent, to vaccine producers in India and Indonesia. A minimum of 100 million doses of the Indian model, Corbevax, had been provided at roughly $3 (£2.38) in line with dose. The builders selected an reasonably priced vaccine era: necessarily generating a protein in yeast thru microbial fermentation. The crew are hoping to use one of the crucial courses realized from this enjoy to their paintings on antiparasitic vaccines, he says.Parasites pose many demanding situations to vaccine developersOf path, large power and fiscal sources have been poured into the advent of more than one Covid-19 vaccines. However this is not the one explanation why the ones vaccines gave the impression moderately briefly. “There is no query that parasites are way more difficult objectives than viruses,” Hotez says. “In comparison to a coronavirus vaccine, which is concerning the lowest putting fruit there may be…it is not as easy with one thing like a hookworm vaccine,” he says.One technical problem of operating with parasites is their monumental genetic range, which may make it tough to focus on a particular species or strainA hookworm is a parasitic malicious program that feeds on intestinal blood, resulting in anaemia and nutrient deficiencies. “Bring to mind it as an animal. You are making a vaccine towards an animal,” Hotez says.Nearly all current vaccines paintings towards micro organism and viruses, there are these days no vaccines towards fungi any place on this planet, and there is only one form of vaccine – the anti-malarial one – towards parasites. Parasites continuously have refined tactics of evading a number’s immune device. They adapt to their hosts all over complicated lifestyles cycles, involving a number of developmental levels. “Every a kind of levels, both in an animal or a human host, has other proteins which can be expressed within the other lifestyles levels. And that makes it extra difficult to spot what the objectives may well be of the parasite for building of a vaccine,” says O’Brien. 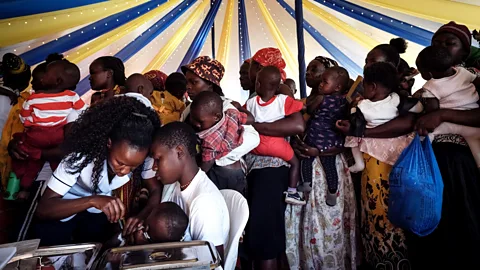 Getty ImagesMalaria is the 1st parasitic illness to be focused via a vaccine (Credit score: Getty Pictures)This lifestyles cycle complexity is likely one of the causes that parasites are not all the time simple to tradition in a laboratory. In different phrases, it may be difficult to easily produce extra of them beneath managed prerequisites, on the proper degree of building, for analysis functions. Probabilities together with cultivating parasites in analysis animals or in a laboratory, slightly than of their same old hosts. Epidemiologist Miriam Tendler coordinates the Sm14 Anti Helminth Vaccine Initiative on the Oswaldo Cruz Basis (Fiocruz) in Rio de Janeiro. Particularly, the crew research parasitic worms, together with schistosomes, which have an effect on some 240 million other people globally and these days have restricted remedy choices. Schistosomes are only one form of helminths, a gaggle of worms (together with hookworms) which usually motive continual illness in lower-income nations.One technical problem of operating with parasites is their monumental genetic range, which may make it tough to focus on a particular species or pressure. Tendler and her colleagues discovered a workaround via figuring out a not unusual key element in lots of helminth species. They discovered that the protein Sm14 is found in more than one species of helminths that motive illness in people and cattle, now not simply schistosomiasis.Tendler and her crew have now evolved a vaccine towards schistosomiasis, and it has finished some Section 2 medical trials. She remembers that within the early days of growing this vaccine, she and her crew needed to extract the protein from grownup worms. However after figuring out, sequencing and cloning this recombinant protein, they may be able to now produce litres of it in fermenters.As a result of different types of worms produce the protein Sm14, the schistosomiasis vaccine that the crew is growing may additionally paintings towards a number of different illnesses brought about via other helminth species, says Tendler. Thus, a unmarried form of vaccine, in numerous formulations, may just lend a hand offer protection to kids towards schistosomiasis, farm animals towards fascioliasis, or even puppy canine towards heartworm.Financing antiparasitic vaccinesTendler’s crew has been operating in parallel at the human and non-human variations of the Sm14 vaccine, and insights from this joint analysis have helped them to succeed in the present degree of building. The human schistosomiasis vaccine is these days in medical trials in Senegal, and Tendler expects it to in any case be to be had inside of 3 years. “It is a giant thrill,” she says, of her crew’s good fortune.This parallel vaccine building in people and animals will have additionally helped to transport ahead conversations concerning the important want for vaccines to fight parasitic worms, which is able to proceed to reinfect individuals who are living in affected spaces. “The affect on high quality of lifestyles for people, principally kids, may be very, very top,” Tendler says.
Getty ImagesMalaria is the 1st parasitic illness to be focused via a vaccine (Credit score: Getty Pictures)This lifestyles cycle complexity is likely one of the causes that parasites are not all the time simple to tradition in a laboratory. In different phrases, it may be difficult to easily produce extra of them beneath managed prerequisites, on the proper degree of building, for analysis functions. Probabilities together with cultivating parasites in analysis animals or in a laboratory, slightly than of their same old hosts. Epidemiologist Miriam Tendler coordinates the Sm14 Anti Helminth Vaccine Initiative on the Oswaldo Cruz Basis (Fiocruz) in Rio de Janeiro. Particularly, the crew research parasitic worms, together with schistosomes, which have an effect on some 240 million other people globally and these days have restricted remedy choices. Schistosomes are only one form of helminths, a gaggle of worms (together with hookworms) which usually motive continual illness in lower-income nations.One technical problem of operating with parasites is their monumental genetic range, which may make it tough to focus on a particular species or pressure. Tendler and her colleagues discovered a workaround via figuring out a not unusual key element in lots of helminth species. They discovered that the protein Sm14 is found in more than one species of helminths that motive illness in people and cattle, now not simply schistosomiasis.Tendler and her crew have now evolved a vaccine towards schistosomiasis, and it has finished some Section 2 medical trials. She remembers that within the early days of growing this vaccine, she and her crew needed to extract the protein from grownup worms. However after figuring out, sequencing and cloning this recombinant protein, they may be able to now produce litres of it in fermenters.As a result of different types of worms produce the protein Sm14, the schistosomiasis vaccine that the crew is growing may additionally paintings towards a number of different illnesses brought about via other helminth species, says Tendler. Thus, a unmarried form of vaccine, in numerous formulations, may just lend a hand offer protection to kids towards schistosomiasis, farm animals towards fascioliasis, or even puppy canine towards heartworm.Financing antiparasitic vaccinesTendler’s crew has been operating in parallel at the human and non-human variations of the Sm14 vaccine, and insights from this joint analysis have helped them to succeed in the present degree of building. The human schistosomiasis vaccine is these days in medical trials in Senegal, and Tendler expects it to in any case be to be had inside of 3 years. “It is a giant thrill,” she says, of her crew’s good fortune.This parallel vaccine building in people and animals will have additionally helped to transport ahead conversations concerning the important want for vaccines to fight parasitic worms, which is able to proceed to reinfect individuals who are living in affected spaces. “The affect on high quality of lifestyles for people, principally kids, may be very, very top,” Tendler says. Getty ImagesParasites continuously have difficult lifestyles cycles, which may make growing efficient vaccines towards them tough (Credit score: Getty Pictures)However whilst schistosomiasis and different illnesses brought about via helminths most commonly have an effect on other people in poorer nations, from a cattle point of view, helminths hurt the livelihoods of other people in richer nations as neatly – growing extra of a marketplace incentive. The possible veterinary vaccine towards helminths has been approved to FABP Biotech, a personal corporate spun out of Fiocruz, whilst the human vaccine is being financed essentially via the Brazilian executive.The latter will likely be a “humanitarian vaccine”, Tendler emphasises. The plan is for Fiocruz’s Institute of Era on Immunobiologicals (Bio-Manguinhos) to supply it at not up to $1 (£0.79) a dose, with additional price discounts imaginable as manufacturing scales up steadily to ultimately succeed in the objective of 1 billion doses. There will likely be a limitation at the benefit margin.The hookworm vaccine could also be prone to be manufactured out of doors of the most important multinational pharmaceutical firms. Hotez expects it to be produced via a member of the Growing International locations Vaccine Producers Community, which incorporates Brazil’s Bio-Manguinhos in addition to producers in China, India, South Africa and different nations. “The issue is our era to make vaccines has outpaced our political, social, financial and felony frameworks to get them if truth be told scaled and produced,” says Hotez.The way forward for vaccines for parasitic diseasesAlthough antiparasitic vaccines are badly wanted, they should not be handled as silver bullets, says O’Brien. “There’s no malaria intervention that has absolute best efficiency. Now we have a toolbox of prevention measures,” she says. As a device to cut back the chance and severity of an infection, the malaria vaccine is an addition to, slightly than a substitute of, the opposite measures within the toolbox. Importantly, communities the place the RTS,S vaccine has been piloted have now not diminished their use of mattress nets.Those historical antiparasitic vaccines are anticipated to be adopted via others concentrated on the similar illnesses, which might beef up their velocity of building and their efficacy. Researchers not too long ago reported a mean 78% efficacy charge for the R21 malaria vaccine (which they known as “top efficacy”). This used to be in line with trials in 5 to 17-month-olds in Burkina Faso, Kenya, Mali and Tanzania.For context, “vaccines that give 97% coverage like measles are in many ways the exception slightly than the rule of thumb,” Hotez says.”We mustn’t focal point our consideration somewhat up to we do at the efficacy,” says O’Brien. Whilst it is a very powerful quantity, she believes that what issues extra is the affect, which relies on the get right of entry to to a vaccine and its impact at the burden of illness.There also are some broader advantages to the collection of breakthroughs with malaria vaccines. “The good fortune of this vaccine instils hope for the same victory for an similarly difficult pathogen [helminths] which reasons a vital quantity of morbidity globally, although it receives a lot much less consideration and less sources,” says Jeffrey Bethony, a microbiologist at George Washington College in Washington, DC.Simply as an identical vaccine applied sciences could also be used throughout HIV and coronavirus vaccines, the methods used for malaria vaccines are helpful in regard to different varieties of blood-feeding parasites, says Bethony. “A emerging tide lifts all boats right here,” he says. Hotez hopes that the precedent atmosphere will prolong now not simplest to the technical sides of growing vaccines for disregarded tropical illnesses, but additionally to getting the ones vaccines the place they are wanted. “Some of the extra fascinating portions of this could also be one of the vital extra terrifying portions,” Hotez says. Whilst “it is a great feeling to understand that you are pioneering this very cutting edge type for offering get right of entry to to innovation to the poorest other people in the world, it is usually terrifying as a result of there is no highway map,” he says.
Getty ImagesParasites continuously have difficult lifestyles cycles, which may make growing efficient vaccines towards them tough (Credit score: Getty Pictures)However whilst schistosomiasis and different illnesses brought about via helminths most commonly have an effect on other people in poorer nations, from a cattle point of view, helminths hurt the livelihoods of other people in richer nations as neatly – growing extra of a marketplace incentive. The possible veterinary vaccine towards helminths has been approved to FABP Biotech, a personal corporate spun out of Fiocruz, whilst the human vaccine is being financed essentially via the Brazilian executive.The latter will likely be a “humanitarian vaccine”, Tendler emphasises. The plan is for Fiocruz’s Institute of Era on Immunobiologicals (Bio-Manguinhos) to supply it at not up to $1 (£0.79) a dose, with additional price discounts imaginable as manufacturing scales up steadily to ultimately succeed in the objective of 1 billion doses. There will likely be a limitation at the benefit margin.The hookworm vaccine could also be prone to be manufactured out of doors of the most important multinational pharmaceutical firms. Hotez expects it to be produced via a member of the Growing International locations Vaccine Producers Community, which incorporates Brazil’s Bio-Manguinhos in addition to producers in China, India, South Africa and different nations. “The issue is our era to make vaccines has outpaced our political, social, financial and felony frameworks to get them if truth be told scaled and produced,” says Hotez.The way forward for vaccines for parasitic diseasesAlthough antiparasitic vaccines are badly wanted, they should not be handled as silver bullets, says O’Brien. “There’s no malaria intervention that has absolute best efficiency. Now we have a toolbox of prevention measures,” she says. As a device to cut back the chance and severity of an infection, the malaria vaccine is an addition to, slightly than a substitute of, the opposite measures within the toolbox. Importantly, communities the place the RTS,S vaccine has been piloted have now not diminished their use of mattress nets.Those historical antiparasitic vaccines are anticipated to be adopted via others concentrated on the similar illnesses, which might beef up their velocity of building and their efficacy. Researchers not too long ago reported a mean 78% efficacy charge for the R21 malaria vaccine (which they known as “top efficacy”). This used to be in line with trials in 5 to 17-month-olds in Burkina Faso, Kenya, Mali and Tanzania.For context, “vaccines that give 97% coverage like measles are in many ways the exception slightly than the rule of thumb,” Hotez says.”We mustn’t focal point our consideration somewhat up to we do at the efficacy,” says O’Brien. Whilst it is a very powerful quantity, she believes that what issues extra is the affect, which relies on the get right of entry to to a vaccine and its impact at the burden of illness.There also are some broader advantages to the collection of breakthroughs with malaria vaccines. “The good fortune of this vaccine instils hope for the same victory for an similarly difficult pathogen [helminths] which reasons a vital quantity of morbidity globally, although it receives a lot much less consideration and less sources,” says Jeffrey Bethony, a microbiologist at George Washington College in Washington, DC.Simply as an identical vaccine applied sciences could also be used throughout HIV and coronavirus vaccines, the methods used for malaria vaccines are helpful in regard to different varieties of blood-feeding parasites, says Bethony. “A emerging tide lifts all boats right here,” he says. Hotez hopes that the precedent atmosphere will prolong now not simplest to the technical sides of growing vaccines for disregarded tropical illnesses, but additionally to getting the ones vaccines the place they are wanted. “Some of the extra fascinating portions of this could also be one of the vital extra terrifying portions,” Hotez says. Whilst “it is a great feeling to understand that you are pioneering this very cutting edge type for offering get right of entry to to innovation to the poorest other people in the world, it is usually terrifying as a result of there is no highway map,” he says.
Why it's so difficult to increase vaccines for parasitic illnesses