The highly-anticipated “visitor big name” of the night time sky has but to ship its grand efficiency — however now we have an replace.For a fast recap, astronomers and stargazers were observing towards the Corona Borealis constellation lately, eagerly looking ahead to the once-in-a-lifetime reignition of a long-dead big name in an explosion robust sufficient to in short fit the brilliance of Polaris, the North Big name. T Coronae Borealis — continuously known as T Cor Bor or T CrB — is house to a white dwarf, a dense, burnt-out big name siphoning subject matter from its spouse big name, which is an enormous pink massive with regards to the top of its lifestyles. This subject matter spirals into an accretion disk across the white dwarf, the place it slowly coats the big name’s floor. Each 80 years or so, the white dwarf manages to acquire sufficient mass to cause a nuclear explosion, sparking an outburst that enhances its in most cases dim magnitude of 10 to a vivid 2.0 — that are meant to appear to be a “new big name” within the night time sky to us.Astronomers’ best possible predictions advised T CrB was once poised to ignite by means of September. But, two months later, the elusive gadget continues to turn indicators that an outburst remains to be coming near near. So, what provides?”We realize it has to occur,” astrophysicist Elizabeth Hays, who’s looking at T CrB on a daily basis the use of NASA’s Fermi gamma-ray area telescope, advised Area.com in a contemporary interview. “We simply cannot pin it all the way down to the month.”Comparable: A ‘new big name’ may seem within the sky any night time now. Here is how you can see the Blaze Big name igniteThe unpredictability stems in part from restricted ancient data of T CrB’s outbursts. Handiest two such eruptions were definitively seen in fresh historical past: on Would possibly 12, 1866, when a celebrity’s outburst in short outshined all of the stars in its constellation, achieving magnitude 2.0, and once more on February 9, 1946, when it peaked at magnitude 3.0. Those occasions seem to apply the big name’s more or less 80-year cycle, suggesting that the following outburst would possibly not happen till 2026.Then again, in February 2015, the gadget brightened in a way harking back to its conduct in 1938, 8 years sooner than its 1946 eruption. This upward thrust in brightness advised T CrB’s outburst was once speeded up to 2023. The gadget additionally continued a “distinctive and mysterious” dimming a few 12 months sooner than its 1946 outburst, and a identical dip began in March ultimate 12 months, prompting astronomers to regulate their predictions to 2024. But, the reason for this pre-eruption dip in brightness stays unclear, making it just a coincidental predictor.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”We were given truly excited when it seemed adore it was once doing identical issues,” stated Hays. “Now we are studying, ‘Oh, there is some other piece we will’t see.'”Additionally, the speed at which the pink massive’s subject matter is being drawn towards the white dwarf would possibly range over time, making it trickier to position a date at the calendar for the outburst, Edward Sion, a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Villanova College in Pennsylvania, advised Area.com.The white dwarf and its pink massive spouse also are separated by means of simply 0.5 AU, or part the typical distance between Earth and the solar, and this proximity introduces complexities within the accretion procedure that don’t seem to be absolutely understood. “There may be numerous uncertainty about the true reasonable accretion charge,” stated Sion.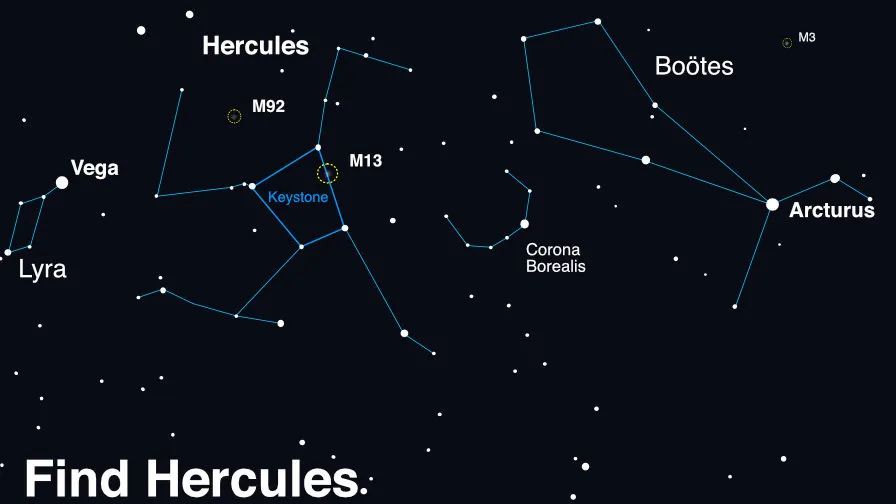 Corona Borealis, the place the “visitor big name” will seem, is positioned between Hercules and Boötes. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Astronomers are the use of this ready length to assemble as a lot information as imaginable. The ultimate time T CrB erupted, there have been no X-ray or gamma-ray telescopes in area, so there’s no information from wavelengths as opposed to optical to make clear what came about sooner than the outburst. Now, the Fermi gamma-ray telescope is solely one of the ground- and space-based telescopes intently tracking the gadget. NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope, along side Swift, INTEGRAL, and the ground-based Very Huge Array in New Mexico, are all concerned within the effort.Those telescopes is not going to simplest seize the instant of the outburst when it happens however can even observe its next decline into the depths of area. Astronomers say this wealth of knowledge will permit them to higher are expecting long term outbursts, and can sooner or later get advantages fashions of the way stars paintings.”This time is truly crucial,” stated Hays. “We are getting the most productive dataset we have now ever had on what does nova appear to be sooner than it is going off.”At the moment, astronomers are poring over to be had information, in search of any trace of an imminent outburst, however “you must watch out to not overinterpret,” Hays added. “Some issues we see alternate would possibly now not essentially have the rest to do with how temporarily the outburst goes to start out — possibly simply the elements within the gadget.”So for now, the wait continues. T CrB is in most cases so faint it is visual simplest via telescopes, past the succeed in of the unaided eye. Astronomers and keen stargazers alike are looking at it intently, poised to each surprise at and catalog its eruption into the intense nova it guarantees to develop into.
Corona Borealis, the place the “visitor big name” will seem, is positioned between Hercules and Boötes. (Symbol credit score: NASA)Astronomers are the use of this ready length to assemble as a lot information as imaginable. The ultimate time T CrB erupted, there have been no X-ray or gamma-ray telescopes in area, so there’s no information from wavelengths as opposed to optical to make clear what came about sooner than the outburst. Now, the Fermi gamma-ray telescope is solely one of the ground- and space-based telescopes intently tracking the gadget. NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope, along side Swift, INTEGRAL, and the ground-based Very Huge Array in New Mexico, are all concerned within the effort.Those telescopes is not going to simplest seize the instant of the outburst when it happens however can even observe its next decline into the depths of area. Astronomers say this wealth of knowledge will permit them to higher are expecting long term outbursts, and can sooner or later get advantages fashions of the way stars paintings.”This time is truly crucial,” stated Hays. “We are getting the most productive dataset we have now ever had on what does nova appear to be sooner than it is going off.”At the moment, astronomers are poring over to be had information, in search of any trace of an imminent outburst, however “you must watch out to not overinterpret,” Hays added. “Some issues we see alternate would possibly now not essentially have the rest to do with how temporarily the outburst goes to start out — possibly simply the elements within the gadget.”So for now, the wait continues. T CrB is in most cases so faint it is visual simplest via telescopes, past the succeed in of the unaided eye. Astronomers and keen stargazers alike are looking at it intently, poised to each surprise at and catalog its eruption into the intense nova it guarantees to develop into.
Why the highly-anticipated ‘new big name’ has but to pop up within the night time sky