Microscopic worms that are living their lives within the extremely radioactive atmosphere of the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone (CEZ) seem to take action totally freed from radiation harm.Nematodes amassed from the realm have proven no signal of wear and tear to their genomes, opposite to what could be anticipated for organisms dwelling in the sort of unhealthy position. The discovering, printed previous this yr, doesn’t mean the CEZ is secure, the researchers say, however reasonably the worms are resilient and in a position to adroitly adapt to prerequisites that could be inhospitable to different species.
This, says a staff of biologists led by way of Sophia Tintori of New York College, may be offering some insights into DNA restore mechanisms that might someday be tailored to be used in human medication.
Because the explosion of a reactor on the Chernobyl Nuclear Energy Plant in April 1986, the realm round it and the within reach the city of Pripyat in Ukraine had been strictly off-limits to any one with out govt approval. The radioactive fabrics deposited into the surroundings divulge organisms to extraordinarily unsafe ranges of ionizing radiation, a great deal improving the chance of mutation, most cancers, and dying.
It is going to be 1000’s of years ahead of ‘Chornobyl’, as it’s spelt in Ukraine, is secure for human habitation once more. Maximum people know that and steer transparent accordingly. However animals … neatly, they do not perceive to stick away. They cross the place they would like, and the exclusion zone has since turn into a ordinary form of radioactive, 2,600-square kilometer (1,000 sq. mile) animal sanctuary.
Assessments of animals that are living within the area have proven transparent genetic variations from animals that do not. However there is nonetheless so much we do not know concerning the results of the crisis at the native ecosystems.
“Chornobyl was once a tragedy of incomprehensible scale, however we nonetheless wouldn’t have a super seize at the results of the crisis on native populations,” Tintori stated on the time. “Did the surprising environmental shift make a selection for species, and even folks inside of a species, which are naturally extra immune to ionizing radiation?”
One strategy to acquire insights into this query is to have a look at nematodes – microscopic roundworms that are living in a spread of habitats (together with the our bodies of different organisms). Nematodes may also be remarkably hardy; there were more than one instances of nematodes reawakening after 1000’s of years frozen in permafrost.
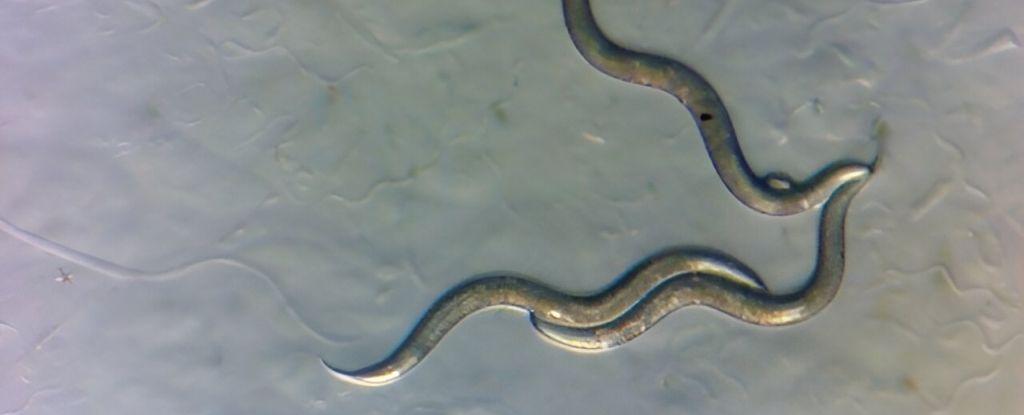
They’ve easy genomes, and are living brief lives, because of this more than one generations may also be studied in a brief area of time. This makes them very good fashion organisms for finding out a spread of items, from organic construction, to DNA restore and toxin reaction. For this reason Tintori and her colleagues went digging in Chornobyl to search out nematodes of the species Oschieus tipulae, which most often lives in soil. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>They amassed loads of nematodes from rotten fruit, leaf muddle, and the soil within the CEZ, the usage of Geiger counters to measure ambient radiation and dressed in protecting fits in opposition to radioactive mud. The researchers cultured just about 300 in their amassed worms in a laboratory, and decided on 15 specimens of O. tipulae for genome sequencing.
Those sequenced genomes had been then in comparison to the sequenced genomes of 5 specimens of O. tipulae from somewhere else on this planet – the Philippines, Germany, america, Mauritius, and Australia.
The CEZ worms had been most commonly extra genetically very similar to every rather than they had been to the opposite worms, with the genetic distance similar to the geographic distance for all the 20-strain pattern. However indicators of DNA harm from the radiation atmosphere had been missing.
The staff sparsely analyzed the worms’ genome, and located no proof of the large-scale chromosomal rearrangements anticipated from a mutagenic atmosphere. Additionally they discovered no correlation between the mutation price of the worms, and the power of the ambient radiation on the location every computer virus hailed from.
In the end, they performed checks at the descendents on every of the 20 computer virus lines to resolve how neatly the inhabitants tolerates DNA harm. Even though every lineage had a unique tolerance degree, this, too, had no correlation with the ambient radiation to which their ancestors had been uncovered.
The staff may most effective conclude that there is not any proof of any genetic have an effect on of the CEZ atmosphere at the genomes of O. tipulae.
And what they did to find may assist researchers check out to determine why some people are extra at risk of most cancers than others.
“Now that we all know which lines of O. tipulae are extra delicate or extra tolerant to DNA harm, we will use those lines to check why other people are much more likely than others to undergo the results of cancer agents,” Tintari stated.
“Serious about how folks reply otherwise to DNA-damaging brokers within the atmosphere is one thing that can assist us have a transparent imaginative and prescient of our personal chance components.”
The analysis has been printed within the Court cases of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.An previous model of this newsletter was once printed in March 2024.
Worms in Chernobyl Zone Seem Mysteriously Unscathed by way of Radiation




![Galaxy Z Fold 7 proves thinner than the ‘international’s slimmest foldable’ in side-by-side comparability [Video] Galaxy Z Fold 7 proves thinner than the ‘international’s slimmest foldable’ in side-by-side comparability [Video]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/07/galaxy-z-fold-7-35.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)






