The Y chromosome in primates — together with people — is evolving a lot more unexpectedly than the X chromosome, new analysis on six primate species suggests.For example, people and chimpanzees proportion upwards of 98% in their DNA throughout the entire of the genome, however simply 14% to 27% of the DNA sequences at the human Y chromosome are shared with our closest residing relations. The discovering shocked scientists, for the reason that people and chimpanzees diverged simply 7 million years in the past — a blip in evolutionary phrases.”I be expecting my genome to be very other to that of micro organism or bugs as a result of numerous time has elapsed, evolutionarily talking,” find out about co-author Brandon Pickett, a postdoctoral fellow on the Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute (NHGRI) on the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, instructed Are living Science. “However from different primates, I be expecting it to be lovely equivalent.”Comparable: Genomes of 51 animal species mapped in report time, developing ‘evolutionary time device’It isn’t transparent precisely why the Y chromosome is evolving so unexpectedly. For starters there may be just a unmarried replica of the Y chromosome in line with cellular — in primates, women folk raise two copies of the X chromosome, whilst men raise an X and a Y chromosome ––the Y chromosome performs a crucial position in sperm manufacturing and fertility. Having just a unmarried replica of the Y chromosome items a vulnerability ––if adjustments occur to happen, there is not any 2nd chromosome to behave as a backup. And adjustments are more likely to happen because of one thing known as mutation bias. The Y chromosome could also be so liable to exchange as it generates many sperm. This calls for quite a lot of DNA replication. And each time DNA is copied, there is a probability for errors to creep in. Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly for your inbox.Scientists have prior to now sequenced the primate genome for all 16 consultant households.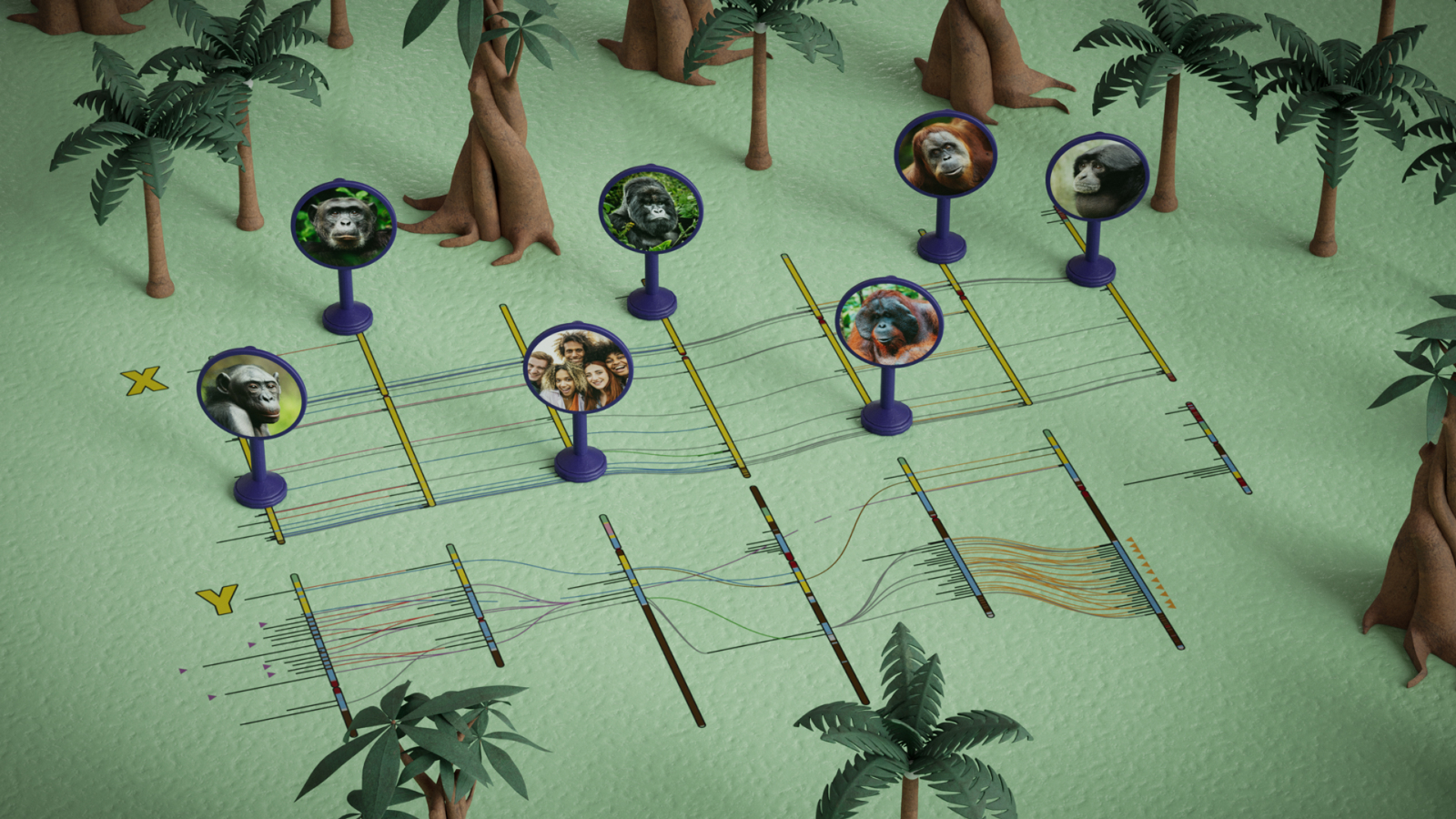  Whole X and Y chromosome sequences from six primate species expose species range and insights into evolution. (Symbol credit score: Ernesto Del Aguila III, Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute (CC BY))Within the new find out about, revealed Might 29 within the magazine Nature, scientists when put next the intercourse chromosomes of 5 nice ape species — chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), bonobos (Pan paniscus), western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) and Bornean and Sumatran orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus and Pongo abelii) — and yet one more distantly associated with people, siamang gibbons (Symphalangus syndactylus).The crew studied the chromosomes the use of telomere-to-telomere (T2T) sequencing. T2T can appropriately series repetitive components, together with the protecting telomere “caps” of chromosomes that experience confirmed tough to learn previously, Pickett stated. The researchers used computing instrument to make comparisons between the sequencing effects, by means of developing alignments to show which portions of the chromosome had modified and which portions had stayed the similar.The chromosomal X and Y sequences of each and every of the six species had been additionally in comparison to the human X and Y chromosome, already sequenced in an previous studywith the T2T means. The findings printed that throughout all of the studied species, the Y chromosome developed unexpectedly. Even species in the similar genus have very other Y chromosomes to each other. For example, chimpanzees and bonobos diverged simply 1 million to two million years in the past, but there’s a dramatic distinction of their Y chromosome lengths, stated Christian Roos, a senior scientist on the Primate Genetics Laboratory, German Primate Heart, who used to be now not concerned within the find out about.In some circumstances the adaptation in duration — led to by means of chromosome losses or duplications that happen when DNA is copied — amounted to as much as about part of the seen variations. For instance, the Y chromosome from the Sumatran orangutan is two times so long as the gibbon’s Y chromosome. Against this, the find out about discovered that the X chromosome used to be extremely conserved around the primate species, as could be anticipated for a construction with a crucial position in replica. One explanation why the Y turns out to have thrived in spite of one of these prime charge of mutation is that throughout all of the studied species, it accommodates stretches of extremely repetitive genetic subject matter, equivalent to palindromic repeats, the place the series reads the similar ahead and backward. Nestled inside those stretches of repeating DNA are genes. So the repeated DNA might safeguard necessary genes from replication errors and thereby maintain very important organic subject matter, the researchers wrote of their paper. The find out about did have boundaries despite the fact that; it checked out just a unmarried consultant for each and every primate species, and it could not say how a lot the Y chromosome would range inside animals of the similar species, Pickett stated.
Whole X and Y chromosome sequences from six primate species expose species range and insights into evolution. (Symbol credit score: Ernesto Del Aguila III, Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute (CC BY))Within the new find out about, revealed Might 29 within the magazine Nature, scientists when put next the intercourse chromosomes of 5 nice ape species — chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), bonobos (Pan paniscus), western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) and Bornean and Sumatran orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus and Pongo abelii) — and yet one more distantly associated with people, siamang gibbons (Symphalangus syndactylus).The crew studied the chromosomes the use of telomere-to-telomere (T2T) sequencing. T2T can appropriately series repetitive components, together with the protecting telomere “caps” of chromosomes that experience confirmed tough to learn previously, Pickett stated. The researchers used computing instrument to make comparisons between the sequencing effects, by means of developing alignments to show which portions of the chromosome had modified and which portions had stayed the similar.The chromosomal X and Y sequences of each and every of the six species had been additionally in comparison to the human X and Y chromosome, already sequenced in an previous studywith the T2T means. The findings printed that throughout all of the studied species, the Y chromosome developed unexpectedly. Even species in the similar genus have very other Y chromosomes to each other. For example, chimpanzees and bonobos diverged simply 1 million to two million years in the past, but there’s a dramatic distinction of their Y chromosome lengths, stated Christian Roos, a senior scientist on the Primate Genetics Laboratory, German Primate Heart, who used to be now not concerned within the find out about.In some circumstances the adaptation in duration — led to by means of chromosome losses or duplications that happen when DNA is copied — amounted to as much as about part of the seen variations. For instance, the Y chromosome from the Sumatran orangutan is two times so long as the gibbon’s Y chromosome. Against this, the find out about discovered that the X chromosome used to be extremely conserved around the primate species, as could be anticipated for a construction with a crucial position in replica. One explanation why the Y turns out to have thrived in spite of one of these prime charge of mutation is that throughout all of the studied species, it accommodates stretches of extremely repetitive genetic subject matter, equivalent to palindromic repeats, the place the series reads the similar ahead and backward. Nestled inside those stretches of repeating DNA are genes. So the repeated DNA might safeguard necessary genes from replication errors and thereby maintain very important organic subject matter, the researchers wrote of their paper. The find out about did have boundaries despite the fact that; it checked out just a unmarried consultant for each and every primate species, and it could not say how a lot the Y chromosome would range inside animals of the similar species, Pickett stated.