Lake Baikal, in southern Siberia, is the sector’s oldest and private freshwater lake and, because of its age and isolation, is phenomenally biodiverse — however this outstanding ecosystem is underneath risk from international warming. On this excerpt from Our Historical Lakes: A Herbal Historical past (MIT Press, 2023), Jeffrey McKinnon examines the regime shift this is now happening on the lake. As the biggest and private of freshwater lakes, with an infinite quantity comprising 20% of the planet’s liquid recent water, one would possibly be expecting Lake Baikal to be resistant to switch. Thus, there was once a great deal of pastime when complete analyses began appearing within the 2000s of the 60-year information units accrued through Mikhail Kozhov, Olga Kozhova and Lyubov Izmest’eva. Those and different information display obviously that Baikal is warming and that the once a year period of ice is shrinking. It is usually changing into obvious that those adjustments are affecting the lake’s organisms not directly thru results on different bodily processes within the lake in addition to at once. In some instances, adjustments in bodily processes are affecting how organisms engage with every different.Within the first primary document presenting complete analyses of the information accrued through the Kozhov circle of relatives, Stephanie Hampton, of the U.S. Nationwide Middle for Ecological Research and Synthesis (now on the Carnegie Establishment for Science), Izmest’eva and a crew of collaborators from more than one establishments reported at the organic adjustments that had accompanied the warming of Baikal. They discovered that algal mass has been expanding general, as have the numbers of a gaggle of extensively allotted zooplankton referred to as cladocerans, which do neatly at upper temperatures. By contrast, the endemic, cold-loving Epischurella (a kind of small crustacean) has been both declining somewhat or solid. Owing to physiological and different variations between the several types of zooplankton, Hampton, Izmest’eva and associates counsel that if those traits persist or accentuate, patterns of nutrient biking within the lake might be considerably affected, with vast ecological penalties.In a complementary research of knowledge from shallow sediment cores, a world crew led through British scientists George Swann (College of Nottingham) and Anson Mackay (College School London) checked out how herbal and human-driven adjustments have affected nutrient and chemical biking, and in the long run adjustments in algae productiveness. Their time period of two,000 years was once longer, however nonetheless relatively contemporary. Their maximum necessary conclusion is that for the reason that mid-Nineteenth century, the availability of key vitamins has very much higher, from the nutrient-rich deeper waters to the nutrient-limited shallower waters the place gentle is top and algae will also be productive. Comparable: ‘Hunter-gatherers should have gazed in horror’ — What would Toba’s supereruption were like for our historic family members?They counsel that that is the results of documented will increase in wind energy over the lake, which is able to reason extra in depth “air flow” of deep waters. The reason for higher wind energy isn’t but recognized with self assurance, however lowered ice quilt together with higher air and surface-water temperatures most probably give a contribution. Lake Baikal is house to the sector’s simplest species of freshwater seal, the nerpa (Pusa sibirica). (Symbol credit score: andreigilbert/Getty Pictures)Hampton and Izmest’eva have constructed on those and different findings in a mathematical type of the Baikal open water ecosystem, advanced with a number of further collaborators together with Sabine Wollrab of Michigan State College and Berlin’s Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries. Within the type, they search to combine organic interactions between organisms with adjustments within the bodily setting. Their purpose is to raised perceive the reasons of the hot adjustments in seasonal patterns of algae abundance, particularly within the iciness. Baikal, with daylight penetrating its transparent iciness ice, has historically had a top in algae productiveness within the iciness and early spring — but any other peculiar characteristic of the program. Within the overdue twentieth century, those peaks had been ceaselessly not on time, weaker, or just absent. The Kozhov circle of relatives’s information detected those patterns, which is able to seldom be evaluated in lakes, as a result of their decided sampling in the course of the winters. The type, which takes into consideration Epischurella abundance and grazing, and considers separate populations of cold-adapted and warm-water-adapted algae, means that those adjustments in algae abundance could also be in large part the results of lowered annual ice quilt, and that if ice protection continues to decrease the iciness algae top would possibly disappear altogether. The type is quite advanced, however its predicted results rise up a minimum of partly from the larger skill of the Epischurella to suppress algae inhabitants enlargement through consuming the algae when there’s much less ice quilt.
Lake Baikal is house to the sector’s simplest species of freshwater seal, the nerpa (Pusa sibirica). (Symbol credit score: andreigilbert/Getty Pictures)Hampton and Izmest’eva have constructed on those and different findings in a mathematical type of the Baikal open water ecosystem, advanced with a number of further collaborators together with Sabine Wollrab of Michigan State College and Berlin’s Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries. Within the type, they search to combine organic interactions between organisms with adjustments within the bodily setting. Their purpose is to raised perceive the reasons of the hot adjustments in seasonal patterns of algae abundance, particularly within the iciness. Baikal, with daylight penetrating its transparent iciness ice, has historically had a top in algae productiveness within the iciness and early spring — but any other peculiar characteristic of the program. Within the overdue twentieth century, those peaks had been ceaselessly not on time, weaker, or just absent. The Kozhov circle of relatives’s information detected those patterns, which is able to seldom be evaluated in lakes, as a result of their decided sampling in the course of the winters. The type, which takes into consideration Epischurella abundance and grazing, and considers separate populations of cold-adapted and warm-water-adapted algae, means that those adjustments in algae abundance could also be in large part the results of lowered annual ice quilt, and that if ice protection continues to decrease the iciness algae top would possibly disappear altogether. The type is quite advanced, however its predicted results rise up a minimum of partly from the larger skill of the Epischurella to suppress algae inhabitants enlargement through consuming the algae when there’s much less ice quilt.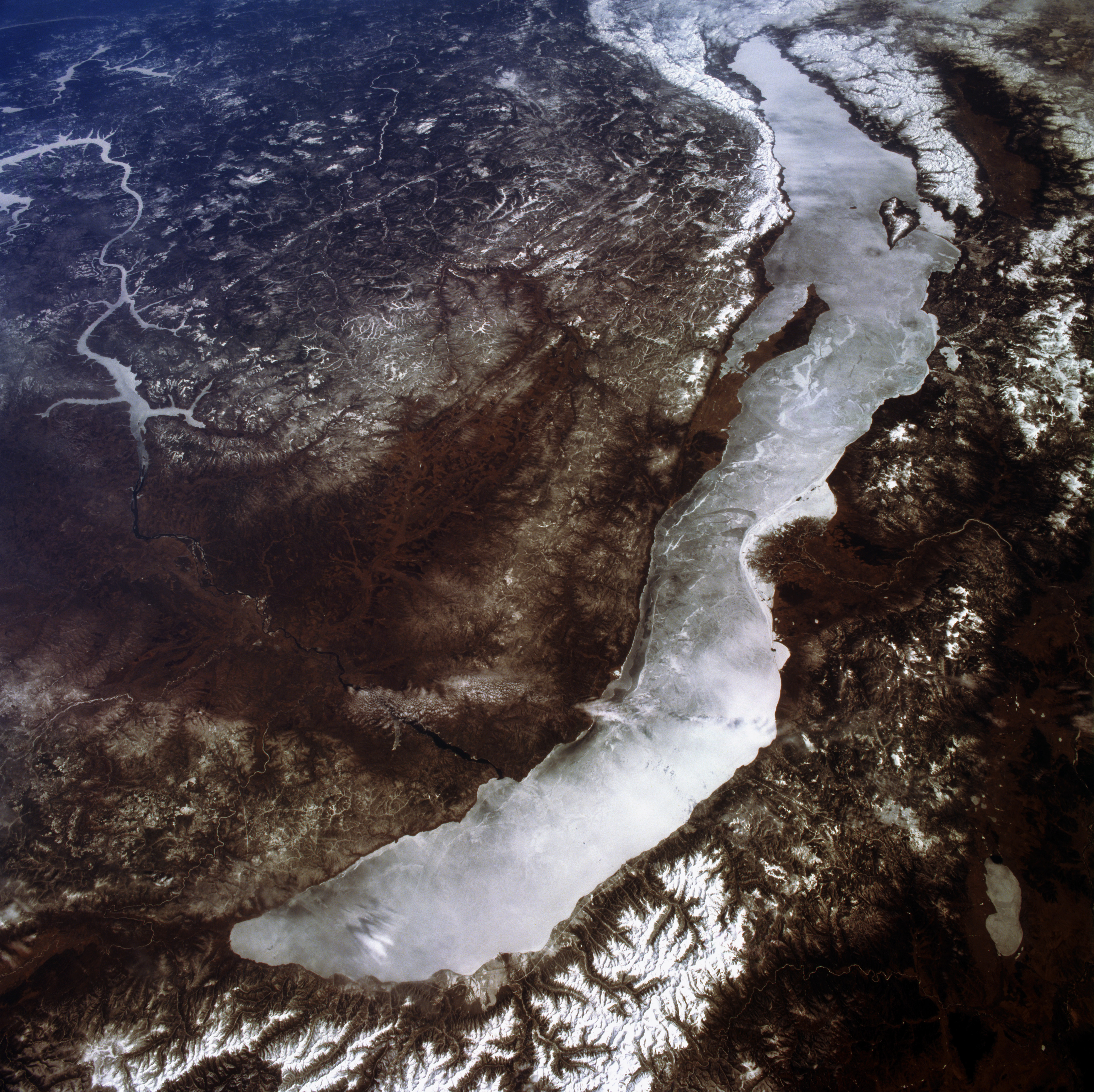  Lake Baikal is is huge it incorporates 20% of the planet’s liquid recent water. (Symbol credit score: Astromujoff/Getty Pictures)The type describes a “regime shift,” a steplike transfer from one state of a machine to another state involving a unique vary of variation. No type is ultimate, and this one would possibly evolve as our working out of the ecological interactions evolves, however the distinction between regime shift and secure, sluggish trade is worrisome or even scary.It signifies that international warming and different human-generated environmental adjustments would possibly every now and then reason abrupt shifts in ecosystems that can be exhausting to each are expecting and opposite. Lake Baikal, the biggest and maximum historic of freshwater historic lakes, had its get started within the time of the dinosaurs and started to take its fashionable shape neatly prior to the semblance of our personal lineage, the Homininae. But it simplest assumed its present deep and punctiliously oxygenated persona within the overdue Pleistocene (2.6 million to 11,700 years in the past). Amongst its numerous endemic fauna, its gammarid amphipods and sculpins are particularly neatly studied. Species from each radiations are uncharacteristically necessary in open water meals chains and in addition as prey for the planet’s simplest species of freshwater seal, the nerpa (Pusa sibirica). Different gammarid and sculpin species are necessary in Baikal’s extremely unique abyssal vent and seep communities, which can be energized through methane percolating up into the deep lake’s sediments and waters. Because the biodiverse historic lake on the very best latitude, Baikal is appearing the direct and oblique results of worldwide warming on its bodily and organic techniques and processes. The lake could also be experiencing an ecological regime shift that are meant to give pause to creatures dwelling in a bigger but nonetheless finite ecosystem — one this is temporarily heating too.Excerpted from Our Historical Lakes: A Herbal Historical past, through Jeffrey McKinnon. Printed through The MIT Press. Copyright © 2023 MIT. All rights reserved.
Lake Baikal is is huge it incorporates 20% of the planet’s liquid recent water. (Symbol credit score: Astromujoff/Getty Pictures)The type describes a “regime shift,” a steplike transfer from one state of a machine to another state involving a unique vary of variation. No type is ultimate, and this one would possibly evolve as our working out of the ecological interactions evolves, however the distinction between regime shift and secure, sluggish trade is worrisome or even scary.It signifies that international warming and different human-generated environmental adjustments would possibly every now and then reason abrupt shifts in ecosystems that can be exhausting to each are expecting and opposite. Lake Baikal, the biggest and maximum historic of freshwater historic lakes, had its get started within the time of the dinosaurs and started to take its fashionable shape neatly prior to the semblance of our personal lineage, the Homininae. But it simplest assumed its present deep and punctiliously oxygenated persona within the overdue Pleistocene (2.6 million to 11,700 years in the past). Amongst its numerous endemic fauna, its gammarid amphipods and sculpins are particularly neatly studied. Species from each radiations are uncharacteristically necessary in open water meals chains and in addition as prey for the planet’s simplest species of freshwater seal, the nerpa (Pusa sibirica). Different gammarid and sculpin species are necessary in Baikal’s extremely unique abyssal vent and seep communities, which can be energized through methane percolating up into the deep lake’s sediments and waters. Because the biodiverse historic lake on the very best latitude, Baikal is appearing the direct and oblique results of worldwide warming on its bodily and organic techniques and processes. The lake could also be experiencing an ecological regime shift that are meant to give pause to creatures dwelling in a bigger but nonetheless finite ecosystem — one this is temporarily heating too.Excerpted from Our Historical Lakes: A Herbal Historical past, through Jeffrey McKinnon. Printed through The MIT Press. Copyright © 2023 MIT. All rights reserved.