Science & Exploration
20/09/2024
1229 perspectives
29 likes
XRISM printed the construction, movement and temperature of the fabric round a supermassive black hollow and in a supernova remnant in unparalleled element. Astronomers offered the primary clinical result of the brand new X-ray telescope nowadays, lower than a yr after the telescope’s release.
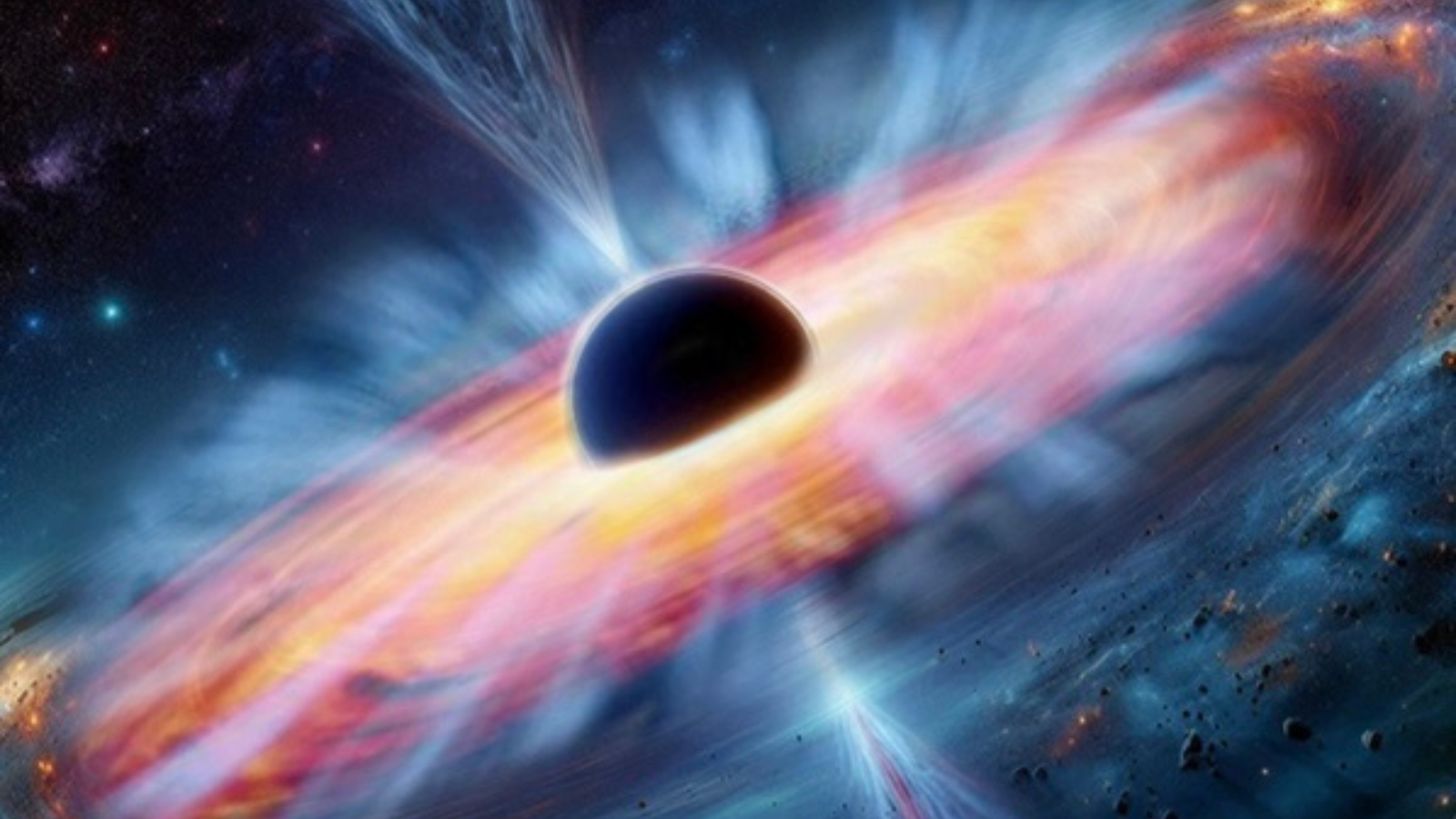
What do a big black hollow and the stays of an enormous, exploded megastar have in not unusual? Those are each dramatic celestial phenomena the place extraordinarily scorching gasoline produces extremely lively X-ray gentle that the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Undertaking (XRISM) can see.In its first printed effects, XRISM, a challenge led by way of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) with participation from ESA, displays its distinctive functions to show the rate and temperature of scorching scorching gasoline, referred to as plasma, and the third-dimensional buildings of subject matter surrounding a black hollow and an exploded megastar. “Those new observations supply the most important data in figuring out how black holes develop by way of taking pictures surrounding topic, and be offering a brand new perception into the lifestyles and loss of life of big stars. They show off the challenge’s remarkable capacity in exploring the high-energy Universe,” says ESA XRISM Venture Scientist Matteo Guainazzi.
Supernova remnant N132D
In one in every of its “dawn” observations, XRISM interested in N132D, a supernova remnant positioned within the Massive Magellanic Cloud about 160 000 light-years from Earth. This interstellar ‘bubble’ of scorching gasoline used to be expelled by way of the explosion of an overly huge megastar roughly 3000 years in the past.The use of its Get to the bottom of tool, XRISM exposed the construction round N132D intimately. Opposite to prior assumptions of a easy round shell, scientists discovered that the remnant of N132D is formed like a doughnut. The use of the Doppler impact, they measured the rate (pace) at which the new plasma within the remnant is transferring in opposition to or clear of us, and established that that is increasing on the obvious pace of round 1200 km/s
Sizzling scorching iron inside supernova remnant N132D
Get to the bottom of additionally printed that the remnant comprises iron that has an abnormal temperature of 10 billion levels Kelvin. The iron atoms have been heated throughout the supernova explosion via violent surprise waves spreading inwards, a phenomenon that have been predicted by way of concept, however by no means seen ahead of.Supernova remnants like N132D hang necessary clues into how stars evolve and the way (heavy) components which might be very important to our lifestyles, like iron, are generated and unfold out in interstellar area. But, earlier X-ray observatories have all the time had issue revealing how the plasma’s pace and temperature have been allotted.
Supermassive black hollow in galaxy NGC 4151
XRISM has additionally shed new gentle at the mysterious construction surrounding a supermassive black hollow. Specializing in the spiral galaxy NGC 4151, positioned 62 million light-years clear of us, XRISM’s observations be offering an unparalleled view of the fabric very as regards to the galaxy’s central black hollow, which has a mass 30 million instances that of the Solar.XRISM captured the distribution of the topic circling and in the long run falling into the black hollow over a large radius, spanning from 0.001 to 0.1 light-years, this is from a couple of distance similar to the Solar–Uranus separation to 100 instances that.
XRISM’s find out about of supermassive black hollow in galaxy NGC 4151
Via figuring out the motions of iron atoms from their X-ray signature, scientists mapped out a series of buildings surrounding the enormous black hollow: from the disk ‘feeding’ the black hollow the entire approach out to the doughnut-shaped torus.Those findings supply a very important piece of the puzzle in figuring out how black holes develop by way of gobbling up surrounding topic.Even though radio and infrared observations have printed the presence of a doughnut-shaped torus round black holes in different galaxies, XRISM’s spectroscopic method is the primary, and these days best solution to observe down how the gasoline close to the central ‘monster’ is formed and strikes.
Artist influence of the supermassive black hollow in NGC 4151
Taking a look Forward: Long term Observations and Discoveries
Within the closing months, the XRISM science group has diligently labored on setting up the tools’ efficiency and refine the knowledge research strategies by way of looking at 60 key goals. In parallel,104 new set of observations have been decided on from the over 300 proposed submissions from scientists international.XRISM will habits observations in line with the a hit proposals over the following yr; because of its remarkable efficiency in orbit, surpassing even preliminary expectancies, this guarantees many extra thrilling discoveries to return.
About XRISM
XRISM in a nutshell
The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Undertaking (XRISM) introduced on 7 September 2023. This can be a collaboration between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) and NASA, with vital participation from ESA. In go back for offering {hardware} and clinical recommendation, ESA is allotted 8% of XRISM’s to be had looking at time.Observations made the use of XRISM will supplement the ones from ESA’s XMM-Newton X-ray telescope, and might be a very good basis for observations deliberate with ESA’s long run large-class challenge NewAthena. The latter is being designed to seriously exceed the clinical efficiency of present spectroscopic and survey X-ray observatories.
Notes for editors
Those effects by way of the XRISM Collaboration are approved for newsletter within the Astronomical Society of Japan and The Astrophysical Magazine. Preprints are to be had right here and right here unencumber on XRISM web page.
Touch:
ESA Media family members
media@esa.int
Like
Thanks for liking
You will have already appreciated this web page, you’ll best love it as soon as!