The Global Area Station is one thing of an issue kid.The orbital outpost is plagued by way of cracks, coolant and air leaks, even a shocking scent that not too long ago wafted into the station from a just-arrived Russian Development shipment send. And the station has high-speed, shut encounters with area junk once in a while that make the ability a dangerous place of abode. So, there is escalating concern that the getting old complicated has change into a questionable house for crews to be secure and sound.Maintaining Global Area Station (ISS) operations thru 2030 would possibly due to this fact be reasonably touch-and-go, previous to its deliberate 2031 “secure, managed deorbit” into faraway ocean territory. And a few persons are beginning to query simply how secure that suicide dive shall be, as it would finally end up polluting Earth’s air and water.Elvis Presley maneuverThe coming demise plunge would possibly neatly be classified the Elvis Presley maneuver, one who renders the ISS “only a hunk, a hunk of burning love,” as its temperature rises upper and better whilst diving violently into Earth’s surroundings.Comparable: Watery graves: Must we be ditching giant spacecraft over Earth’s oceans?The most probably ocean zone for plopping the ISS down in a managed style is inside the South Pacific Oceanic Uninhabited Space, a area round Level Nemo officially referred to as “the oceanic pole of inaccessibility.” That house is further from land than another level on Earth and is incessantly classified the arena’s biggest “spacecraft cemetery.”This faraway seascape is ready 1,450 nautical miles (2,685 kilometers) from the closest piece of dry land. The nearest terra firma is Ducie Island, a part of the Pitcairn Islands, to the north; Motu Nui, some of the Easter Islands, to the northeast; and Maher Island, a part of Antarctica, to the south.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!However, the station’s deliberate end-of-life plunge is stirring up fear in environmental and area analysis circles, with experts weighing the professionals and cons of any devoted ISS “retirement.”There are the ones questioning in regards to the incineration and implications for Earth’s surroundings and sea waters. In a similar fashion, what a couple of “hit or miss” state of affairs that has chunks of the station achieving the bottom because of a botched reentry procedure?Very little warningEarlier this yr, the Aerospace Protection Advisory Panel (ASAP), an advisory committee that experiences to NASA and Congress, issued its 2023 annual record. Inside its pages, it steered and reemphasized an ASAP advice from the former yr that “a managed deorbit capacity will have to be advanced for the ISS once practicable.”Whilst the getting old {hardware} issues to the ceaselessly coming near finish of the ISS’ existence and the desire for making plans a managed deorbit, “it will have to even be famous {that a} vital or catastrophic failure may happen with very little caution, necessitating a direct secure disposal of the broken station,” the ASAP identified.”The urgency of defining a deorbit plan, first highlighted in 2012, is now much more urgent given the ceaselessly coming near end-of-life date,” the ASAP said in its most up-to-date report back to NASA.Comparable: The Global Area Station will ultimately die by way of fireBest possibility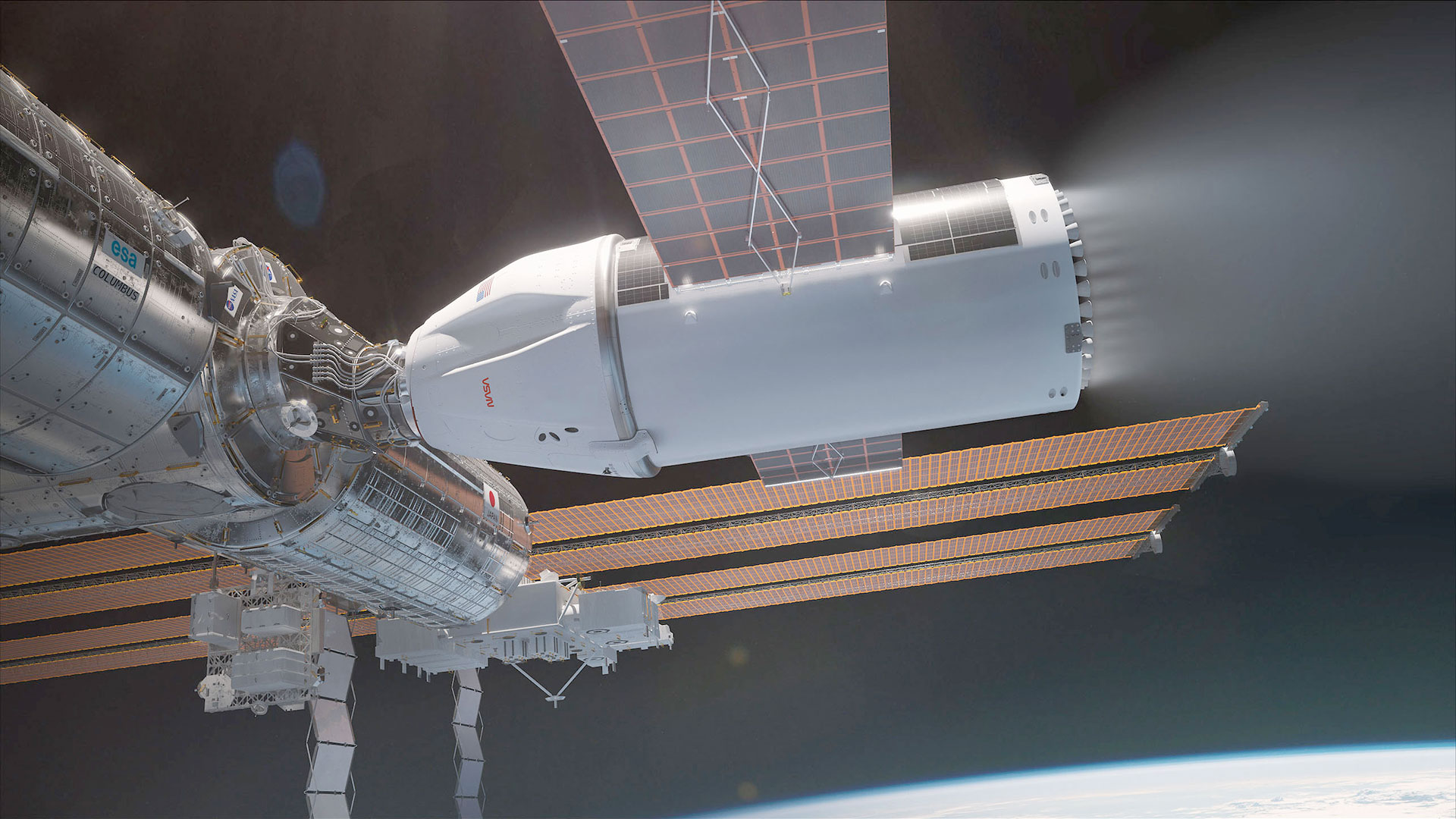 Representation of the deliberate SpaceX-provided United States Deorbit Car, which is able to information the Global Area Station to a fiery loss of life. (Symbol credit score: SpaceX)Ultimate June, NASA introduced it had picked SpaceX to design america Deorbit Car (USDV), with a freelance value as much as $843 million. An area company white paper on deliberately deorbiting the ISS concluded that “the use of a U.S.-developed deorbit automobile, with a last goal in a faraway a part of the sea, is the most suitable option for station’s finish of existence.”Given NASA’s number of SpaceX to take down the entire construction immediately, “it sort of feels the procedural trail is already laid out,” mentioned Leonard Schulz, a researcher on the Technische Universität Braunschweig’s Institute of Geophysics and Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany.”Making an allowance for the massive mass of 450 heaps — part of human made reentry mass into the ambience in 2019, a 3rd of the reentry mass of 2023 — it simplest complements the ambience drawback prompted by way of reentry,” Schulz advised Area.com. “We will more than likely have a look sooner or later at what this reentry may convey to the ambience in the case of launched ingredients.”Oceanic and atmospheric pollutionPhysicist Luciano Anselmo works on the Area Flight Dynamics Laboratory within the Institute of Knowledge Science and Applied sciences in Pisa, Italy.Considerations and court cases in regards to the particles dumped into the oceans by way of reentering area items make a large number of sense in idea, Anselmo advised Area.com.”On the other hand, in science and era, quantitative arguments are related as neatly, and reentering area items are an overly minor contributor to ocean air pollution,” mentioned Anselmo. For the reason that get started of the distance age, the mass reentered from orbit and dispersed on land, oceans and the ambience is at the order of a number of tens of 1000’s of metric heaps, he mentioned — not up to the mass of a unmarried battleship sunk right through International Struggle II.”Or even the ISS, with simply round 400 [metric] heaps, could be negligible in comparison to the mass of all of the ships and load sunk yearly, to not point out all different varieties of marine waste dumping and air pollution,” Anselmo mentioned.Placing it in relative quantitative phrases, orbital reentries — together with that of the ISS, and perhaps area launches as neatly — aren’t but an important supply of oceanic air pollution in comparison to different anthropogenic actions and herbal phenomena, added Anselmo.”On the other hand, it will not be mentioned for the higher surroundings, the place the have an effect on of area launches and reentries is more than likely changing into vital, and whose imaginable penalties aren’t but absolutely assessed,” Anselmo steered.Comparable: Are we able to clear up the satellite tv for pc air air pollution drawback? Listed here are 4 imaginable fixesControlled dumping
Representation of the deliberate SpaceX-provided United States Deorbit Car, which is able to information the Global Area Station to a fiery loss of life. (Symbol credit score: SpaceX)Ultimate June, NASA introduced it had picked SpaceX to design america Deorbit Car (USDV), with a freelance value as much as $843 million. An area company white paper on deliberately deorbiting the ISS concluded that “the use of a U.S.-developed deorbit automobile, with a last goal in a faraway a part of the sea, is the most suitable option for station’s finish of existence.”Given NASA’s number of SpaceX to take down the entire construction immediately, “it sort of feels the procedural trail is already laid out,” mentioned Leonard Schulz, a researcher on the Technische Universität Braunschweig’s Institute of Geophysics and Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany.”Making an allowance for the massive mass of 450 heaps — part of human made reentry mass into the ambience in 2019, a 3rd of the reentry mass of 2023 — it simplest complements the ambience drawback prompted by way of reentry,” Schulz advised Area.com. “We will more than likely have a look sooner or later at what this reentry may convey to the ambience in the case of launched ingredients.”Oceanic and atmospheric pollutionPhysicist Luciano Anselmo works on the Area Flight Dynamics Laboratory within the Institute of Knowledge Science and Applied sciences in Pisa, Italy.Considerations and court cases in regards to the particles dumped into the oceans by way of reentering area items make a large number of sense in idea, Anselmo advised Area.com.”On the other hand, in science and era, quantitative arguments are related as neatly, and reentering area items are an overly minor contributor to ocean air pollution,” mentioned Anselmo. For the reason that get started of the distance age, the mass reentered from orbit and dispersed on land, oceans and the ambience is at the order of a number of tens of 1000’s of metric heaps, he mentioned — not up to the mass of a unmarried battleship sunk right through International Struggle II.”Or even the ISS, with simply round 400 [metric] heaps, could be negligible in comparison to the mass of all of the ships and load sunk yearly, to not point out all different varieties of marine waste dumping and air pollution,” Anselmo mentioned.Placing it in relative quantitative phrases, orbital reentries — together with that of the ISS, and perhaps area launches as neatly — aren’t but an important supply of oceanic air pollution in comparison to different anthropogenic actions and herbal phenomena, added Anselmo.”On the other hand, it will not be mentioned for the higher surroundings, the place the have an effect on of area launches and reentries is more than likely changing into vital, and whose imaginable penalties aren’t but absolutely assessed,” Anselmo steered.Comparable: Are we able to clear up the satellite tv for pc air air pollution drawback? Listed here are 4 imaginable fixesControlled dumping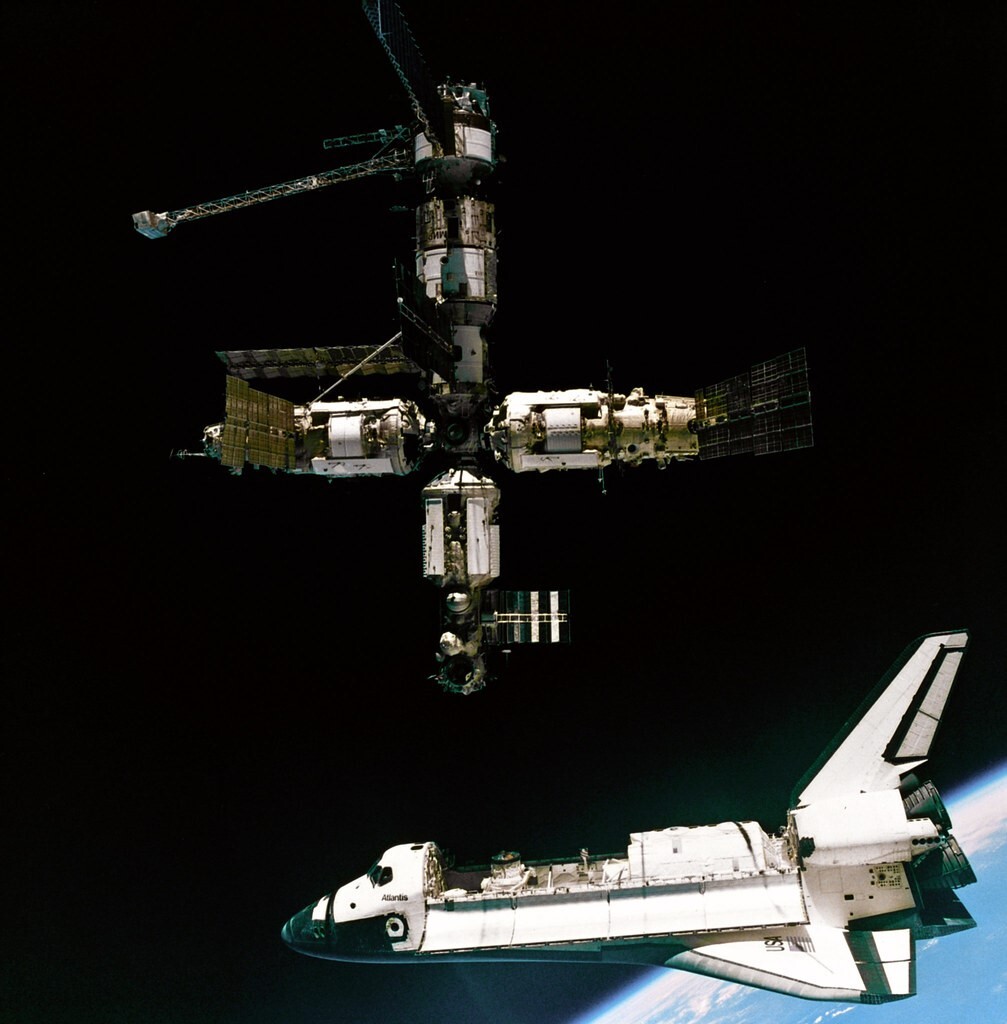 Russia’s Mir area station made a managed reentry, a dumping of the 130-ton outpost over the South Pacific Ocean close to Nadi, Fiji in 2001. (Symbol credit score: NASA)In the meantime, there are others comparing the deep-sixing of the ISS. As an example, the U.S. Environmental Coverage Company’s Place of job of Water is taking a look into the complicated factor.Advocacy teams in quest of pathways to offer protection to our watery global, such because the Ocean Conservancy, have additionally expressed fear about using ocean waters as a dumping flooring for all means of human leftovers, be it plastics, tires, radioactive waste or area junk.Some other voice within the ISS deorbit dialogue is David Santillo, senior scientist for Greenpeace Global on the College of Exeter’s Greenpeace Analysis Laboratories in the UK.Santillo advised Area.com that Greenpeace has a long-standing hobby within the dumping of area {hardware} over Earth’s oceans. That engagement harkens again to the deorbiting of Russia’s Mir area station in 2001. Managed reentry of the 130-ton Mir came about over the South Pacific Ocean, close to Nadi, Fiji.Lacking criminal framework
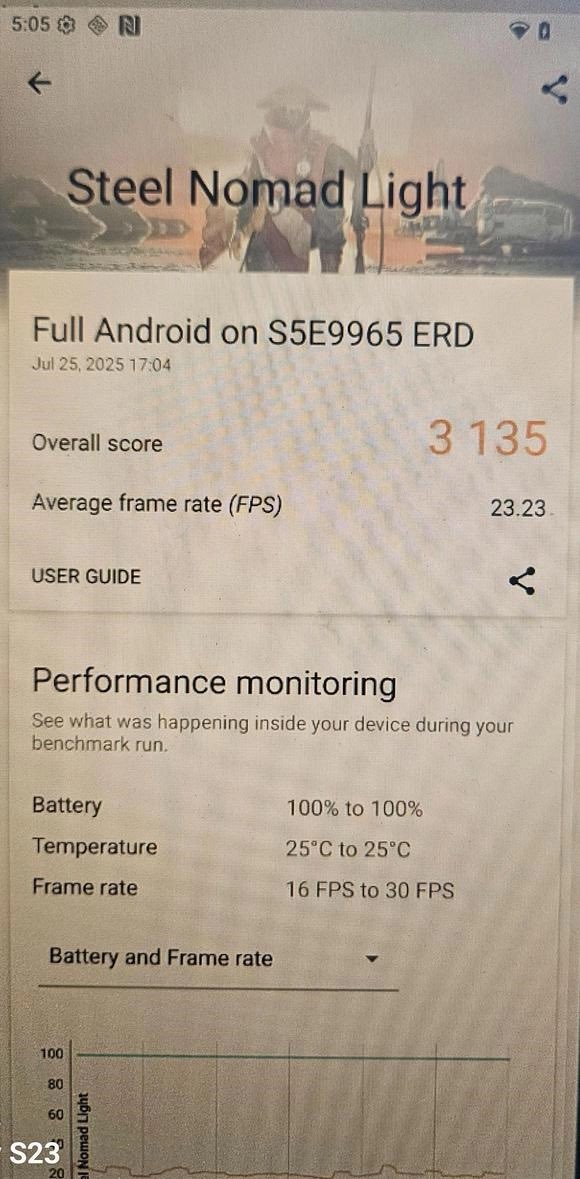
Russia’s Mir area station made a managed reentry, a dumping of the 130-ton outpost over the South Pacific Ocean close to Nadi, Fiji in 2001. (Symbol credit score: NASA)In the meantime, there are others comparing the deep-sixing of the ISS. As an example, the U.S. Environmental Coverage Company’s Place of job of Water is taking a look into the complicated factor.Advocacy teams in quest of pathways to offer protection to our watery global, such because the Ocean Conservancy, have additionally expressed fear about using ocean waters as a dumping flooring for all means of human leftovers, be it plastics, tires, radioactive waste or area junk.Some other voice within the ISS deorbit dialogue is David Santillo, senior scientist for Greenpeace Global on the College of Exeter’s Greenpeace Analysis Laboratories in the UK.Santillo advised Area.com that Greenpeace has a long-standing hobby within the dumping of area {hardware} over Earth’s oceans. That engagement harkens again to the deorbiting of Russia’s Mir area station in 2001. Managed reentry of the 130-ton Mir came about over the South Pacific Ocean, close to Nadi, Fiji.Lacking criminal framework The disposal of area {hardware} and the ensuing have an effect on on Earth’s stratosphere has drawn the eye of atmospheric researchers. (Symbol credit score: Chelsea Thompson/NOAA)”As issues stand, there’s no world criminal framework taking a look at this, which is why we raised the problem all the ones years in the past in the case of Mir, and why we now have adopted up since,” Santillo mentioned.Santillo urged that the London Conference and London Protocol, an international conference output to offer protection to the marine atmosphere from human actions, can be a logical position to take the ISS deorbiting problems up and most likely start up rule-setting procedures. It will supply some consistency of means the world over, Santillo mentioned, “however to this point there are not any explicit provisions in position, and it’ll take some years but to get there, if we will even get settlement on this kind of method ahead.”However as time is going on and hobby in tips on how to safely kill off the ISS grows, extra organizations are prone to flag the rising factor of sea disposal of jettisoned area {hardware}.Any individual goes to be unsatisfied
The disposal of area {hardware} and the ensuing have an effect on on Earth’s stratosphere has drawn the eye of atmospheric researchers. (Symbol credit score: Chelsea Thompson/NOAA)”As issues stand, there’s no world criminal framework taking a look at this, which is why we raised the problem all the ones years in the past in the case of Mir, and why we now have adopted up since,” Santillo mentioned.Santillo urged that the London Conference and London Protocol, an international conference output to offer protection to the marine atmosphere from human actions, can be a logical position to take the ISS deorbiting problems up and most likely start up rule-setting procedures. It will supply some consistency of means the world over, Santillo mentioned, “however to this point there are not any explicit provisions in position, and it’ll take some years but to get there, if we will even get settlement on this kind of method ahead.”However as time is going on and hobby in tips on how to safely kill off the ISS grows, extra organizations are prone to flag the rising factor of sea disposal of jettisoned area {hardware}.Any individual goes to be unsatisfied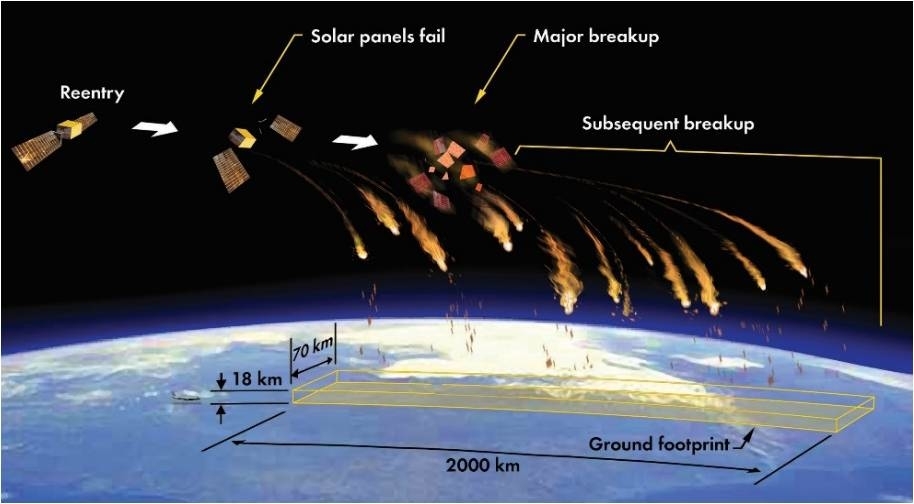 The focused on of spacecraft down to choose issues on Earth is a mild operation. (Symbol credit score: The Aerospace Company)”Obviously, those other folks are extra fearful in regards to the ocean atmosphere than the distance atmosphere, which is honest, however there are few choices, with out of control reentry being the worst,” mentioned Darren McKnight, senior technical fellow at LeoLabs, an organization that screens job in area to expose threats to security and safety.”If nobody can pay to stay the ISS in orbit, the place if it can not maneuver [it] could be a sitting duck for possible collisions, then managed as opposed to out of control reentry is the query,” McKnight mentioned.If you were given ingenious, McKnight identified, you might want to take the ISS aside and convey it down in items, an overly dear proposition. Or, bundle it up and ship it to both the next Earth orbit or an get away trajectory clear of our planet, both of which might even be very dear, he mentioned.”I am a little involved that this factor isn’t in regards to the present ISS however about long term very massive area stations. Additional, there’s ongoing ‘fear’ about mass that will get vaporized upon reentry. Some persons are involved that we must check out not to have items crumble in orbit; we must attempt to have them live to tell the tale to reentry,” McKnight mentioned.”So, obviously someone goes to be unsatisfied,” he concluded.
The focused on of spacecraft down to choose issues on Earth is a mild operation. (Symbol credit score: The Aerospace Company)”Obviously, those other folks are extra fearful in regards to the ocean atmosphere than the distance atmosphere, which is honest, however there are few choices, with out of control reentry being the worst,” mentioned Darren McKnight, senior technical fellow at LeoLabs, an organization that screens job in area to expose threats to security and safety.”If nobody can pay to stay the ISS in orbit, the place if it can not maneuver [it] could be a sitting duck for possible collisions, then managed as opposed to out of control reentry is the query,” McKnight mentioned.If you were given ingenious, McKnight identified, you might want to take the ISS aside and convey it down in items, an overly dear proposition. Or, bundle it up and ship it to both the next Earth orbit or an get away trajectory clear of our planet, both of which might even be very dear, he mentioned.”I am a little involved that this factor isn’t in regards to the present ISS however about long term very massive area stations. Additional, there’s ongoing ‘fear’ about mass that will get vaporized upon reentry. Some persons are involved that we must check out not to have items crumble in orbit; we must attempt to have them live to tell the tale to reentry,” McKnight mentioned.”So, obviously someone goes to be unsatisfied,” he concluded.
Will the Global Area Station’s 2031 demise dive reason air pollution issues?