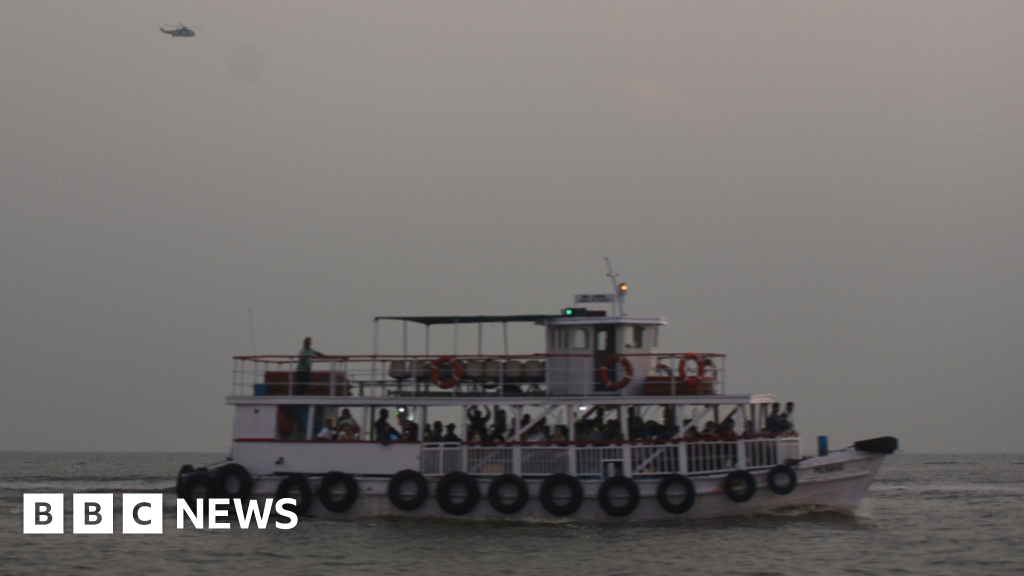
Magnify / From left to proper, zooming in from the globular cluster to the web site of its black hollow.ESA/Hubble & NASA, M. Häberle
Supermassive black holes seem to are living on the middle of each and every galaxy and to have performed so since galaxies shaped early within the historical past of the Universe. These days, alternatively, we will’t solely provide an explanation for their life, since it is tough to know how they might develop briefly sufficient to achieve the cutoff for supermassive as briefly as they did.
A conceivable little bit of proof was once lately discovered via the use of about two decades of knowledge from the Hubble Area Telescope. The knowledge comes from a globular cluster of stars that is considered the stays of a dwarf galaxy and displays {that a} crew of stars close to the cluster’s core are transferring so rapid that they must had been ejected from it solely. That signifies that one thing huge is protecting them there, which the researchers argue is a unprecedented intermediate-mass black hollow, weighing in at over 8,000 occasions the mass of the Solar.
Shifting rapid
The quick-moving stars are living in Omega Centauri, the most important globular cluster within the Milky Manner. With an estimated 10 million stars, it is a crowded atmosphere, however observations are aided via its relative proximity, at “simplest” 17,000 light-years away. The ones observations had been hinting that there may well be a central black hollow throughout the globular cluster, however the proof has no longer been decisive.
The brand new paintings, performed via a big global crew, used over 500 pictures of Omega Centauri, taken via the Hubble Area Telescope over the process two decades. This allowed them to trace the movement of stars throughout the cluster, permitting an estimate in their velocity relative to the cluster’s middle of mass. Whilst this has been performed prior to now, the newest knowledge allowed an replace that decreased the uncertainty within the stars’ speed.
Throughout the replace knowledge, plenty of stars close to the cluster’s middle stood out for his or her excessive velocities: seven of them had been transferring rapid sufficient that the gravitational pull of the cluster is not sufficient to stay them there. All seven must had been misplaced from the cluster inside of 1,000 years, despite the fact that the uncertainties remained huge for 2 of them. In accordance with the dimensions of the cluster, there mustn’t also be a unmarried foreground celebrity between the Hubble and the Omega Cluster, so those in reality appear to be throughout the cluster regardless of their speed.
The most straightforward rationalization for that’s that there is an extra mass retaining them in position. That would probably be a number of huge items, however the shut proximity of these kinds of stars to the middle of the cluster want a unmarried, compact object. This means that a black hollow.
In accordance with the velocities, the researchers estimate that the item has a mass of a minimum of 8,200 occasions that of the Solar. A few stars seem to be accelerating; if that holds up according to additional observations, it will point out that the black hollow is over 20,000 sun plenty. That puts it firmly inside of black hollow territory, although smaller than supermassive black holes, which can be considered as the ones with kind of one million sun plenty or extra. And it is significantly higher than you would be expecting from black holes shaped during the dying of a celebrity, which are not anticipated to be a lot higher than 100 occasions the Solar’s mass.
This puts it within the class of intermediate-mass black holes, of which there are just a handful of doable sightings, none of them universally authorized. So, it is a important discovering if for no different reason why than it can be the least debatable recognizing of an intermediate-mass black hollow but.
What’s this telling us?
For now, there are nonetheless really extensive uncertainties in one of the vital main points right here—however possibilities for making improvements to the placement exist. Observations with the Webb Area Telescope may probably select up the faint emissions from gasoline that is falling into the black hollow. And it might monitor the seven stars known right here. Its spectrographs may additionally probably select up the pink and blue shifts in mild led to via the celebrity’s movement. Its location at a substantial distance from Hubble may additionally supply a extra detailed third-dimensional image of Omega Centauri’s central construction.
Figuring this out may probably let us know extra about how black holes develop to supermassive scales. Previous doable sightings of intermediate-mass black holes have additionally are available in globular clusters, which would possibly recommend that they are a normal characteristic of enormous gatherings of stars.
However Omega Centauri differs from many different globular clusters, which frequently comprise huge populations of stars that each one shaped at kind of the similar time, suggesting the clusters shaped from a unmarried massive cloud of fabrics. Omega Centauri has stars with a huge vary of ages, which is likely one of the explanation why folks assume it is the stays of a dwarf galaxy that was once sucked into the Milky Manner.
If that is the case, then its central black hollow is an analog of the supermassive black holes present in exact dwarf galaxies—which raises the query of why it is only intermediate-mass. Did one thing about its interactions with the Milky Manner intervene with the black hollow’s expansion?
And, in any case, none of this sheds mild on how any black hollow grows to be so a lot more huge than any celebrity it would conceivably have shaped from. Getting a greater sense of this black hollow’s historical past may provide extra viewpoint on some questions which might be lately vexing astronomers.
Nature, 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07511-z (About DOIs).